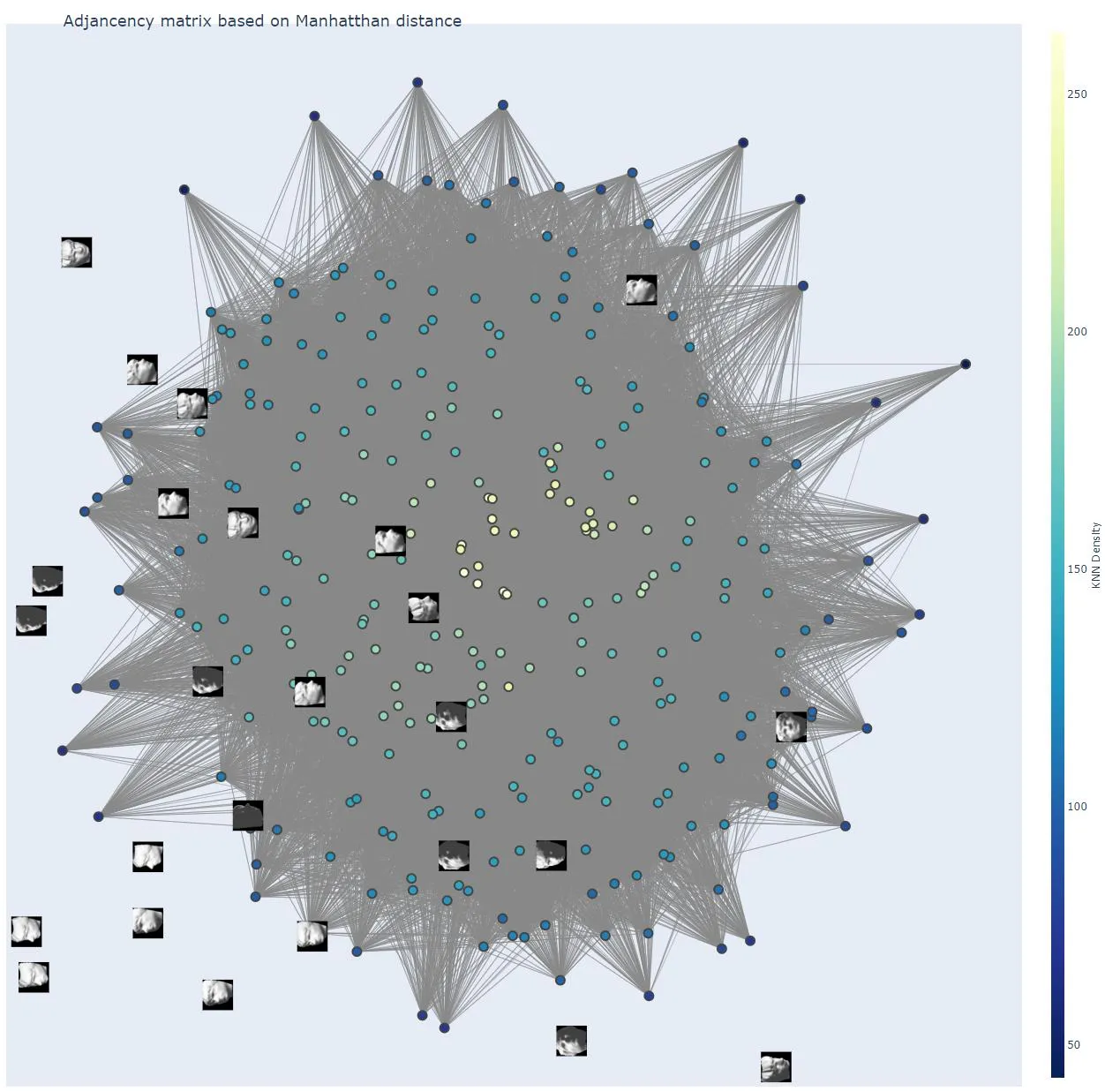
我正在使用Plotly显示一个网络图,并尝试显示属于特定数据点的示例图像(每个数据点都是一个64x64的雕塑亮度图)。 我有两个问题:
- 我正在使用数据点坐标来定位图像,但它们没有对齐。 我尝试使用
xanchor/yanchor来修复它,但它没有起作用。 - 虽然我正在绘制100张图像,但只有少数几张实际可见。 如果我放大可视化,我可以看到更多的图像,但我想强制Plotly显示所有图像。 我尝试了
layer ='above',但没有起作用。 - 如果有一种方法将图像与实际数据点链接起来,那将是很好的,但我不知道如何做到这一点。
def plot_graph(G, plot_title, dataset, coordinates=None):
if coordinates == None:
coordinates = nx.drawing.spring_layout(G, weight=None)
edge_x = []
edge_y = []
for edge in G.edges():
x0, y0 = coordinates[edge[0]]
x1, y1 = coordinates[edge[1]]
edge_x.extend([x0, x1])
edge_y.extend([y0, y1])
edge_trace = go.Scatter(x=edge_x,
y=edge_y,
line=dict(width=0.5, color='#888'),
hoverinfo='none',
mode='lines'
)
node_x = []
node_y = []
for node in G.nodes():
x, y = coordinates[node]
node_x.append(x)
node_y.append(y)
colorbar_attrs = dict(thickness=15, title='KNN Density', xanchor='left', titleside='right')
marker_attrs = dict(showscale=True,
colorscale='YlGnBu',
reversescale=True,
color=[], size=10,
colorbar=colorbar_attrs,
line_width=2)
node_trace = go.Scatter(x=node_x, y=node_y, mode='markers', hoverinfo='text', marker=marker_attrs)
node_adjacencies = []
node_text = []
for node, adjacencies in enumerate(G.adjacency()):
node_adjacencies.append(len(adjacencies[1]))
node_text.append('K-Nearest Neighbors: '+str(len(adjacencies[1])))
node_trace.marker.color = node_adjacencies
node_trace.text = node_text
fig = go.Figure(data=[edge_trace, node_trace],
layout=go.Layout(
title='<br> {}'.format(plot_title),
titlefont_size=18,
showlegend=False,
hovermode='closest',
margin=dict(b=20,l=5,r=5,t=40),
xaxis=dict(showgrid=False, zeroline=False, showticklabels=False),
yaxis=dict(showgrid=False, zeroline=False, showticklabels=False))
)
num_images = 100
num_faces = dataset.shape[0]
sample_images = np.random.choice(num_faces, num_images, replace=False)
greys = cm.get_cmap('Greys_r')
for index in sample_images:
greyscale = np.apply_along_axis(greys, 0, dataset[index]).reshape((64, 64, 4))*255
greyscale = greyscale.astype(np.uint8)
im = pilim.fromarray(greyscale)
fig.add_layout_image(dict(
source=im,
x=coordinates[index][0],
y=coordinates[index][1],
sizex=0.03,
sizey=0.03,
layer='above'
))
return fig
我得到的是这个: