我有一组3D点,我使用了scipy.spatial.Delaunay进行三角剖分/四面体剖分。现在我有所有四面体的唯一面集,并希望在3D中可视化这些面。
是否有任何Python库(或具有Python包装器的库)可以做到这一点?
我有一组3D点,我使用了scipy.spatial.Delaunay进行三角剖分/四面体剖分。现在我有所有四面体的唯一面集,并希望在3D中可视化这些面。
是否有任何Python库(或具有Python包装器的库)可以做到这一点?
这也可以使用matplotlib的三维绘图来完成(无需mayavi包)。
以下代码是这样一个函数的最初简单实现。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d
from scipy.spatial import Delaunay
def plot_tri_simple(ax, points, tri):
for tr in tri.simplices:
pts = points[tr, :]
ax.plot3D(pts[[0,1],0], pts[[0,1],1], pts[[0,1],2], color='g', lw='0.1')
ax.plot3D(pts[[0,2],0], pts[[0,2],1], pts[[0,2],2], color='g', lw='0.1')
ax.plot3D(pts[[0,3],0], pts[[0,3],1], pts[[0,3],2], color='g', lw='0.1')
ax.plot3D(pts[[1,2],0], pts[[1,2],1], pts[[1,2],2], color='g', lw='0.1')
ax.plot3D(pts[[1,3],0], pts[[1,3],1], pts[[1,3],2], color='g', lw='0.1')
ax.plot3D(pts[[2,3],0], pts[[2,3],1], pts[[2,3],2], color='g', lw='0.1')
ax.scatter(points[:,0], points[:,1], points[:,2], color='b')
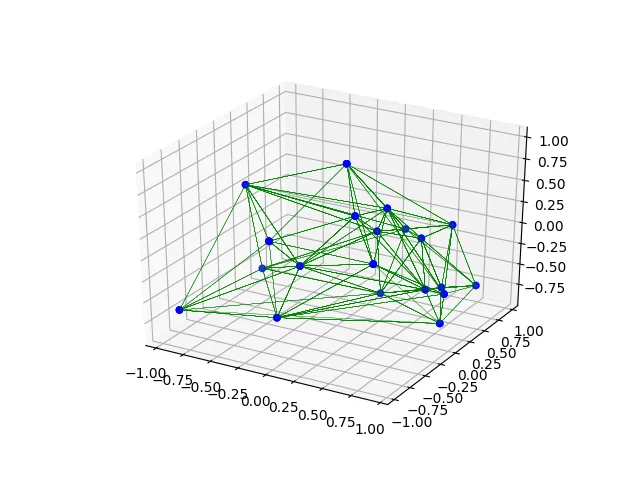
np.random.seed(0)
x = 2.0 * np.random.rand(20) - 1.0
y = 2.0 * np.random.rand(20) - 1.0
z = 2.0 * np.random.rand(20) - 1.0
points = np.vstack([x, y, z]).T
tri = Delaunay(points)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
plot_tri(ax, points, tri)
collect_edges仅处理每条边一次,并在绘图函数中使用np.nan值绘制边缘线段,只需一次绘图命令。
使用新函数运行上述测试代码的结果得到了相同的图形,但在我的计算机上运行时间提高了80倍(300毫秒比3.6毫秒)。
def plot_tri_2(ax, points, tri):
edges = collect_edges(tri)
x = np.array([])
y = np.array([])
z = np.array([])
for (i,j) in edges:
x = np.append(x, [points[i, 0], points[j, 0], np.nan])
y = np.append(y, [points[i, 1], points[j, 1], np.nan])
z = np.append(z, [points[i, 2], points[j, 2], np.nan])
ax.plot3D(x, y, z, color='g', lw='0.1')
ax.scatter(points[:,0], points[:,1], points[:,2], color='b')
def collect_edges(tri):
edges = set()
def sorted_tuple(a,b):
return (a,b) if a < b else (b,a)
# Add edges of tetrahedron (sorted so we don't add an edge twice, even if it comes in reverse order).
for (i0, i1, i2, i3) in tri.simplices:
edges.add(sorted_tuple(i0,i1))
edges.add(sorted_tuple(i0,i2))
edges.add(sorted_tuple(i0,i3))
edges.add(sorted_tuple(i1,i2))
edges.add(sorted_tuple(i1,i3))
edges.add(sorted_tuple(i2,i3))
return edges
mayavi.mlab.triangular_mesh()。import numpy as np
from mayavi import mlab
vertices = np.array([[0, 1, 0, 0],[0, 0, 1, 0],[0, 0, 0, 1]])
faces = np.array([[0, 1, 0, 0],[1, 2, 1, 2],[2, 3, 3, 3]])
mlab.triangular_mesh(vertices[0,:], vertices[1,:], vertices[2,:], faces.T)
mlab.show()