我有一个矩阵数据,想用热图可视化它。行代表物种,所以我想在行旁边显示系统发生树,并按照树的顺序重新排列热图中的行。我知道R语言中的heatmap函数可以创建层次聚类热图,但如何使用我的系统发生聚类替代绘图中默认创建的距离聚类呢?
如何使用固定的外部分层聚类创建热图
4
首先,您需要使用包ape将数据读入为phylo对象。
library(ape)
dat <- read.tree(file="your/newick/file")
#or
dat <- read.tree(text="((A:4.2,B:4.2):3.1,C:7.3);")
以下内容仅适用于超度树。接下来的步骤是将您的系统发育树转换为类
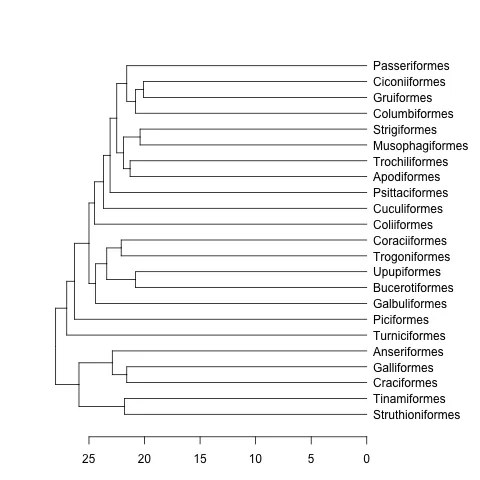
dendrogram。这里提供一个例子:data(bird.orders) #This is already a phylo object
hc <- as.hclust(bird.orders) #Compulsory step as as.dendrogram doesn't have a method for phylo objects.
dend <- as.dendrogram(hc)
plot(dend, horiz=TRUE)
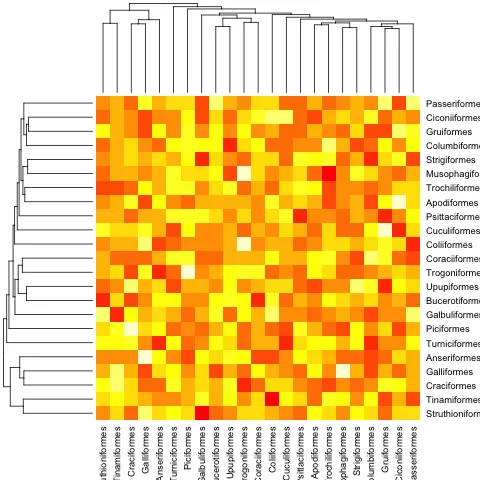
mat <- matrix(rnorm(23*23),nrow=23, dimnames=list(sample(bird.orders$tip, 23), sample(bird.orders$tip, 23))) #Some random data to plot
首先,我们需要根据系统发育树的顺序对矩阵进行排序:
ord.mat <- mat[bird.orders$tip,bird.orders$tip]
然后将其输入到
heatmap中:heatmap(ord.mat, Rowv=dend, Colv=dend)
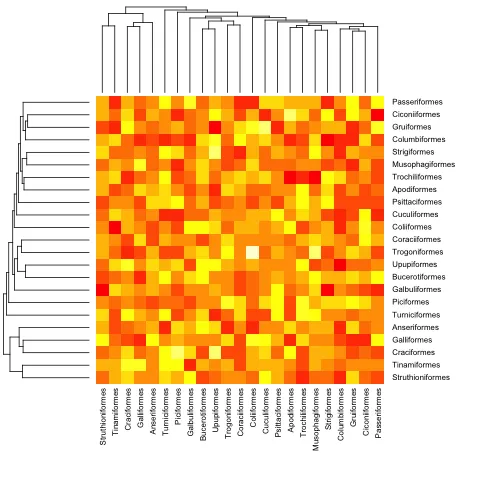
编辑:这里有一个处理超度量树和非超度量树的函数。
heatmap.phylo <- function(x, Rowp, Colp, ...){
# x numeric matrix
# Rowp: phylogenetic tree (class phylo) to be used in rows
# Colp: phylogenetic tree (class phylo) to be used in columns
# ... additional arguments to be passed to image function
x <- x[Rowp$tip, Colp$tip]
xl <- c(0.5, ncol(x)+0.5)
yl <- c(0.5, nrow(x)+0.5)
layout(matrix(c(0,1,0,2,3,4,0,5,0),nrow=3, byrow=TRUE),
width=c(1,3,1), height=c(1,3,1))
par(mar=rep(0,4))
plot(Colp, direction="downwards", show.tip.label=FALSE,
xlab="",ylab="", xaxs="i", x.lim=xl)
par(mar=rep(0,4))
plot(Rowp, direction="rightwards", show.tip.label=FALSE,
xlab="",ylab="", yaxs="i", y.lim=yl)
par(mar=rep(0,4), xpd=TRUE)
image((1:nrow(x))-0.5, (1:ncol(x))-0.5, x,
xaxs="i", yaxs="i", axes=FALSE, xlab="",ylab="", ...)
