停止matplotlib在图例中重复标签
1
plt.legend需要以下参数:
- 一个包含
Artist对象的坐标轴句柄列表 - 一个包含字符串的标签列表
这些参数都是可选的,默认值为plt.gca().get_legend_handles_labels()。
你可以在调用legend之前将重复的标签放入字典中以删除它们。这是因为字典不能有重复的键。
例如:
对于 Python 版本<3.7
from collections import OrderedDict
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
handles, labels = plt.gca().get_legend_handles_labels()
by_label = OrderedDict(zip(labels, handles))
plt.legend(by_label.values(), by_label.keys())
Python版本> 3.7
自Python 3.7起,默认情况下,字典会保留输入顺序。因此,不需要使用collections模块中的OrderedDict。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
handles, labels = plt.gca().get_legend_handles_labels()
by_label = dict(zip(labels, handles))
plt.legend(by_label.values(), by_label.keys())
plt.legend 的文档。
handles, labels = ax.get_legend_handles_labels()
handle_list, label_list = [], []
for handle, label in zip(handles, labels):
if label not in label_list:
handle_list.append(handle)
label_list.append(label)
plt.legend(handle_list, label_list)
1
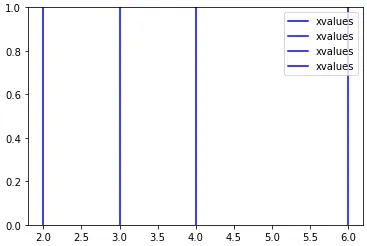
我不知道这是否可以被视为“优雅”,但您可以将标签设为变量,第一次使用后将其设置为"_nolegend_":
my_label = "xvalues"
xvalues = [2,3,4,6]
for x in xvalues:
plt.axvline(x, color='b', label=my_label)
my_label = "_nolegend_"
plt.legend()
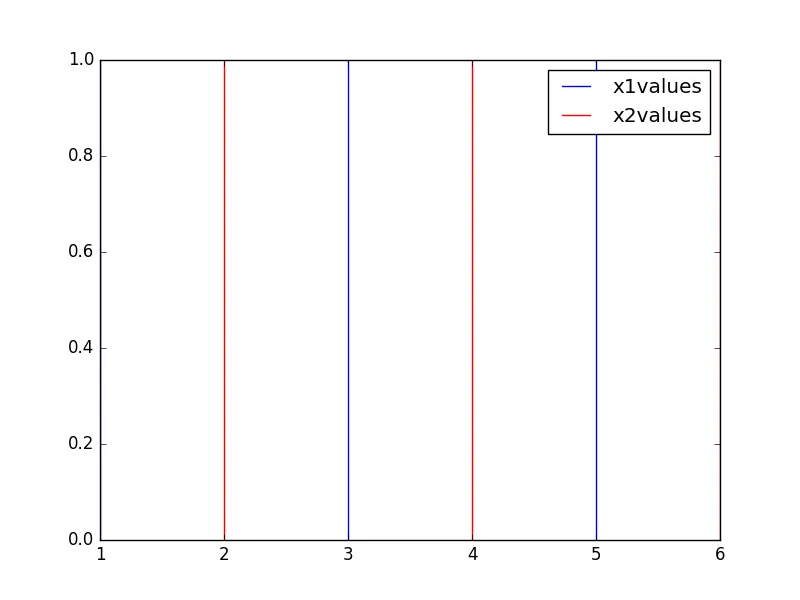
如果你需要放置多个标签,可以使用标签字典进行泛化:
my_labels = {"x1" : "x1values", "x2" : "x2values"}
x1values = [1, 3, 5]
x2values = [2, 4, 6]
for x in x1values:
plt.axvline(x, color='b', label=my_labels["x1"])
my_labels["x1"] = "_nolegend_"
for x in x2values:
plt.axvline(x, color='r', label=my_labels["x2"])
my_labels["x2"] = "_nolegend_"
plt.legend()
问题 - 3D数组
import numpy as np
a = np.random.random((2, 100, 4))
b = np.random.random((2, 100, 4))
c = np.random.random((2, 100, 4))
解决方案-字典唯一性
对于我的情况_nolegend_(bli和DSM)不起作用,label if i==0也不行。 ecatmur的答案使用get_legend_handles_labels并使用collections.OrderedDict将图例缩小。 Fons证明了这可以在没有导入的情况下实现。
与这些答案相符的是,我建议使用dict来保证唯一标签。
# Step-by-step
ax = plt.gca() # Get the axes you need
a = ax.get_legend_handles_labels() # a = [(h1 ... h2) (l1 ... l2)] non unique
b = {l:h for h,l in zip(*a)} # b = {l1:h1, l2:h2} unique
c = [*zip(*b.items())] # c = [(l1 l2) (h1 h2)]
d = c[::-1] # d = [(h1 h2) (l1 l2)]
plt.legend(*d)
或者
plt.legend(*[*zip(*{l:h for h,l in zip(*ax.get_legend_handles_labels())}.items())][::-1])
也许不如Matthew Bourque的解决方案易读易记。欢迎进行代码高尔夫。
示例
import numpy as np
a = np.random.random((2, 100, 4))
b = np.random.random((2, 100, 4))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1)
ax.plot(*a, 'C0', label='a')
ax.plot(*b, 'C1', label='b')
ax.legend(*[*zip(*{l:h for h,l in zip(*ax.get_legend_handles_labels())}.items())][::-1])
# ax.legend() # Old, ^ New
plt.show()
1
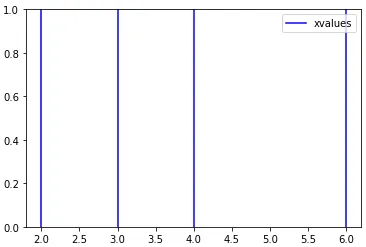
plt.gca().get_legend_handles_labels()[1]会返回一个名称列表,在绘图时可以通过以下代码检查标签是否已在列表中(label= name[i] if name[i] not in plt.gca().get_legend_handles_labels()[1] else '')。对于给定的示例,该解决方案的代码如下:import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
xvalues = [2,3,4,6]
for x in xvalues:
plt.axvline(x,color='b',\
label= 'xvalues' if 'xvalues' \
not in plt.gca().get_legend_handles_labels()[1] else '')
plt.legend()
这段代码比https://dev59.com/ymYr5IYBdhLWcg3wi6zd#13589144要短得多,比https://dev59.com/3GIk5IYBdhLWcg3wUsrv#19386045更加灵活,因为它可用于任何类型的循环和循环中的任何绘图函数。 但是,在进行许多循环时,它可能比https://dev59.com/ymYr5IYBdhLWcg3wi6zd#13589144慢。
对我个人来说,这些代码片段没有起作用。我正在绘制两个不同组的数据,并使用两种不同的颜色。当我只想看到每种颜色一个标记时,图例会显示两个红色标记和两个蓝色标记。我将粘贴一个简化版本的有效代码:
导入语句
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.legend_handler import HandlerLine2D
绘制数据
points_grp, = plt.plot(x[grp_idx], y[grp_idx], color=c.c[1], marker=m, ms=4, lw=0, label=leglab[1])
points_ctrl, = plt.plot(x[ctrl_idx], y[ctrl_idx], color=c.c[0], marker=m, ms=4, lw=0, label=leglab[0])
添加图例。
points_dict = {points_grp: HandlerLine2D(numpoints=1),points_ctrl: HandlerLine2D(numpoints=1)}
leg = ax.legend(fontsize=12, loc='upper left', bbox_to_anchor=(1, 1.03),handler_map=points_dict)
原文链接