使用Python计算矢量场的散度
7
给大家一个提示:
上面的函数并不能计算矢量场的散度。它们是对标量场A的导数求和:
结果 = dA / dx + dA / dy
与矢量场不同(以三维为例):
结果 = sum dAi / dxi = dAx / dx + dAy / dy + dAz / dz
向下投票!这在数学上是错误的。
干杯!
5
import numpy as np
def divergence(field):
"return the divergence of a n-D field"
return np.sum(np.gradient(field),axis=0)
1
基于Juh_的答案,但根据矢量场公式的正确散度进行了修改
def divergence(f):
"""
Computes the divergence of the vector field f, corresponding to dFx/dx + dFy/dy + ...
:param f: List of ndarrays, where every item of the list is one dimension of the vector field
:return: Single ndarray of the same shape as each of the items in f, which corresponds to a scalar field
"""
num_dims = len(f)
return np.ufunc.reduce(np.add, [np.gradient(f[i], axis=i) for i in range(num_dims)])
Matlab的文档使用了这个确切的公式(向下滚动到矢量场的发散)
@user2818943的答案很好,但可以稍加优化:
def divergence(F):
""" compute the divergence of n-D scalar field `F` """
return reduce(np.add,np.gradient(F))
Timeit:
F = np.random.rand(100,100)
timeit reduce(np.add,np.gradient(F))
# 1000 loops, best of 3: 318 us per loop
timeit np.sum(np.gradient(F),axis=0)
# 100 loops, best of 3: 2.27 ms per loop
大约快了7倍:
sum 隐式地从梯度场列表中构建一个三维数组,这些列表是由np.gradient返回的。使用reduce可以避免这种情况。
在您的问题中,
div[A * grad(F)]是什么意思?
- 关于
A * grad(F):A是一个二维数组,grad(f)是一个2d数组列表。因此,我认为它的含义是将每个梯度场与A相乘。 - 关于在(由
A缩放的)梯度场上应用散度不清楚。根据定义,div(F) = d(F)/dx + d(F)/dy + ...。我猜这只是一种表述错误。
1,将元素Bi的加和乘以相同的因子A可以因式分解:Sum(A*Bi) = A*Sum(Bi)
因此,您可以使用以下方法获得加权梯度:
A*divergence(F)。如果
A是一个因子列表,每个维度对应一个因子,则解决方案如下:def weighted_divergence(W,F):
"""
Return the divergence of n-D array `F` with gradient weighted by `W`
̀`W` is a list of factors for each dimension of F: the gradient of `F` over
the `i`th dimension is multiplied by `W[i]`. Each `W[i]` can be a scalar
or an array with same (or broadcastable) shape as `F`.
"""
wGrad = return map(np.multiply, W, np.gradient(F))
return reduce(np.add,wGrad)
result = weighted_divergence(A,F)
2
np.ufunc.reduce(np.add, [np.gradient(F[i], axis=i) for i in range(len(F))])。 - DanielFunction
np.gradient() is defined as: np.gradient(f) = df/dx, df/dy, df/dz +...But we need to define func divergence as: divergence (f) = dfx/dx + dfy/dy + dfz/dz +... =
np.gradient(fx) + np.gradient(fy) + np.gradient(fz) + ...Let's test and compare with example of divergence in matlab.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
NY = 50
ymin = -2.
ymax = 2.
dy = (ymax -ymin )/(NY-1.)
NX = NY
xmin = -2.
xmax = 2.
dx = (xmax -xmin)/(NX-1.)
def divergence(f):
num_dims = len(f)
return np.ufunc.reduce(np.add, [np.gradient(f[i], axis=i) for i in range(num_dims)])
y = np.array([ ymin + float(i)*dy for i in range(NY)])
x = np.array([ xmin + float(i)*dx for i in range(NX)])
x, y = np.meshgrid( x, y, indexing = 'ij', sparse = False)
Fx = np.cos(x + 2*y)
Fy = np.sin(x - 2*y)
F = [Fx, Fy]
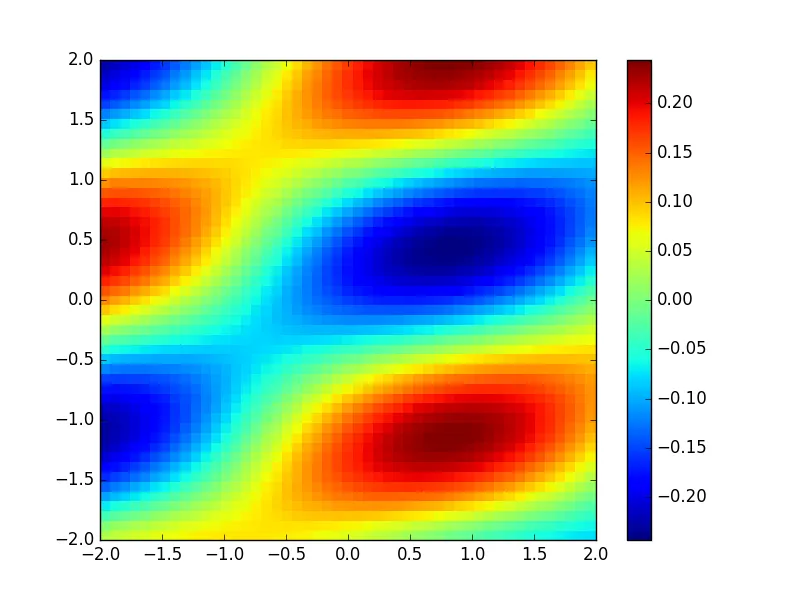
g = divergence(F)
plt.pcolormesh(x, y, g)
plt.colorbar()
plt.savefig( 'Div' + str(NY) +'.png', format = 'png')
plt.show()
---------- 更新版本:包含差分步骤 ----------------
感谢@henry的评论,np.gradient默认步长为1,因此结果可能存在一些不匹配。我们可以提供自定义的差分步长。
#https://dev59.com/vGgu5IYBdhLWcg3wTFOi#47905007
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import make_axes_locatable
NY = 50
ymin = -2.
