我一直在使用RStudio中的caret包中的gbm来查找故障发生的概率。
我使用Youden's J方法找到了最佳分类的阈值,为0.63。现在如何使用这个阈值呢?我认为最好的方法是将阈值某种方式纳入到caret的gbm模型中,以获得更准确的预测,然后再次在训练数据上运行该模型?目前默认值为0.5,我找不到明显的更新阈值的方法。
或者,阈值只是用于将测试数据的预测分成正确的类别吗?这似乎更直观,但是如何反映基于新阈值应更新的概率的ROC_AUC图的变化呢?
任何帮助都将不胜感激。谢谢。
编辑:我正在处理的完整代码如下:
library(datasets)
library(caret)
library(MLeval)
library(dplyr)
data(iris)
data <- as.data.frame(iris)
# create class
data$class <- ifelse(data$Species == "setosa", "yes", "no")
# split into train and test
train <- data %>% sample_frac(.70)
test <- data %>% sample_frac(.30)
# Set up control function for training
ctrl <- trainControl(method = "cv",
number = 5,
returnResamp = 'none',
summaryFunction = twoClassSummary,
classProbs = T,
savePredictions = T,
verboseIter = F)
# Set up trainng grid - this is based on a hyper-parameter tune that was recently done
gbmGrid <- expand.grid(interaction.depth = 10,
n.trees = 20000,
shrinkage = 0.01,
n.minobsinnode = 4)
# Build a standard classifier using a gradient boosted machine
set.seed(5627)
gbm_iris <- train(class ~ .,
data = train,
method = "gbm",
metric = "ROC",
tuneGrid = gbmGrid,
verbose = FALSE,
trControl = ctrl)
# Calcuate best thresholds
caret::thresholder(gbm_iris, threshold = seq(.01,0.99, by = 0.01), final = TRUE, statistics = "all")
pred <- predict(gbm_iris, newdata = test, type = "prob")
roc <- evalm(data.frame(pred, test$class))
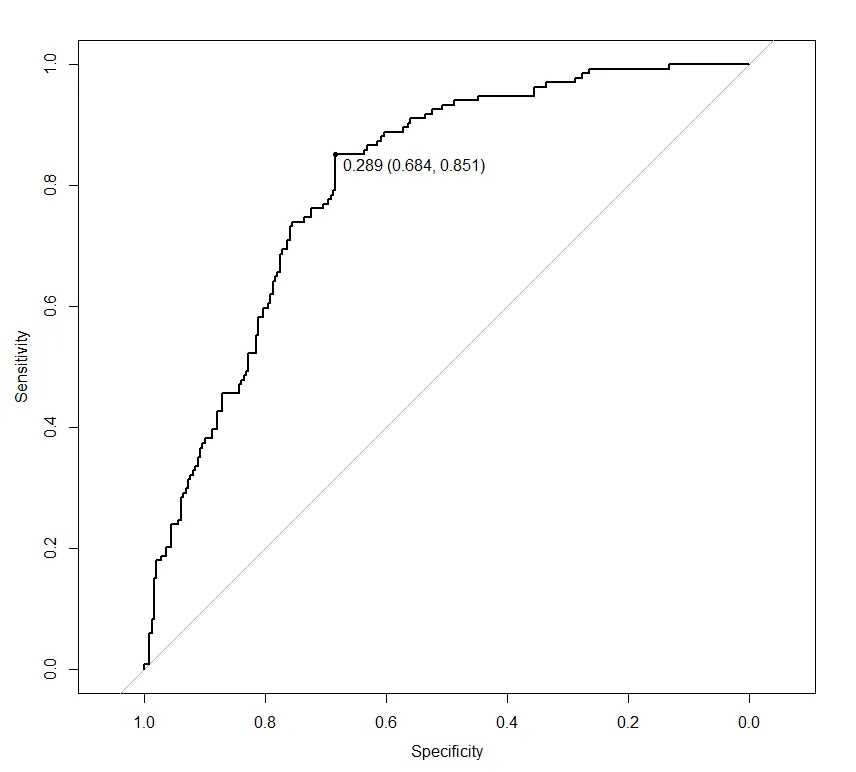
carets的thresholder函数找到了我的最佳阈值,如下所示:thres <- caret::thresholder(gbm, threshold = seq(.01,0.99, by = 0.01), final = TRUE, statistics = "all")。从中我使用Youden's J得出了一个值为0.63,这给了我最好的FPR,但也降低了TPR。 - SB21gbm模型的阈值呢?更改模型中的阈值是否是最佳方法?谢谢。 - SB21All_train.rds。你能否发布一个可重现的示例,其中包含内置数据集。您可以通过预测概率并手动设置阈值来更改caret中的预测阈值。 - missuse