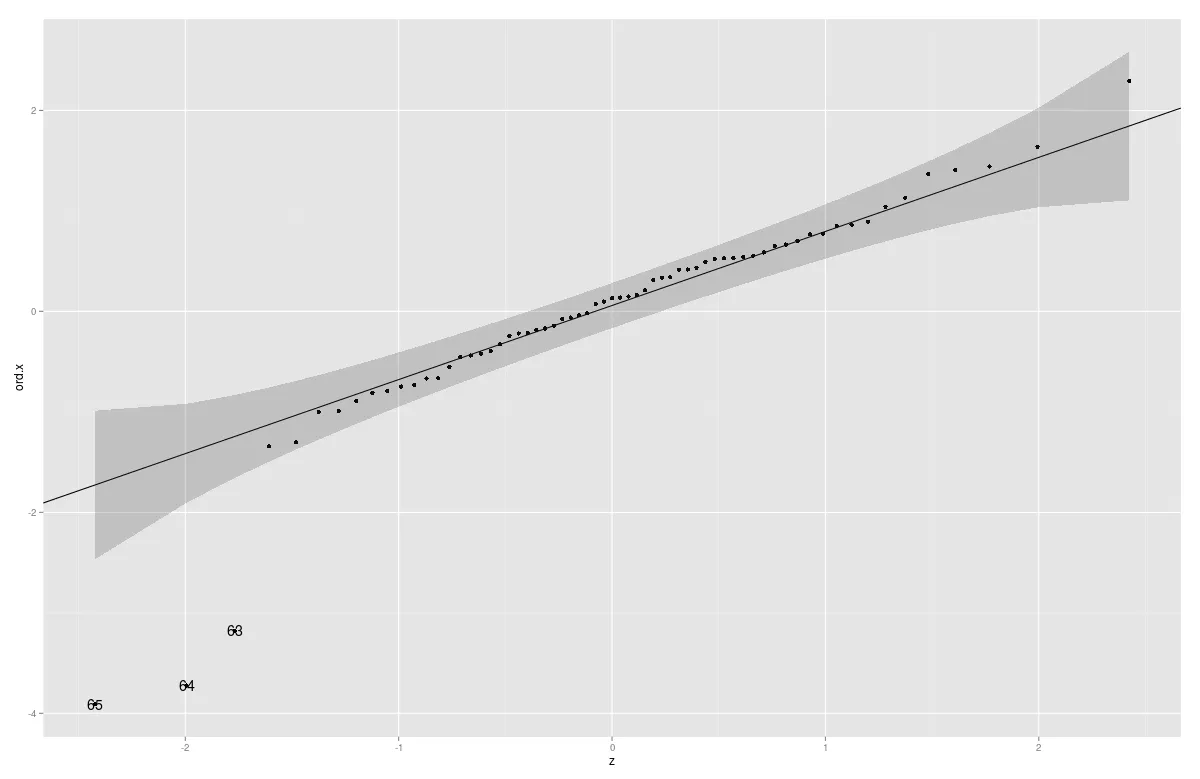
自3.0版本以来,一个等同于下面的
stat_qq_line已经
出现在官方ggplot2代码中。
旧版本:
从2.0版本开始,ggplot2有一个经过充分记录的扩展接口;因此,我们现在可以轻松地为qqline编写一个新的统计方法(我已经第一次完成了这个任务,所以欢迎改进):
qq.line <- function(data, qf, na.rm) {
q.sample <- quantile(data, c(0.25, 0.75), na.rm = na.rm)
q.theory <- qf(c(0.25, 0.75))
slope <- diff(q.sample) / diff(q.theory)
intercept <- q.sample[1] - slope * q.theory[1]
list(slope = slope, intercept = intercept)
}
StatQQLine <- ggproto("StatQQLine", Stat,
required_aes = c('sample'),
compute_group = function(data, scales,
distribution = stats::qnorm,
dparams = list(),
na.rm = FALSE) {
qf <- function(p) do.call(distribution, c(list(p = p), dparams))
n <- length(data$sample)
theoretical <- qf(stats::ppoints(n))
qq <- qq.line(data$sample, qf = qf, na.rm = na.rm)
line <- qq$intercept + theoretical * qq$slope
data.frame(x = theoretical, y = line)
}
)
stat_qqline <- function(mapping = NULL, data = NULL, geom = "line",
position = "identity", ...,
distribution = stats::qnorm,
dparams = list(),
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE) {
layer(stat = StatQQLine, data = data, mapping = mapping, geom = geom,
position = position, show.legend = show.legend, inherit.aes = inherit.aes,
params = list(distribution = distribution,
dparams = dparams,
na.rm = na.rm, ...))
}
这也可以泛化到分布上(就像
stat_qq一样),并可按以下方式使用:
> test.data <- data.frame(sample=rnorm(100, 10, 2))
> test.data.2 <- data.frame(sample=rt(100, df=2))
> ggplot(test.data, aes(sample=sample)) + stat_qq() + stat_qqline()
> ggplot(test.data.2, aes(sample=sample)) + stat_qq(distribution=qt, dparams=list(df=2)) +
+ stat_qqline(distribution=qt, dparams=list(df=2))
很遗憾,由于qqline在单独的层上,我找不到“重复使用”分布参数的方法,但这只应该是一个小问题。