ymax = 2.
dy = (ymax -ymin )/(NY-1.)
NX = NY
xmin = -2.
xmax = 2.
dx = (xmax -xmin)/(NX-1.)
def divergence(f,h):
"""
div(F) = dFx/dx + dFy/dy + ...
g = np.gradient(Fx,dx, axis=1)+ np.gradient(Fy,dy, axis=0) #2D
g = np.gradient(Fx,dx, axis=2)+ np.gradient(Fy,dy, axis=1) +np.gradient(Fz,dz,axis=0) #3D
"""
num_dims = len(f)
return np.ufunc.reduce(np.add, [np.gradient(f[i], h[i], axis=i) for i in range(num_dims)])
y = np.array([ ymin + float(i)*dy for i in range(NY)])
x = np.array([ xmin + float(i)*dx for i in range(NX)])
x, y = np.meshgrid( x, y, indexing = 'ij', sparse = False)
Fx = np.cos(x + 2*y)
Fy = np.sin(x - 2*y)
F = [Fx, Fy]
h = [dx, dy]
print('plotting')
rows = 1
cols = 2
#plt.clf()
plt.figure(figsize=(cols*3.5,rows*3.5))
plt.minorticks_on()
#g = np.gradient(Fx,dx, axis=1)+np.gradient(Fy,dy, axis=0) # equivalent to our func
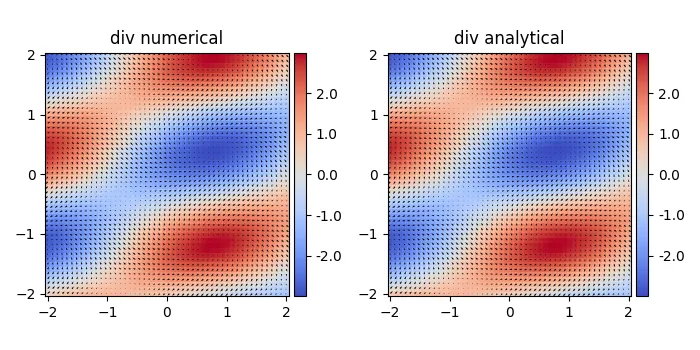
g = divergence(F,h)
ax = plt.subplot(rows,cols,1,aspect='equal',title='div numerical')
#im=plt.pcolormesh(x, y, g)
im = plt.pcolormesh(x, y, g, shading='nearest', cmap=plt.cm.get_cmap('coolwarm'))
plt.quiver(x,y,Fx,Fy)
divider = make_axes_locatable(ax)
cax = divider.append_axes("right", size="5%", pad=0.05)
cbar = plt.colorbar(im, cax = cax,format='%.1f')
g = -np.sin(x+2*y) -2*np.cos(x-2*y)
ax = plt.subplot(rows,cols,2,aspect='equal',title='div analytical')
im=plt.pcolormesh(x, y, g)
im = plt.pcolormesh(x, y, g, shading='nearest', cmap=plt.cm.get_cmap('coolwarm'))
plt.quiver(x,y,Fx,Fy)
divider = make_axes_locatable(ax)
cax = divider.append_axes("right", size="5%", pad=0.05)
cbar = plt.colorbar(im, cax = cax,format='%.1f')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig( 'divergence.png', format = 'png')
plt.show()
5
numpy.gradient 的色条范围比解析结果略小。我周围的人通常不关心颜色范围。如果有人能解释一下为什么,我会很高兴的。@_@ - John Paul Qiang Chennp.gradient(f) = df/dx, df/dy, df/dz[,] <+>... - Atcold在@paul_chen的回答基础上,针对Matplotlib 3.3.0进行了一些补充(需要传递一个阴影参数,我猜默认的颜色映射已经改变了)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
NY = 20; ymin = -2.; ymax = 2.
dy = (ymax -ymin )/(NY-1.)
NX = NY
xmin = -2.; xmax = 2.
dx = (xmax -xmin)/(NX-1.)
