编辑:
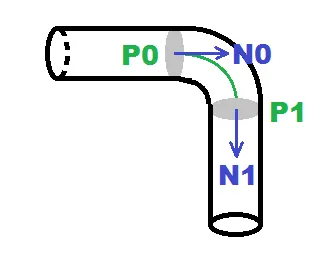
附上一个逼真的管道草图。
所以假设这条曲线不像地狱一样颤动,蓝色线表示圆,红色线表示中心点,绿色线表示中心路径。
Clarification
tube has the same circular diameter everywhere so no distortion due to bending is present !!! input is 2 endpoints points (centers of tube) P0,P1 and 2 vectors (normal/direction of tube) N0,N1
Solution
Use Interpolation cubic for example this one
p(t)=a0+a1*t+a2*t*t+a3*t*t*t
t=<0,1.0>
so write equations for the known data, solve a0,a1,a2,a3 coefficients for each axis you need (2D: x,y) and then you can get the center point and its normal in any point along the bend side which is what you need.
Now some generic equations:
p(t)=a0+a1*t+ a2*t*t+ a3*t*t*t // circle center position
n(t)= a1 +2.0*a2*t +3.0*a3*t*t // circle orientation
p,n,a0,a1,a2,a3 are vectors !!!t is scalarNow add the known data
I. t=0 -> p(0)=P0
P0=a0
a0=P0
II. t=0 -> n(0)=N0
N0=a1
a1=N0
III. t=1 -> p(1)=P1
P1=a0+a1+a2+a3
P1=P0+N0+a2+a3
a2=P1-P0-N0-a3
IV. t=1 -> n(1)=N1
N1=a1+2.0*a2+3.0*a3
N1=N0+2.0*(P1-P0-N0-a3)+3.0*a3
a3=N1+N0-2.0*(P1-P0)
III.
a2=P1-P0-N0-(N1+N0-2.0*(P1-P0))
a2=P1-P0-N0-N1-N0+2.0*(P1-P0)
a2=P1-P0-N1+2.0*(P1-P0-N0)
a2=3.0*(P1-P0)-N1-2.0*N0
So if I did not make any silly mistake then coefficients are:
a0=P0
a1=N0
a2=3.0*(P1-P0)-N1-2.0*N0
a3=N1+N0-2.0*(P1-P0)
So now just encode generic equations into some function with input parameter t and output p(t) and n(t) and/or render circle or tube segment and the call this in for loop for example like this:
for (t=0.0;t<=1.0;t+=0.1) f(t);
[编辑1] C++实现
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void glCircle3D(double *pos,double *nor,double r,bool _fill)
{
int i,n=36;
double a,da=divide(pi2,n),p[3],dp[3],x[3],y[3];
if (fabs(nor[0]-nor[1])>1e-6) vector_ld(x,nor[1],nor[0],nor[2]);
else if (fabs(nor[0]-nor[2])>1e-6) vector_ld(x,nor[2],nor[1],nor[0]);
else if (fabs(nor[1]-nor[2])>1e-6) vector_ld(x,nor[0],nor[2],nor[1]);
else vector_ld(x,1.0,0.0,0.0);
vector_mul(x,x,nor);
vector_mul(y,x,nor);
vector_len(x,x,r);
vector_len(y,y,r);
if (_fill)
{
glBegin(GL_TRIANGLE_FAN);
glVertex3dv(pos);
}
else glBegin(GL_LINE_STRIP);
for (a=0.0,i=0;i<=n;i++,a+=da)
{
vector_mul(dp,x,cos(a)); vector_add(p,pos,dp);
vector_mul(dp,y,sin(a)); vector_add(p,p ,dp);
glVertex3dv(p);
}
glEnd();
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void tube(double *P0,double *N0,double *P1,double *N1,double R)
{
int i;
double a0[3],a1[3],a2[3],a3[3],p[3],n[3],t,tt,ttt;
// compute coefficients
for (i=0;i<3;i++)
{
a0[i]=P0[i];
a1[i]=N0[i];
a2[i]=(3.0*(P1[i]-P0[i]))-N1[i]-(2.0*N0[i]);
a3[i]=N1[i]+N0[i]-2.0*(P1[i]-P0[i]);
}
// step through curve from t=0 to t=1
for (t=0.0;t<=1.0;t+=0.02)
{
tt=t*t;
ttt=tt*t;
// compute circle position and orientation
for (i=0;i<3;i++)
{
p[i]=a0[i]+(a1[i]*t)+(a2[i]*tt)+(a3[i]*ttt);
n[i]=a1[i]+(2.0*a2[i]*t)+(3.0*a3[i]*tt);
}
// render it
glCircle3D(p,n,R,false);
}
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void test()
{
// tube parameters
double P0[3]={-1.0, 0.0, 0.0},N0[3]={+1.0,-1.0, 0.0},p[3];
double P1[3]={+1.0,+1.0, 0.0},N1[3]={ 0.0,+1.0, 0.0};
// just normalize normals to size 3.1415...
vector_len(N0,N0,M_PI);
vector_len(N1,N1,M_PI);
// draw normals to visula confirmation of tube direction
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glColor3f(0.0,0.0,1.0); vector_add(p,P0,N0); glVertex3dv(P0); glVertex3dv(p);
glColor3f(0.0,0.0,1.0); vector_add(p,P1,N1); glVertex3dv(P1); glVertex3dv(p);
glEnd();
// render tube
glColor3f(1.0,1.0,1.0); tube(P0,N0,P1,N1,0.2);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
在视觉上,当法线大小为M_PI(3.1415 ...)时,它的效果最佳。这是上面代码的效果:
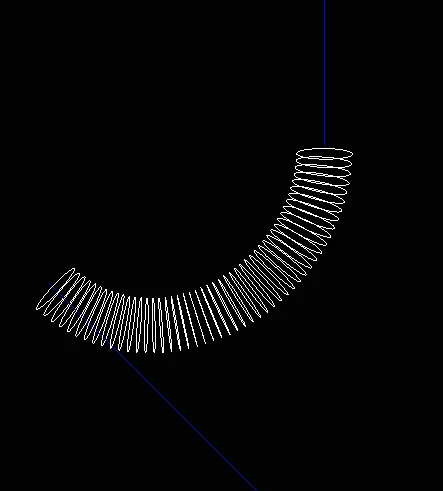
我的代码使用了自定义向量库,所以你只需要编写以下函数:
vector_ld(a,x,y,z); //a[]={ x,y,z }
vector_mul(a,b,c); //a[]=b[] x c[]
vector_mul(a,b,c); //a[]=b[] * c
vector_add(a,b,c); //a[]=b[] + c[]
vector_sub(a,b,c); //a[]=b[] - c[]
vector_len(a,b,c); //a[]=b[]* c / |b[]|
这很容易(希望我没有忘记复制什么...)...