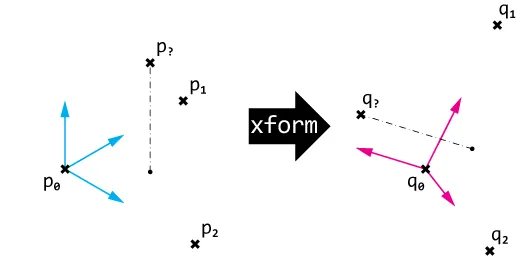
我正在使用PyMel为Autodesk Maya编程Python函数。我有三个3D点;p0,p1,p2。然后它们进行刚性变换,所以变换后(仿射变换)它们的新位置是;q0,q1,q2。在变换之前,我还有第四个点;p3。我想计算它在相同变换后的位置;q4。因此,我需要计算变换矩阵,然后将其应用于p4。我不知道该如何做。List =对象数组。
import pymel.core as pm
import pymel.core.datatypes as dt
p0 = dt.Vector(pm.getAttr(list[0]+".tx"), pm.getAttr(list[0]+".ty"), pm.getAttr(list[0]+".tz"))
p1 = dt.Vector(pm.getAttr(list[1]+".tx"), pm.getAttr(list[1]+".ty"), pm.getAttr(list[1]+".tz"))
p2 = dt.Vector(pm.getAttr(list[2]+".tx"), pm.getAttr(list[2]+".ty"), pm.getAttr(list[2]+".tz")
p3 = dt.Vector(pm.getAttr(list[3]+".tx"), pm.getAttr(list[3]+".ty"), pm.getAttr(list[3]+".tz"))
从Maya场景中的动画对象中读取3D点。因此在另一个帧上,我运行此代码以获取
q0 = dt.Vector(pm.getAttr(list[0]+".tx"), pm.getAttr(list[0]+".ty"), pm.getAttr(list[0]+".tz"))
q1 = dt.Vector(pm.getAttr(list[1]+".tx"), pm.getAttr(list[1]+".ty"), pm.getAttr(list[1]+".tz"))
q2 = dt.Vector(pm.getAttr(list[2]+".tx"), pm.getAttr(list[2]+".ty"), pm.getAttr(list[2]+".tz"))
#q3 = TransformationMatrix between (p0,p1,p2) and (q0,q1,q2), applied to p3
我尝试使用向量进行计算,但由于除以零而出现错误...所以我想一个转换矩阵应该可以解决这个问题。
我有一个截止日期,需要帮助解决这个问题! 请帮帮我!
我需要这个函数“solve_affine”,但它只应该从每组中取3个点,而不是4个。而且我不能使用numpy...