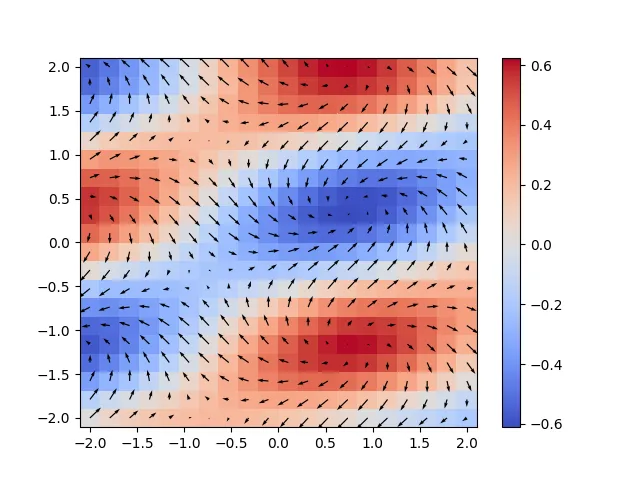
def divergence(f):
num_dims = len(f)
return np.ufunc.reduce(np.add, [np.gradient(f[i], axis=i) for i in range(num_dims)])
y = np.array([ ymin + float(i)*dy for i in range(NY)])
x = np.array([ xmin + float(i)*dx for i in range(NX)])
x, y = np.meshgrid( x, y, indexing = 'ij', sparse = False)
Fx = np.cos(x + 2*y)
Fy = np.sin(x - 2*y)
F = [Fx, Fy]
g = divergence(F)
plt.pcolormesh(x, y, g, shading='nearest', cmap=plt.cm.get_cmap('coolwarm'))
plt.colorbar()
plt.quiver(x,y,Fx,Fy)
plt.savefig( 'Div.png', format = 'png')
1
在Matlab中,差分作为内置函数被包含在其中,但在NumPy中却没有。这是一种或许值得投入到pylab中的东西,pylab是一个致力于创建可行的开源替代Matlab的努力。
编辑:现在称为http://www.scipy.org/stackspec.html。之前计算散度的尝试都出现了错误!让我来给你展示一下:
我们有以下向量场 F:
F(x) = cos(x+2y)
F(y) = sin(x-2y)
如果我们使用Mathematica计算散度:
Div[{Cos[x + 2*y], Sin[x - 2*y]}, {x, y}]
我们得到:
-2 Cos[x - 2 y] - Sin[x + 2 y]
在 y [-1,2] 和 x [-2,2] 范围内具有最大值的:
N[Max[Table[-2 Cos[x - 2 y] - Sin[x + 2 y], {x, -2, 2 }, {y, -2, 2}]]] = 2.938
使用此处给出的散度方程:
def divergence(f):
num_dims = len(f)
return np.ufunc.reduce(np.add, [np.gradient(f[i], axis=i) for i in range(num_dims)])
我们得到了一个最大值约为0.625
正确的散度函数: Python计算散度
我认为@Daniel的答案不正确,特别是当输入按顺序排列时[Fx, Fy, Fz, ...]。
一个简单的测试用例
请参阅MATLAB代码:
a = [1 2 3;1 2 3; 1 2 3];
b = [[7 8 9] ;[1 5 8] ;[2 4 7]];
divergence(a,b)
这将给出结果:
ans =
-5.0000 -2.0000 0
-1.5000 -1.0000 0
2.0000 0 0
丹尼尔的解决方案:
def divergence(f):
"""
Daniel's solution
Computes the divergence of the vector field f, corresponding to dFx/dx + dFy/dy + ...
:param f: List of ndarrays, where every item of the list is one dimension of the vector field
:return: Single ndarray of the same shape as each of the items in f, which corresponds to a scalar field
"""
num_dims = len(f)
return np.ufunc.reduce(np.add, [np.gradient(f[i], axis=i) for i in range(num_dims)])
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3]] * 3)
b = np.array([[7, 8, 9], [1, 5, 8], [2, 4, 7]])
div = divergence([a, b])
print(div)
pass
这将会提供:
[[1. 1. 1. ]
[4. 3.5 3. ]
[2. 2.5 3. ]]
解释
Daniel的解决方案的错误在于,在Numpy中,x轴是最后一个轴而不是第一个轴。当使用np.gradient(x, axis=0)时,Numpy实际上给出了y方向的梯度(当x是一个二维数组时)。
我的解决方案
这是基于Daniel的答案的我的解决方案。
def divergence(f):
"""
Computes the divergence of the vector field f, corresponding to dFx/dx + dFy/dy + ...
:param f: List of ndarrays, where every item of the list is one dimension of the vector field
:return: Single ndarray of the same shape as each of the items in f, which corresponds to a scalar field
"""
num_dims = len(f)
return np.ufunc.reduce(np.add, [np.gradient(f[num_dims - i - 1], axis=i) for i in range(num_dims)])
在我的测试案例中,它提供了与MATLAB divergence 相同的结果。
1
原文链接