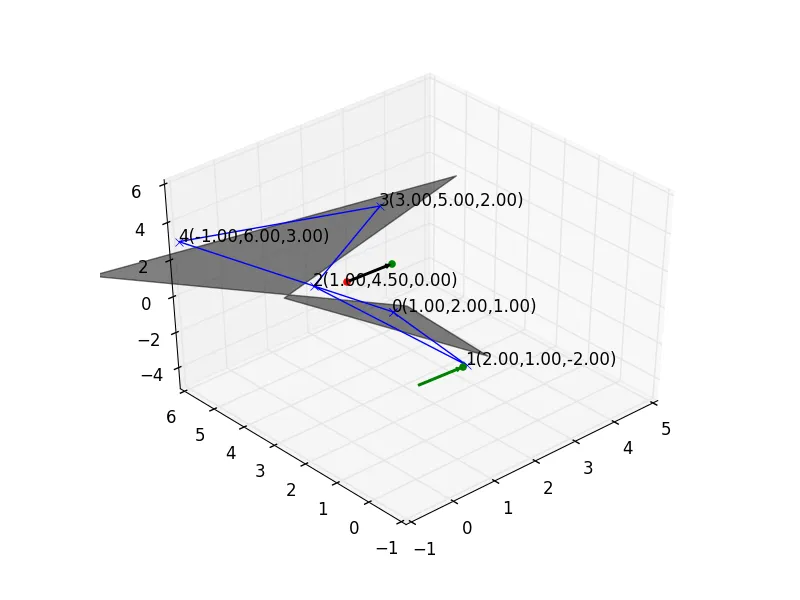
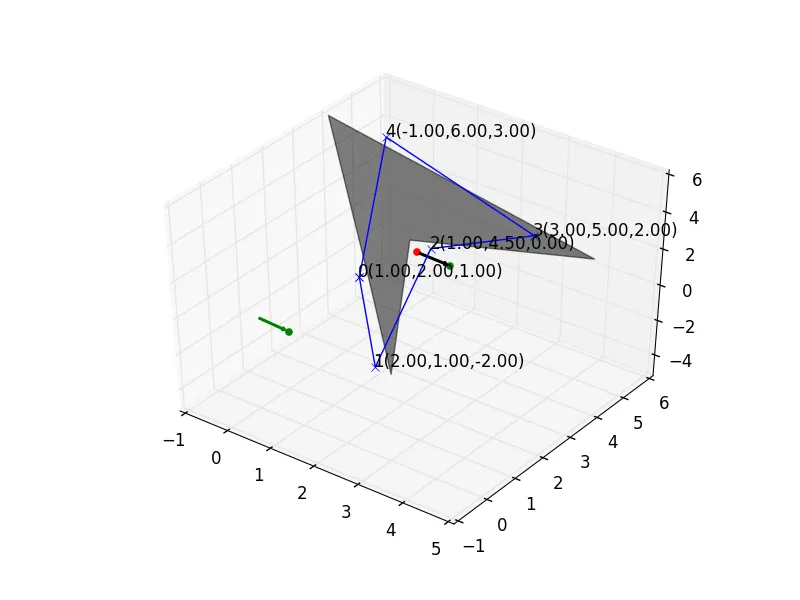
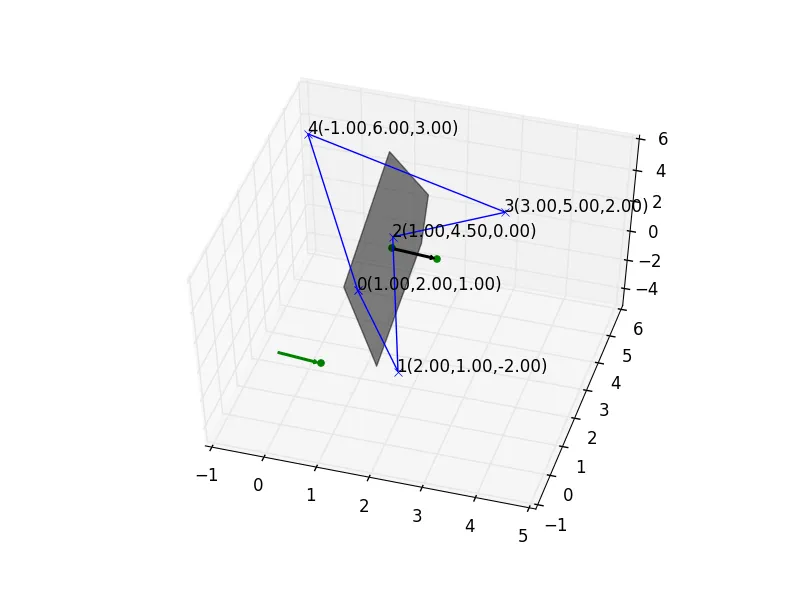
我正在使用以下函数尝试将一组顶点投影到平面上,从而将多面体映射为多边形。我的平面由法向量和一个点(在此称为重心)定义。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from numpy import linalg as la
#######################################################################################################
#this part is for drawing the vector arrow
#copy pasted
#https://dev59.com/hmAh5IYBdhLWcg3wDfuy
#######################################################################################################
from matplotlib.patches import FancyArrowPatch
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import proj3d
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.art3d import Poly3DCollection
import matplotlib.cm as cm#for color selection
import itertools
class Arrow3D(FancyArrowPatch):
def __init__(self, xs, ys, zs, *args, **kwargs):
FancyArrowPatch.__init__(self, (0,0), (0,0), *args, **kwargs)
self._verts3d = xs, ys, zs
def draw(self, renderer):
xs3d, ys3d, zs3d = self._verts3d
xs, ys, zs = proj3d.proj_transform(xs3d, ys3d, zs3d, renderer.M)
self.set_positions((xs[0],ys[0]),(xs[1],ys[1]))
FancyArrowPatch.draw(self, renderer)
#######################################################################################################
#function to project onto the plane
#takes normal vector of the plane, the centroid of the plane and vertices to be projected as argument
#returns the position vector of the projected point on the plane
#######################################################################################################
def planeprojection(normalvector,centroid,vertices):
shape = vertices.shape#shape of vertex array, can be one vertex or multiple vertices to project
if len(shape)==1:#meaning there is only one vertex
vertex = vertices
#dot product of position vector to the vertex from plane and normal vector
dotscalar = np.dot(np.subtract(vertex,centroid),normalvector)
#now returning the position vector of the projection onto the plane
return np.subtract(vertex,dotscalar*normalvector)
else:
#array to store projectedvectors
projectedvectors = np.zeros((shape[0],shape[1]))
#now projecting onto plane, one by one
for counter in range(shape[0]):
vertex = vertices[counter,:]
print vertex
dotscalar = np.dot(np.subtract(centroid,vertex),normalvector)
print dotscalar
#now returning the position vector of the projection onto the plane
projectedvectors[counter,:] = np.subtract(vertex,dotscalar*normalvector)
#now returning the vectors projected
return projectedvectors
#######################################################################################################
###normalising function
#######################################################################################################