par(mar=rep(0,4))
plot(NA, axes=FALSE, ylab="", xlab="", yaxs="i", xlim=c(0,2), ylim=yl)
text(rep(0,nrow(x)),1:nrow(x),Rowp$tip, pos=4)
par(mar=rep(0,4))
plot(NA, axes=FALSE, ylab="", xlab="", xaxs="i", ylim=c(0,2), xlim=xl)
text(1:ncol(x),rep(2,ncol(x)),Colp$tip, srt=90, pos=2)
}
这是与之前(超度量)示例相同的:
heatmap.phylo(mat, bird.orders, bird.orders)
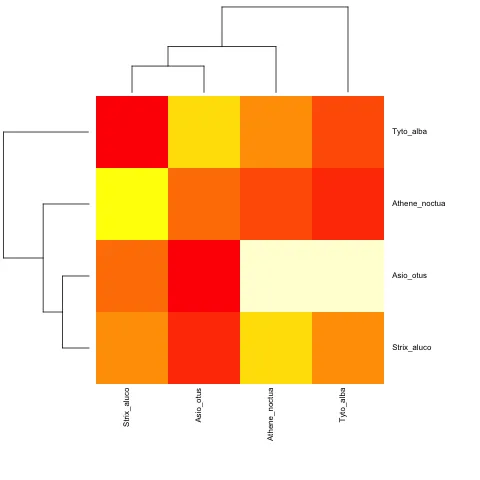
而对于非超度量的情况:
cat("owls(((Strix_aluco:4.2,Asio_otus:4.2):3.1,Athene_noctua:7.3):6.3,Tyto_alba:13.5);",
file = "ex.tre", sep = "\n")
tree.owls <- read.tree("ex.tre")
mat2 <- matrix(rnorm(4*4),nrow=4,
dimnames=list(sample(tree.owls$tip,4),sample(tree.owls$tip,4)))
is.ultrametric(tree.owls)
[1] FALSE
heatmap.phylo(mat2,tree.owls,tree.owls)
6
heatmap.phylo 函数!这是一种独立于deprogram概念的新方法!我非常确定可以将其转换为网格世界!+10!我相信我可以将其转换为网格包(lattice和grid,不确定是否适用于ggplot2)。 - agstudyheatmap.phylo(c, d1, d2)时出现错误:Error in image.default((1:ncol(x)) - 0.5, (1:nrow(x)) - 0.5, x, xaxs = "i", : dimensions of z are not length(x)(-1) times length(y)(-1)。我检查了矩阵维度和两棵树的末端长度,它们确实是一致的。你有什么想法可能是问题所在吗?谢谢。 - RNAheatmap.phylo() 中,image 函数中的 ncol 和 nrow 被交换了。我已经纠正了它。 - RNAheatmap.phylo()函数。然而,当我尝试按照您的示例操作时,出现以下错误信息:
Error in plot.default(0, type = "n", xlim = x.lim, ylim = y.lim, xlab = "", : formal argument "xlab" matched by multiple actual arguments。
