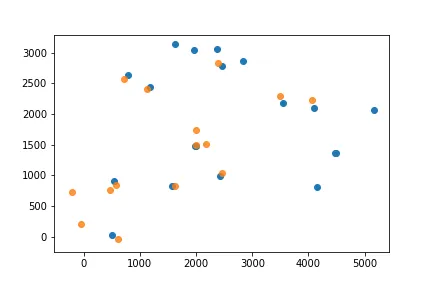
当两个集合包含噪声时,如何对齐两组点(平移+旋转)?
4
- bluewhale
2
1请看这里:https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/186111/find-the-rotation-between-set-of-points - casellimarco
谢谢。这让我了解到了这个概念(RANSAC),我认为这应该是我应该采用的方法:https://medium.com/@angel.manzur/got-outliers-ransac-them-f12b6b5f606e - bluewhale
1个回答
1
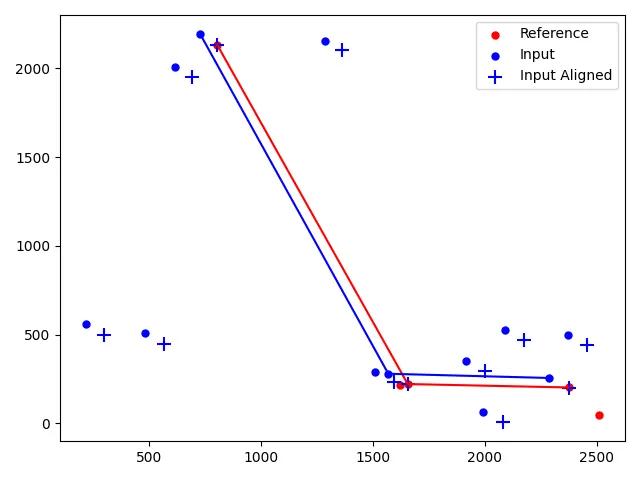
我遇到了同样的问题,并在比较CCD星星观察图表中找到了解决方案,基本思路是找到两组点的三角形的最佳匹配。
然后我使用astroalign软件包计算变换矩阵,并将其对齐到所有点。感谢上帝,它运行得非常好。
import itertools
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import astroalign as aa
def getTriangles(set_X, X_combs):
"""
Inefficient way of obtaining the lengths of each triangle's side.
Normalized so that the minimum length is 1.
"""
triang = []
for p0, p1, p2 in X_combs:
d1 = np.sqrt((set_X[p0][0] - set_X[p1][0]) ** 2 +
(set_X[p0][1] - set_X[p1][1]) ** 2)
d2 = np.sqrt((set_X[p0][0] - set_X[p2][0]) ** 2 +
(set_X[p0][1] - set_X[p2][1]) ** 2)
d3 = np.sqrt((set_X[p1][0] - set_X[p2][0]) ** 2 +
(set_X[p1][1] - set_X[p2][1]) ** 2)
d_min = min(d1, d2, d3)
d_unsort = [d1 / d_min, d2 / d_min, d3 / d_min]
triang.append(sorted(d_unsort))
return triang
def sumTriangles(ref_triang, in_triang):
"""
For each normalized triangle in ref, compare with each normalized triangle
in B. find the differences between their sides, sum their absolute values,
and select the two triangles with the smallest sum of absolute differences.
"""
tr_sum, tr_idx = [], []
for i, ref_tr in enumerate(ref_triang):
for j, in_tr in enumerate(in_triang):
# Absolute value of lengths differences.
tr_diff = abs(np.array(ref_tr) - np.array(in_tr))
# Sum the differences
tr_sum.append(sum(tr_diff))
tr_idx.append([i, j])
# Index of the triangles in ref and in with the smallest sum of absolute
# length differences.
tr_idx_min = tr_idx[tr_sum.index(min(tr_sum))]
ref_idx, in_idx = tr_idx_min[0], tr_idx_min[1]
print("Smallest difference: {}".format(min(tr_sum)))
return ref_idx, in_idx
set_ref = np.array([[2511.268821,44.864124],
[2374.085032,201.922566],
[1619.282942,216.089335],
[1655.866502,221.127787],
[ 804.171659,2133.549517], ])
set_in = np.array([[1992.438563,63.727282],
[2285.793346,255.402548],
[1568.915358, 279.144544],
[1509.720134, 289.434629],
[1914.255205, 349.477788],
[2370.786382, 496.026836],
[ 482.702882, 508.685952],
[2089.691026, 523.18825 ],
[ 216.827439, 561.807396],
[ 614.874621, 2007.304727],
[1286.639124, 2155.264827],
[ 729.566116, 2190.982364]])
# All possible triangles.
ref_combs = list(itertools.combinations(range(len(set_ref)), 3))
in_combs = list(itertools.combinations(range(len(set_in)), 3))
# Obtain normalized triangles.
ref_triang, in_triang = getTriangles(set_ref, ref_combs), getTriangles(set_in, in_combs)
# Index of the ref and in triangles with the smallest difference.
ref_idx, in_idx = sumTriangles(ref_triang, in_triang)
# Indexes of points in ref and in of the best match triangles.
ref_idx_pts, in_idx_pts = ref_combs[ref_idx], in_combs[in_idx]
print ('triangle ref %s matches triangle in %s' % (ref_idx_pts, in_idx_pts))
print ("ref:", [set_ref[_] for _ in ref_idx_pts])
print ("input:", [set_in[_] for _ in in_idx_pts])
ref_pts = np.array([set_ref[_] for _ in ref_idx_pts])
in_pts = np.array([set_in[_] for _ in in_idx_pts])
transf, (in_list,ref_list) = aa.find_transform(in_pts, ref_pts)
transf_in = transf(set_in)
print(f'transformation matrix: {transf}')
plt.scatter(set_ref[:,0],set_ref[:,1], s=100,marker='.', c='r',label='Reference')
plt.scatter(set_in[:,0],set_in[:,1], s=100,marker='.', c='b',label='Input')
plt.scatter(transf_in[:,0],transf_in[:,1], s=100,marker='+', c='b',label='Input Aligned')
plt.plot(ref_pts[:,0],ref_pts[:,1], c='r')
plt.plot(in_pts[:,0],in_pts[:,1], c='b')
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig( 'align_coordinates.png', format = 'png')
plt.show()
- John Chen
网页内容由stack overflow 提供, 点击上面的可以查看英文原文,
原文链接
原文链接