def normalise(v):
norm=np.linalg.norm(v)
if norm==0:
return v
return v/norm
##############################################################################################################
##########points to project####################
##############################################################################################################
xcod = np.array([1,2,1,3,-1,1])
ycod = np.array([2,1,4.5,5.,6,2])
zcod = np.array([1,-2,0,2,3,1])
num = len(xcod)-1
#centroid of the cell
centroid = np.array([np.mean(xcod[0:num]),np.mean(ycod[0:num]),np.mean(zcod[0:num])])
#getting tuples of x,y,z
verts = [zip(xcod,ycod,zcod)]
#numpy array of vertices
vertices =np.array(verts[0])
#normal to the plane
averagenormal = np.array([ 0.91008281, -0.24978471, 0.3306915 ])
#Projecting the vertices now
projectedvertices = planeprojection(averagenormal,centroid,vertices)
#changing the format to tuple for plotting polyhedron surface
projectedverts = [map(tuple,projectedvertices)]
################################################################################
######plotting #################################################################
################################################################################
#also defining the plot in 3d for start plotting
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111,projection = '3d')
#plotting all the points
ax.plot(xcod,ycod,zcod,'x-')
#plotting polyhedron surface
ax.add_collection3d(Poly3DCollection(projectedverts,alpha=0.5,color="k"))
#adding labels for vertice
for i in range(num):
ax.text(xcod[i],ycod[i],zcod[i],'%d(%.2f,%.2f,%.2f)'%(i,xcod[i],ycod[i],zcod[i]))
#drawing vector arrow for averal normal vector
drawvec=Arrow3D([centroid[0],averagenormal[0]+centroid[0]],[centroid[1],averagenormal[1]+centroid[1]],[centroid[2],averagenormal[2]+centroid[2]],mutation_scale=8,lw=1,color='k')
ax.add_artist(drawvec)
#draw average vector from origin as originally found out
drawvec = Arrow3D([0,averagenormal[0]],[0,averagenormal[1]],[0,averagenormal[2]],mutation_scale=8,lw=1,color='g')
ax.add_artist(drawvec)
#plotting averagenormal vector point
ax.scatter(averagenormal[0],averagenormal[1],averagenormal[2],marker = 'o',color="g")
#plotting centroid
ax.scatter(centroid[0],centroid[1],centroid[2],marker = 'o',color="g")
#plotting averagenormal vector point from centroid
ax.scatter(averagenormal[0]+centroid[0],averagenormal[1]+centroid[1],averagenormal[2]+centroid[2],marker = 'o',color="g")#plot show
ax.set_xlim([-1,5])
ax.set_ylim([-1,6])
ax.set_zlim([-5,6])
plt.show()
下面的图中,黑色阴影部分被认为是平面。有些东西不对劲,这不应该是正确的方法吗?
我基本上使用以下公式进行投影,其中Proj(P)是投影到平面上的投影,Centriod是平面上的点,n是法向量。
Proj(P) = P-((P-Centroid).n)n
编辑
更改Nico下面建议的错误,dotscalar = np.dot(np.subtract(vertex,centroid),normalvector) 它可行!