我用Networkx创建了一个图形网络,并使用Mayavi绘制出来。
在创建图形后,我使用
其次,我想知道如何交互式地删除与这些节点相连的节点和边缘。例如,如果我想删除度数小于2的节点和与其相连的边缘,首先我想显示一个交互式图形,其中所有度数小于2的节点都突出显示。用户可以以交互方式选择要删除的节点。通过单击突出显示的节点,可以删除节点和连接边缘。
编辑:我尝试从上面发布的完整代码中包含pos.drop(pos.index [remove],inplace = True)来删除已删除节点的位置。
但是我仍然无法获得正确的输出。
在创建图形后,我使用
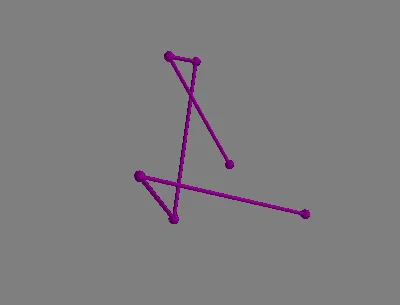
G.remove_nodes_from()删除度数小于2的节点。一旦节点被删除,与这些节点相连的边也会被删除,但是这些节点仍然出现在最终输出中(如下图所示)。import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mayavi import mlab
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
pos = [[0.1, 2, 0.3], [40, 0.5, -10],
[0.1, -40, 0.3], [-49, 0.1, 2],
[10.3, 0.3, 0.4], [-109, 0.3, 0.4]]
pos = pd.DataFrame(pos, columns=['x', 'y', 'z'])
ed_ls = [(x, y) for x, y in zip(range(0, 5), range(1, 6))]
G = nx.Graph()
G.add_edges_from(ed_ls)
remove = [node for node, degree in dict(G.degree()).items() if degree < 2]
G.remove_nodes_from(remove)
pos.drop(pos.index[remove], inplace=True)
print(G.edges)
nx.draw(G)
plt.show()
mlab.figure(1, bgcolor=bgcolor)
mlab.clf()
for i, e in enumerate(G.edges()):
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# the x,y, and z co-ordinates are here
pts = mlab.points3d(pos['x'], pos['y'], pos['z'],
scale_mode='none',
scale_factor=1)
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
pts.mlab_source.dataset.lines = np.array(G.edges())
tube = mlab.pipeline.tube(pts, tube_radius=edge_size)
mlab.pipeline.surface(tube, color=edge_color)
mlab.show() # interactive window
其次,我想知道如何交互式地删除与这些节点相连的节点和边缘。例如,如果我想删除度数小于2的节点和与其相连的边缘,首先我想显示一个交互式图形,其中所有度数小于2的节点都突出显示。用户可以以交互方式选择要删除的节点。通过单击突出显示的节点,可以删除节点和连接边缘。
编辑:我尝试从上面发布的完整代码中包含pos.drop(pos.index [remove],inplace = True)来删除已删除节点的位置。
但是我仍然无法获得正确的输出。


pos,因此你将不得不从字典中删除这些节点。 - Paul Brodersen