我用sklearn.svm.svc()拟合了一个三维特征数据集。我可以使用matplotlib和Axes3D为每个观察点绘制点。我想绘制决策边界以查看拟合情况。我尝试适应二维示例来绘制决策边界,但没有成功。我了解到clf.coef_是垂直于决策边界的向量。如何绘制它以查看它在哪里分割点?
2个回答
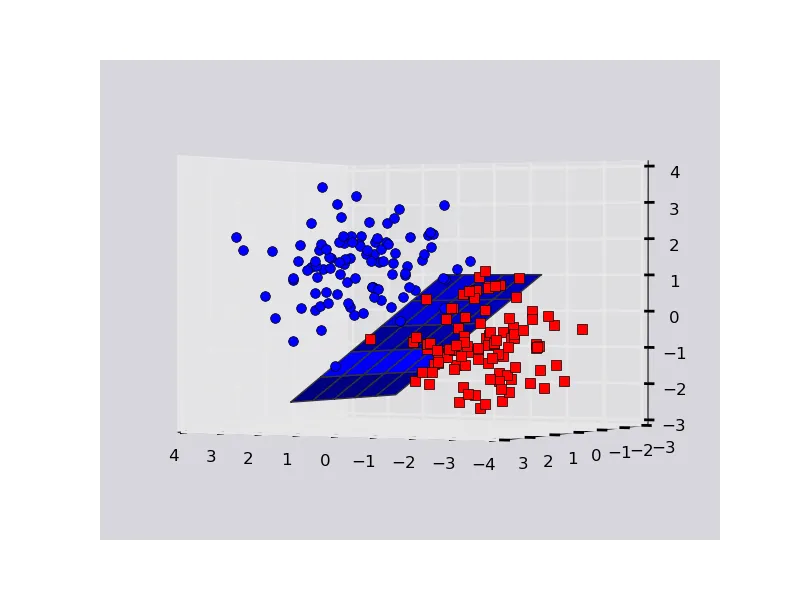
12
这是一个玩具数据集的示例。请注意,在matplotlib中进行三维绘图可能会有些奇怪。有时候,位于平面后方的点可能看起来像在前方,因此您可能需要调整旋转图表以确定发生了什么。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from sklearn.svm import SVC
rs = np.random.RandomState(1234)
# Generate some fake data.
n_samples = 200
# X is the input features by row.
X = np.zeros((200,3))
X[:n_samples/2] = rs.multivariate_normal( np.ones(3), np.eye(3), size=n_samples/2)
X[n_samples/2:] = rs.multivariate_normal(-np.ones(3), np.eye(3), size=n_samples/2)
# Y is the class labels for each row of X.
Y = np.zeros(n_samples); Y[n_samples/2:] = 1
# Fit the data with an svm
svc = SVC(kernel='linear')
svc.fit(X,Y)
# The equation of the separating plane is given by all x in R^3 such that:
# np.dot(svc.coef_[0], x) + b = 0. We should solve for the last coordinate
# to plot the plane in terms of x and y.
z = lambda x,y: (-svc.intercept_[0]-svc.coef_[0][0]*x-svc.coef_[0][1]*y) / svc.coef_[0][2]
tmp = np.linspace(-2,2,51)
x,y = np.meshgrid(tmp,tmp)
# Plot stuff.
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.plot_surface(x, y, z(x,y))
ax.plot3D(X[Y==0,0], X[Y==0,1], X[Y==0,2],'ob')
ax.plot3D(X[Y==1,0], X[Y==1,1], X[Y==1,2],'sr')
plt.show()
编辑 (上面评论中的关键数学线性代数语句):
