我试图从在R中切割(
此外,我不能仅使用原始hclust的聚类,因为(令人沮丧的是),
cut)到一定高度的树状图中提取分类信息。对于hclust对象,可以使用cutree轻松完成此操作,但我无法弄清如何在dendrogram对象上执行此操作。此外,我不能仅使用原始hclust的聚类,因为(令人沮丧的是),
cutree的类编号与cut的类编号不同。hc <- hclust(dist(USArrests), "ave")
classification<-cutree(hc,h=70)
dend1 <- as.dendrogram(hc)
dend2 <- cut(dend1, h = 70)
str(dend2$lower[[1]]) #group 1 here is not the same as
classification[classification==1] #group 1 here
有没有办法让分类彼此映射,或者从 dendrogram 对象中提取较低层次的成员(也许可以巧妙地使用 dendrapply?)以一种更类似于 cutree 的格式呈现?
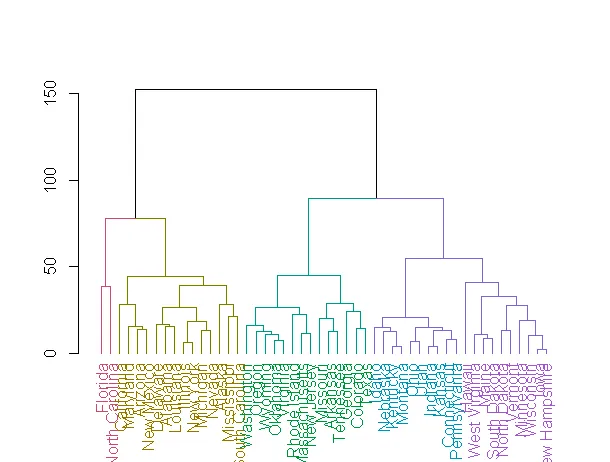
color_branches(dend1, k = 4)中提取组分配? - user2117258