我正在使用Pandas 0.10.1版本
考虑以下数据框:
Date State City SalesToday SalesMTD SalesYTD
20130320 stA ctA 20 400 1000
20130320 stA ctB 30 500 1100
20130320 stB ctC 10 500 900
20130320 stB ctD 40 200 1300
20130320 stC ctF 30 300 800
我该如何按州分组小计?
State City SalesToday SalesMTD SalesYTD
stA ALL 50 900 2100
stA ctA 20 400 1000
stA ctB 30 500 1100
我尝试使用数据透视表,但我只能在列中得到小计。
table = pivot_table(df, values=['SalesToday', 'SalesMTD','SalesYTD'],\
rows=['State','City'], aggfunc=np.sum, margins=True)
我可以用 Excel 的数据透视表来实现这个。
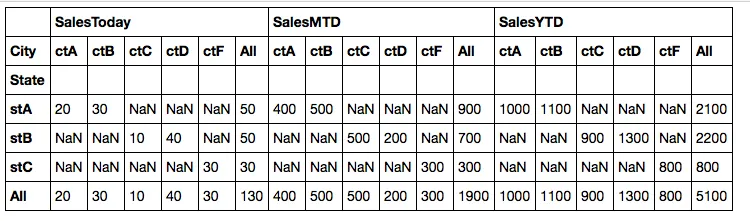
rows不是一个参数。我指定了一个由3列组成的索引,但输出结果只返回总计而不是索引列的小计。 - datalifenyc