# The equation of the separating plane is given by all x in R^3 such that:
# np.dot(coefficients, x_vector) + intercept_value = 0.
# We should solve for the last coordinate: x_vector[2] == z
# to plot the plane in terms of x and y.
- Matt Hancock
4
4
您无法可视化许多特征的决策面。这是因为维度太多,没有办法可视化N维表面。
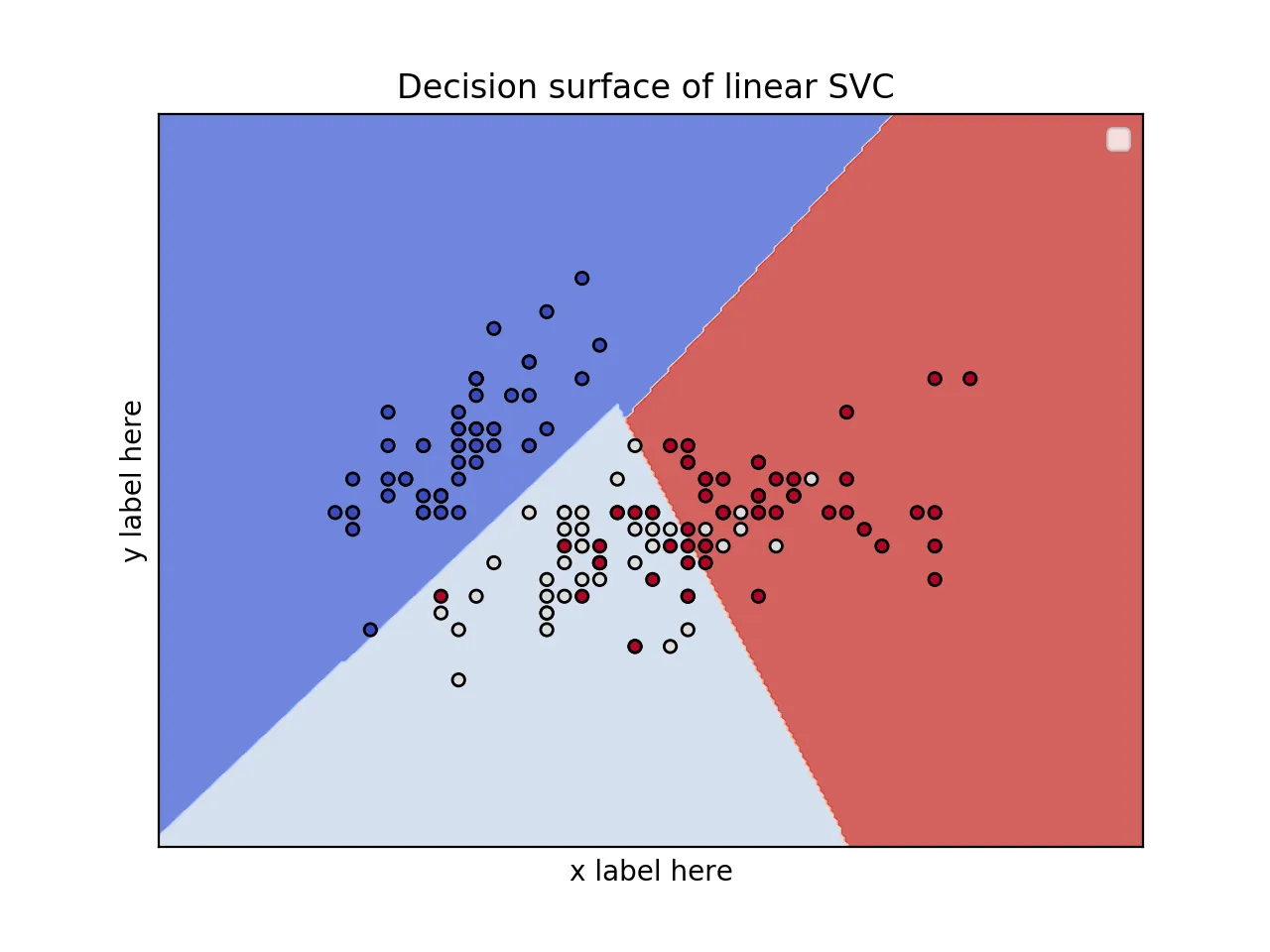
但是,您可以使用2个特征并按如下方式绘制漂亮的决策面。
我也在这里写了一篇文章: https://towardsdatascience.com/support-vector-machines-svm-clearly-explained-a-python-tutorial-for-classification-problems-29c539f3ad8?source=friends_link&sk=80f72ab272550d76a0cc3730d7c8af35 第1种情况:对于2个特征和使用鸢尾花数据集的2D图。
但是,您可以使用2个特征并按如下方式绘制漂亮的决策面。
我也在这里写了一篇文章: https://towardsdatascience.com/support-vector-machines-svm-clearly-explained-a-python-tutorial-for-classification-problems-29c539f3ad8?source=friends_link&sk=80f72ab272550d76a0cc3730d7c8af35 第1种情况:对于2个特征和使用鸢尾花数据集的2D图。
from sklearn.svm import SVC
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import svm, datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, :2] # we only take the first two features.
y = iris.target
def make_meshgrid(x, y, h=.02):
x_min, x_max = x.min() - 1, x.max() + 1
y_min, y_max = y.min() - 1, y.max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
return xx, yy
def plot_contours(ax, clf, xx, yy, **params):
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
out = ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, **params)
return out
model = svm.SVC(kernel='linear')
clf = model.fit(X, y)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# title for the plots
title = ('Decision surface of linear SVC ')
