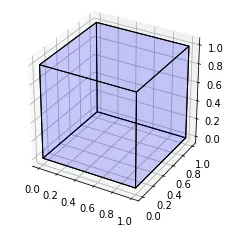
我正在尝试绘制一个长方体。实际上,我是从绘制立方体的Python脚本开始的:
import numpy as np
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
points = np.array([[-1, -1, -1],
[1, -1, -1 ],
[1, 1, -1],
[-1, 1, -1],
[-1, -1, 1],
[1, -1, 1 ],
[1, 1, 1],
[-1, 1, 1]])
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
r = [-1,1]
X, Y = np.meshgrid(r, r)
ax.plot_surface(X,Y,1, alpha=0.5)
ax.plot_surface(X,Y,-1, alpha=0.5)
ax.plot_surface(X,-1,Y, alpha=0.5)
ax.plot_surface(X,1,Y, alpha=0.5)
ax.plot_surface(1,X,Y, alpha=0.5)
ax.plot_surface(-1,X,Y, alpha=0.5)
ax.scatter3D(points[:, 0], points[:, 1], points[:, 2])
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('Z')
plt.show()
为了获得一个长方体,我将点矩阵乘以以下矩阵:
P =
[[2.06498904e-01 -6.30755443e-07 1.07477548e-03]
[1.61535574e-06 1.18897198e-01 7.85307721e-06]
[7.08353661e-02 4.48415767e-06 2.05395893e-01]]
如下:
Z = np.zeros((8,3))
for i in range(8):
Z[i,:] = np.dot(points[i,:],P)
Z = 10.0*Z
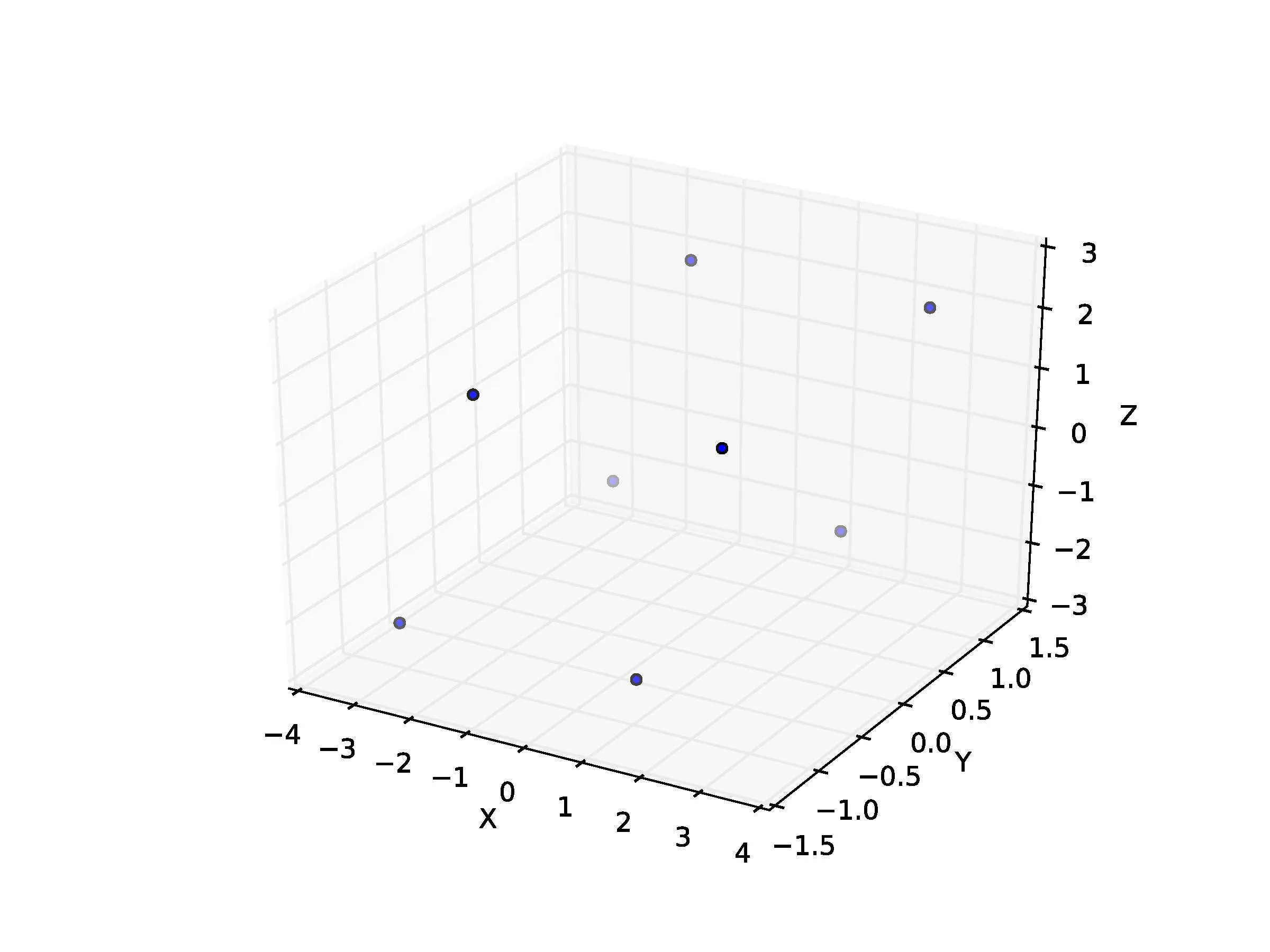
我的想法是这样表示的:
ax.scatter3D(Z[:, 0], Z[:, 1], Z[:, 2])
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('Z')
plt.show()
这就是我得到的:
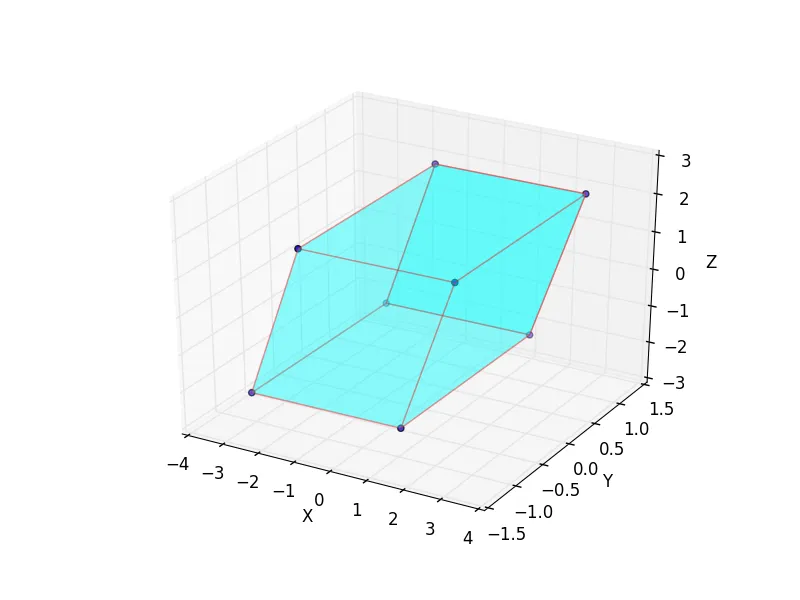
我该如何在这些不同的点上放置表面以形成平行六面体(像上面的立方体一样)?