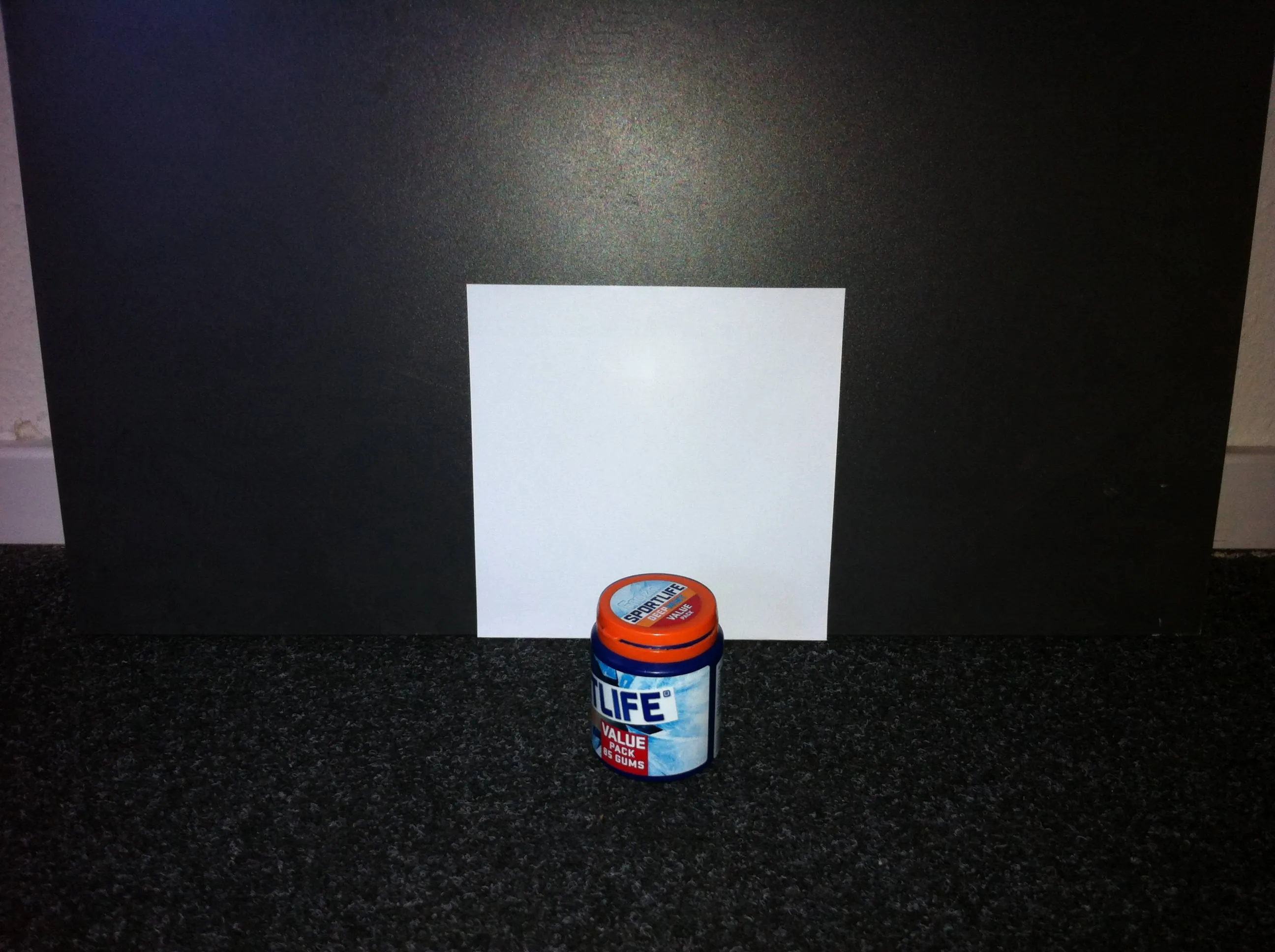
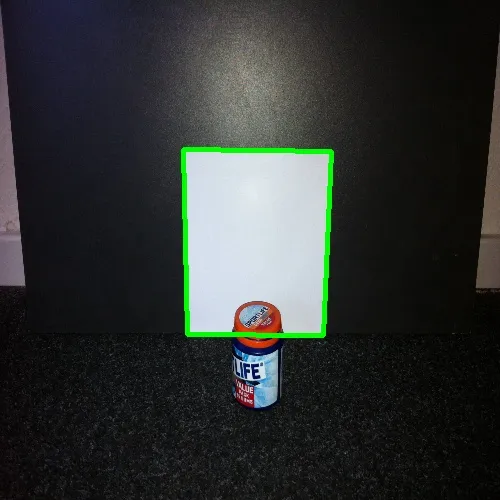
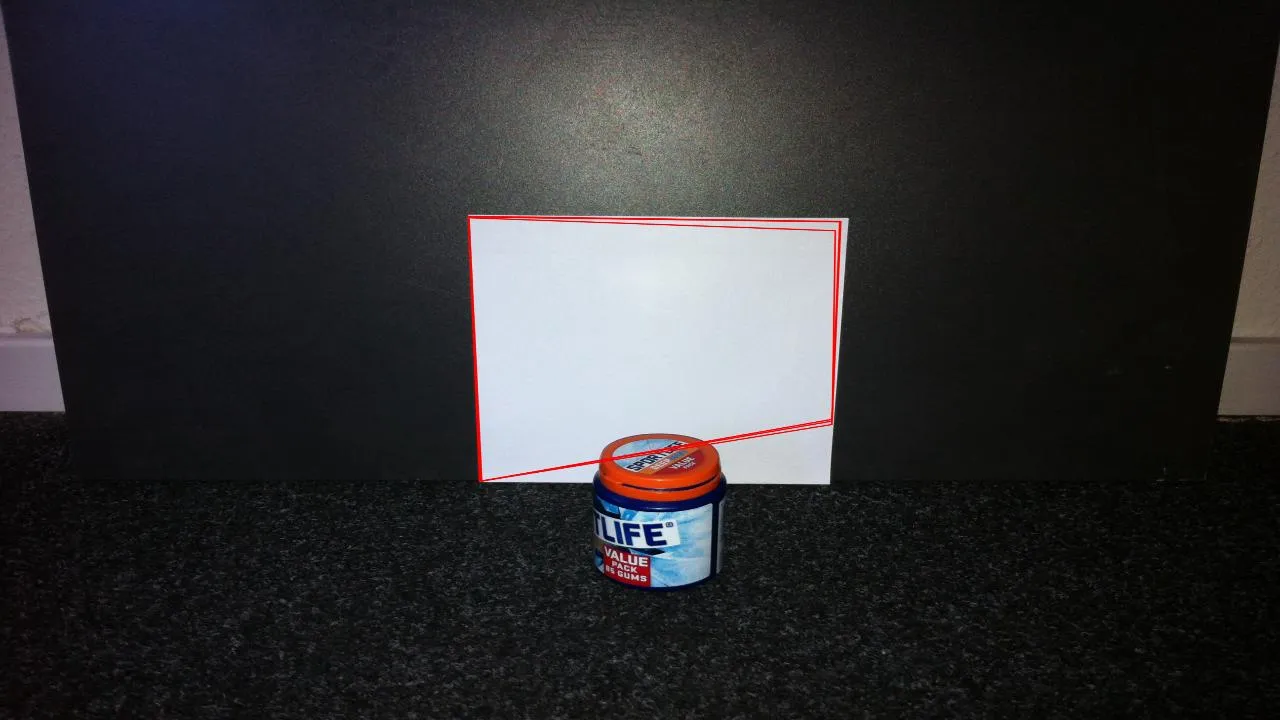
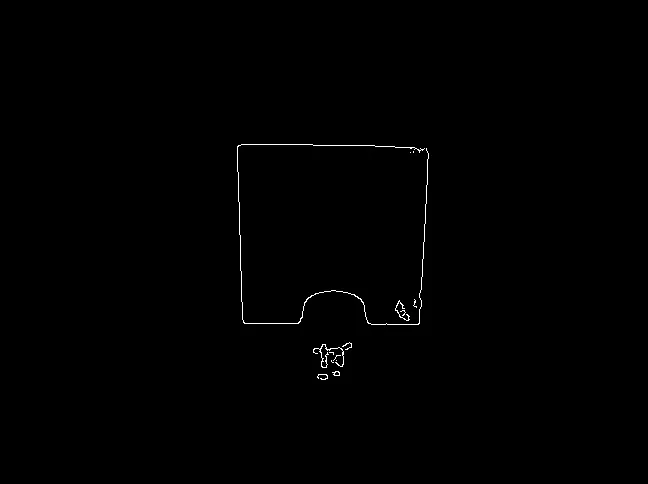
我之前提出了有关正方形检测的问题,而且 karlphillip 给出了一个不错的结果。
现在我想更进一步,找到边缘不完全可见的正方形。看看这个例子:
有什么好的建议吗?我正在使用 karlphillips 的代码:
void find_squares(Mat& image, vector<vector<Point> >& squares)
{
// blur will enhance edge detection
Mat blurred(image);
medianBlur(image, blurred, 9);
Mat gray0(blurred.size(), CV_8U), gray;
vector<vector<Point> > contours;
// find squares in every color plane of the image
for (int c = 0; c < 3; c++)
{
int ch[] = {c, 0};
mixChannels(&blurred, 1, &gray0, 1, ch, 1);
// try several threshold levels
const int threshold_level = 2;
for (int l = 0; l < threshold_level; l++)
{
// Use Canny instead of zero threshold level!
// Canny helps to catch squares with gradient shading
if (l == 0)
{
Canny(gray0, gray, 10, 20, 3); //
// Dilate helps to remove potential holes between edge segments
dilate(gray, gray, Mat(), Point(-1,-1));
}
else
{
gray = gray0 >= (l+1) * 255 / threshold_level;
}
// Find contours and store them in a list
findContours(gray, contours, CV_RETR_LIST, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
// Test contours
vector<Point> approx;
for (size_t i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++)
{
// approximate contour with accuracy proportional
// to the contour perimeter
approxPolyDP(Mat(contours[i]), approx, arcLength(Mat(contours[i]), true)*0.02, true);
// Note: absolute value of an area is used because
// area may be positive or negative - in accordance with the
// contour orientation
if (approx.size() == 4 &&
fabs(contourArea(Mat(approx))) > 1000 &&
isContourConvex(Mat(approx)))
{
double maxCosine = 0;
for (int j = 2; j < 5; j++)
{
double cosine = fabs(angle(approx[j%4], approx[j-2], approx[j-1]));
maxCosine = MAX(maxCosine, cosine);
}
if (maxCosine < 0.3)
squares.push_back(approx);
}
}
}
}
}