# Set-up grid for plotting.
X0, X1 = X[:, 0], X[:, 1]
xx, yy = make_meshgrid(X0, X1)
plot_contours(ax, clf, xx, yy, cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm, alpha=0.8)
ax.scatter(X0, X1, c=y, cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm, s=20, edgecolors='k')
ax.set_ylabel('y label here')
ax.set_xlabel('x label here')
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
ax.set_title(title)
ax.legend()
plt.show()
from sklearn.svm import SVC
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import svm, datasets
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
iris = datasets.load_iris()
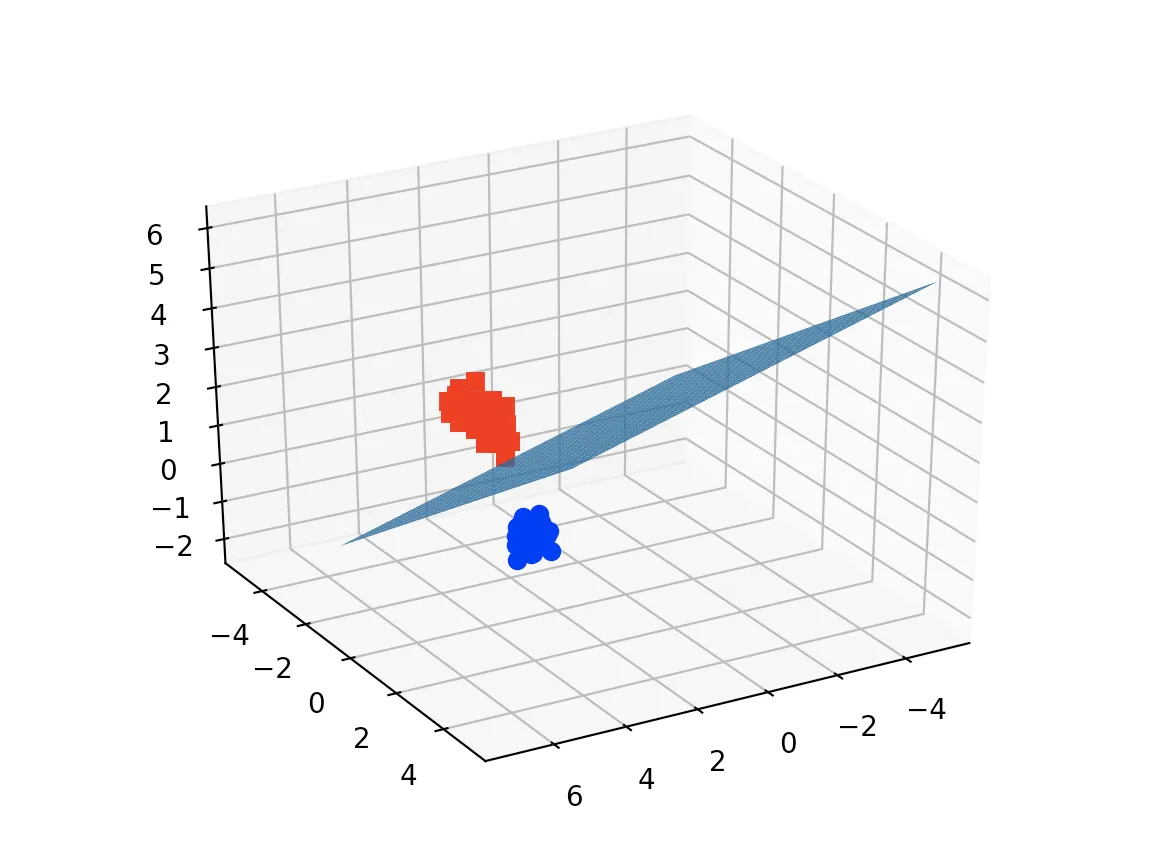
X = iris.data[:, :3] # we only take the first three features.
Y = iris.target
#make it binary classification problem
X = X[np.logical_or(Y==0,Y==1)]
Y = Y[np.logical_or(Y==0,Y==1)]
model = svm.SVC(kernel='linear')
clf = model.fit(X, Y)
# The equation of the separating plane is given by all x so that np.dot(svc.coef_[0], x) + b = 0.
# Solve for w3 (z)
z = lambda x,y: (-clf.intercept_[0]-clf.coef_[0][0]*x -clf.coef_[0][1]*y) / clf.coef_[0][2]
tmp = np.linspace(-5,5,30)
x,y = np.meshgrid(tmp,tmp)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.plot3D(X[Y==0,0], X[Y==0,1], X[Y==0,2],'ob')
ax.plot3D(X[Y==1,0], X[Y==1,1], X[Y==1,2],'sr')
ax.plot_surface(x, y, z(x,y))
ax.view_init(30, 60)
plt.show()
- seralouk
网页内容由stack overflow 提供, 点击上面的可以查看英文原文,
原文链接
原文链接
(-svc.intercept_[0]-svc.coef_[0][0]*x-svc.coef_[0][1]*y)/ svc.coef_[0][2]请注意加粗的部分,应为 "乘以 y" 而非 "y"。 - mescarra