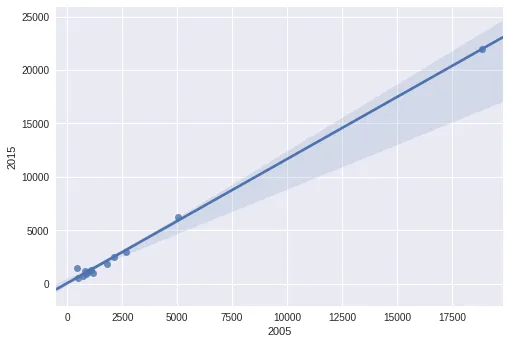
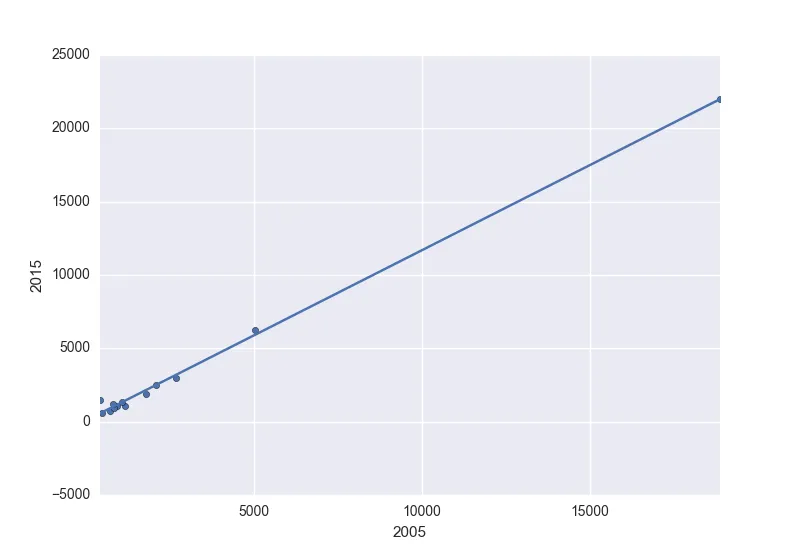
我目前正在使用Pandas和matplotlib进行一些数据可视化工作,我想在散点图上添加一条最佳拟合线。
这是我的代码:
怎么做呢?
这是我的代码:
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as panda
import numpy as np
def PCA_scatter(filename):
matplotlib.style.use('ggplot')
data = panda.read_csv(filename)
data_reduced = data[['2005', '2015']]
data_reduced.plot(kind='scatter', x='2005', y='2015')
plt.show()
PCA_scatter('file.csv')
怎么做呢?