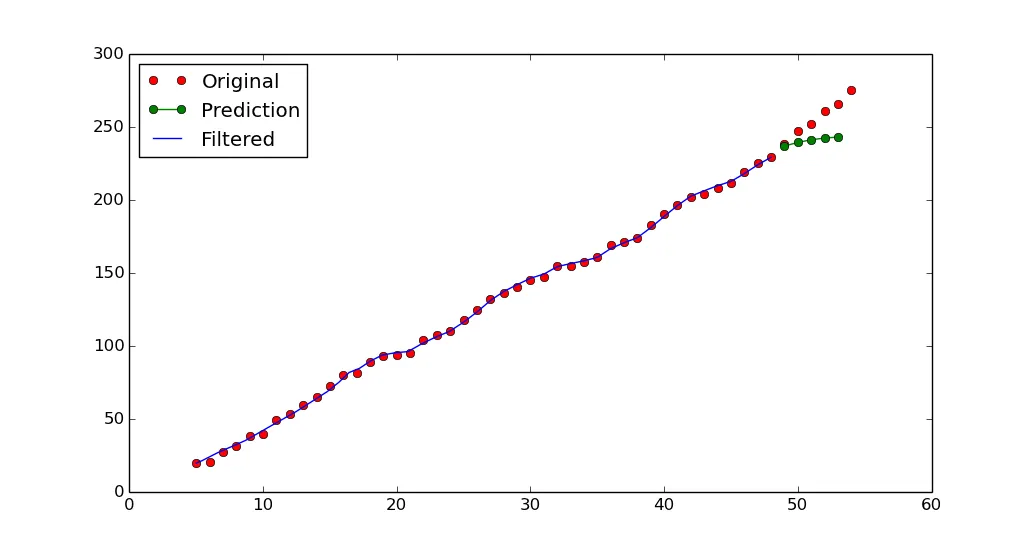
我使用了这里实现的卡尔曼滤波器:https://gist.github.com/alexbw/1867612
我对它有一个非常基本的理解。这是我所拥有的测试代码:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from Kalman import Kalman
n = 50
d = 5
xf = np.zeros(n - d)
yf = np.zeros(n - d)
xp = np.zeros(d)
yp = np.zeros(d)
x = np.zeros(n)
y = np.zeros(n)
for i in range(n):
if i==0:
x[i] = 05
y[i] = 20
KLF = Kalman(6, 2)
elif i< (n - d):
xf[i], yf[i] = KLF.predict()
x[i] = x[i-1] + 1
y[i] = y[i-1] + np.random.random() * 10
NewPoint = np.r_[x[i], y[i]]
KLF.update(NewPoint)
else:
x[i] = x[i-1] + 1
y[i] = y[i-1] + np.random.random() * 10
xp[n - i -1], yp[n - i -1] = KLF.predict()
NewPoint = np.r_[x[i] , yp[n - i -1]]
KLF.update(NewPoint)
plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(x, y, 'ro') #original
plt.plot(xp, yp, 'go-') #predicted kalman
plt.plot(xf, yf, 'b') #kalman filter
plt.legend( ('Original', 'Prediction', 'Filtered') )
plt.show()
我的问题是,如果数据从x=5,y=20开始,为什么卡尔曼滤波要从0开始?这是某种标准行为吗?
谢谢。