要实现这一点,您需要完成几个步骤。
第一步是将您的数据放入一个data.frame()中:
sites.data = data.frame(lon = c(-77.61198, -77.57306, -77.543),
lat = c(35.227792, 35.30288, 35.196),
label = c("PP Site","NOAA", "CRONOS Data"),
colour = c("red","blue","blue"))
现在我们可以使用 gg_map 包获取该地区的地图:
require(gg_map)
map.base <- get_map(location = c(lon = mean(sites.data$lon),
lat = mean(sites.data$lat)),
zoom = 10)
我们需要那张图片的尺寸:
bb <- attr(map.base,"bb")
现在我们开始确定比例尺。首先,我们需要一个函数,根据纬度/经度给出两点之间的距离。为此,我们使用Haversine公式,由Floris在计算两个GPS点之间(x,y)距离中描述:
distHaversine <- function(long, lat){
long <- long*pi/180
lat <- lat*pi/180
dlong = (long[2] - long[1])
dlat = (lat[2] - lat[1])
R = 6371;
a = sin(dlat/2)*sin(dlat/2) + cos(lat[1])*cos(lat[2])*sin(dlong/2)*sin(dlong/2)
c = 2 * atan2( sqrt(a), sqrt(1-a) )
d = R * c
return(d)
}
下一步是确定定义比例尺的点。在这个例子中,我把东西放在了图的左下角,使用我们已经找出的边界框:
sbar <- data.frame(lon.start = c(bb$ll.lon + 0.1*(bb$ur.lon - bb$ll.lon)),
lon.end = c(bb$ll.lon + 0.25*(bb$ur.lon - bb$ll.lon)),
lat.start = c(bb$ll.lat + 0.1*(bb$ur.lat - bb$ll.lat)),
lat.end = c(bb$ll.lat + 0.1*(bb$ur.lat - bb$ll.lat)))
sbar$distance = distHaversine(long = c(sbar$lon.start,sbar$lon.end),
lat = c(sbar$lat.start,sbar$lat.end))
最后,我们可以使用比例尺绘制地图。
ptspermm <- 2.83464567
map.scale <- ggmap(map.base,
extent = "normal",
maprange = FALSE) %+% sites.data +
geom_point(aes(x = lon,
y = lat,
colour = colour)) +
geom_text(aes(x = lon,
y = lat,
label = label),
hjust = 0,
vjust = 0.5,
size = 8/ptspermm) +
geom_segment(data = sbar,
aes(x = lon.start,
xend = lon.end,
y = lat.start,
yend = lat.end)) +
geom_text(data = sbar,
aes(x = (lon.start + lon.end)/2,
y = lat.start + 0.025*(bb$ur.lat - bb$ll.lat),
label = paste(format(distance,
digits = 4,
nsmall = 2),
'km')),
hjust = 0.5,
vjust = 0,
size = 8/ptspermm) +
coord_map(projection="mercator",
xlim=c(bb$ll.lon, bb$ur.lon),
ylim=c(bb$ll.lat, bb$ur.lat))
然后我们保存它...
map.out <- map.scale +
theme_bw(base_size = 8) +
theme(legend.justification=c(1,1),
legend.position = c(1,1))
ggsave(filename ="map.png",
plot = map.out,
dpi = 300,
width = 4,
height = 3,
units = c("in"))
这将使你得到类似于以下的东西:
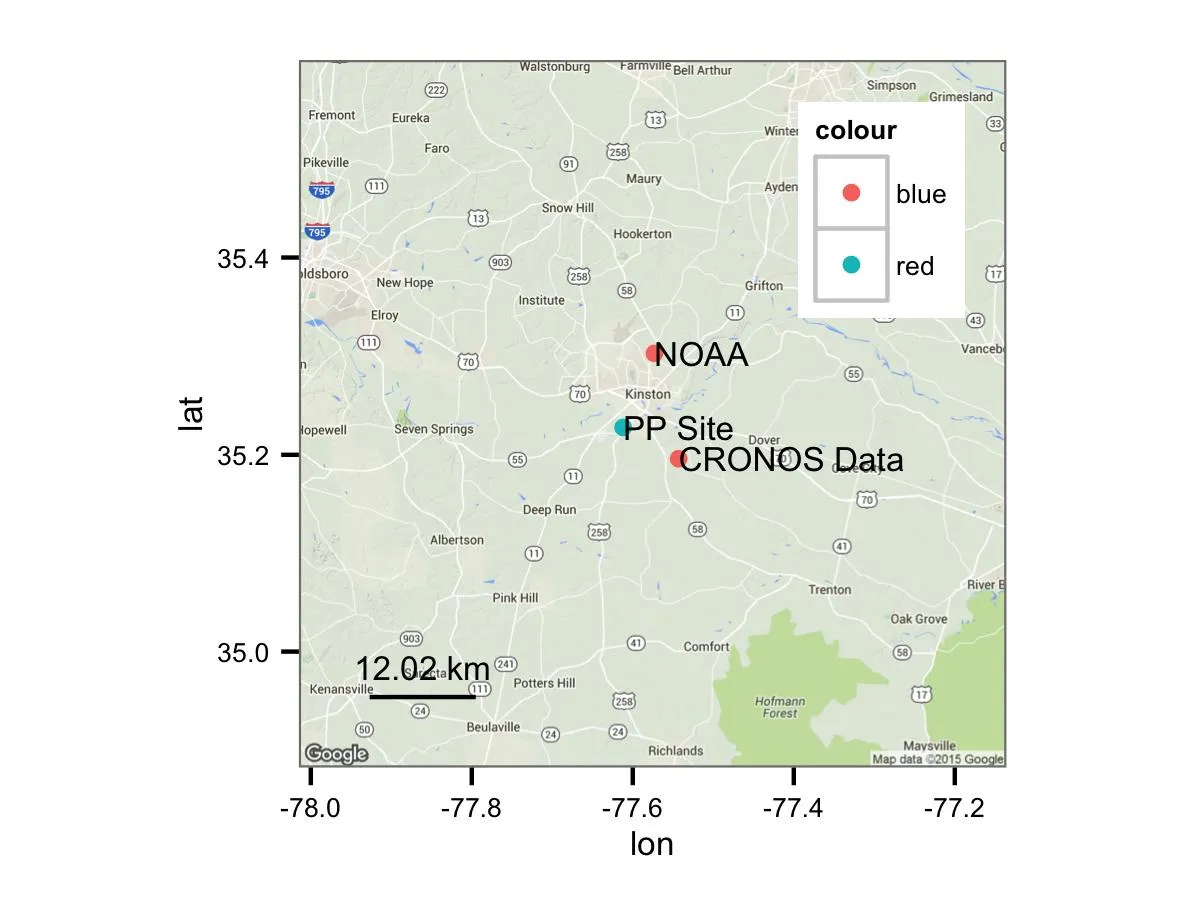
好处在于所有的绘图都使用ggplot2(),因此您可以使用http://ggplot2.org上的文档,使其看起来符合您的需求。



?OSM_scale_lookup和相关的FAQ链接。 - Ricardo Saporta