我希望在Python中计算某些数字的第n个奇次方根。Numpy提供了一个立方根函数,使用该函数可以计算x^(1/3)。
x = np.linspace(-100,100,100)
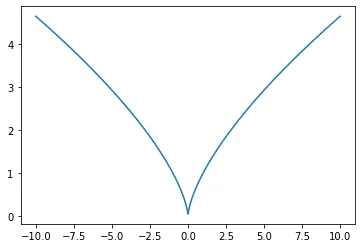
np.cbrt(x)
>>> array([-4.64158883, -4.26859722, -3.81571414, -3.21829795, -2.23144317,
2.23144317, 3.21829795, 3.81571414, 4.26859722, 4.64158883])
然而,如果我想以直接的方式计算其他k阶奇根的相同内容,我有些困难。我无法直接使用np.power,甚至无法计算立方根:
np.power(x,1./3)
>>> array([ nan, nan, nan, nan, nan,
2.23144317, 3.21829795, 3.81571414, 4.26859722, 4.64158883])
(-100.)**(1./3)
>>> ValueError: negative number cannot be raised to a fractional power
我可以计算x的绝对值的第k个奇次方根,然后根据x中负数项的符号进行更改,但我想知道是否有更直接的方法。这是我的当前解决方案:
def kth_root(x,k):
if k % 2 != 0:
res = np.power(np.abs(x),1./k)
return res*np.sign(x)
else:
return np.power(np.abs(x),1./k)
kth_root(x,3)
>>> array([-4.64158883, -4.26859722, -3.81571414, -3.21829795, -2.23144317,
2.23144317, 3.21829795, 3.81571414, 4.26859722, 4.64158883])
np.sign比abs(x)/x更高效。顺便说一下,你需要这样做的原因是通常计算幂时使用对数。 - PM 2Ringprint((-100) ** (1/3)) # (2.3207944168063896+4.019733843830847j)。 - DeepSpace(-100.)**(1./3)也不是 Numpy 吗? - DeepSpace**运算符比-运算符优先级高。 - DeepSpace