我不知道错误可能来自哪里,因为我只是将您的示例复制/粘贴到这里,用于非超度量树...有什么想法吗? - Antonio Canepaape包自那时起改变了他们的代码来绘制系统发育树。只需在heatmap.phylo代码的第13行和第16行中摆脱xlab=''和ylab=''即可正常工作。 - plannapus首先,我会创建一个可重现的示例。如果没有数据,我们就只能猜测您想要什么。因此,请尽量做得更好(特别是您已确认用户)。例如,您可以按以下方式创建newick格式的树:
tree.text='(((XXX:4.2,ZZZ:4.2):3.1,HHH:7.3):6.3,AAA:13.6);'
和@plannpus一样,我正在使用ape将这棵树转换为hclust类。不幸的是,看起来我们只能将超度量树转换为hclust类:从根到每个末端的距离相同。
library(ape)
tree <- read.tree(text='(((XXX:4.2,ZZZ:4.2):3.1,HHH:7.3):6.3,AAA:13.6);')
is.ultrametric(tree)
hc <- as.hclust.phylo(tree)
然后我使用 latticeExtra 的 dendrogramGrob 来绘制我的树形图,使用 lattice 的 levelplot 来绘制热力图。
library(latticeExtra)
dd.col <- as.dendrogram(hc)
col.ord <- order.dendrogram(dd.col)
mat <- matrix(rnorm(4*4),nrow=4)
colnames(mat) <- tree$tip.label
rownames(mat) <- tree$tip.label
levelplot(mat[tree$tip,tree$tip],type=c('g','p'),
aspect = "fill",
colorkey = list(space = "left"),
legend =
list(right =
list(fun = dendrogramGrob,
args =
list(x = dd.col,
side = "right",
size = 10))),
panel=function(...){
panel.fill('black',alpha=0.2)
panel.levelplot.points(...,cex=12,pch=23)
}
)
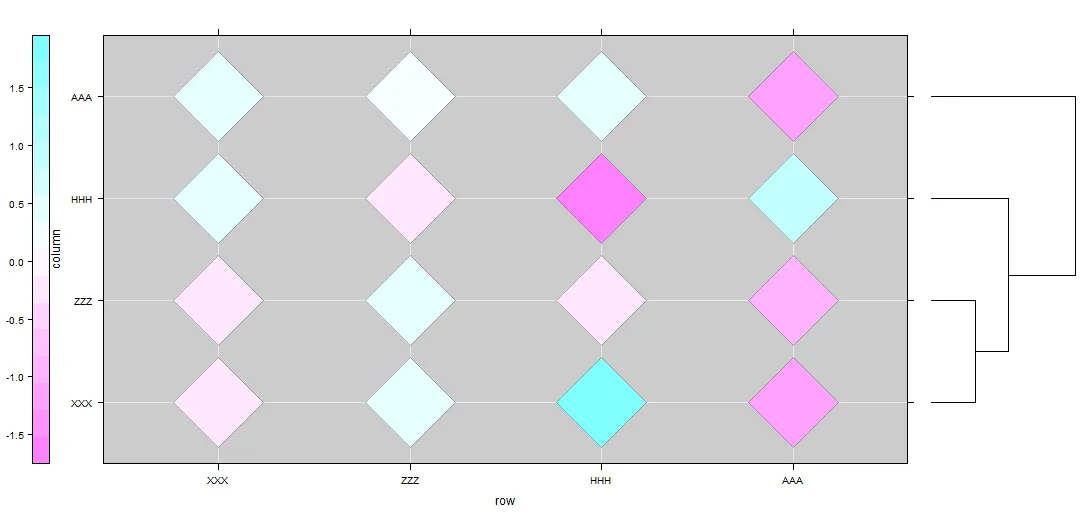
2
我根据plannapus的答案进行了修改,以处理多个树(在此过程中删去了一些我不需要的选项):
library(ape)
heatmap.phylo <- function(x, Rowp, Colp, breaks, col, denscol="cyan", respect=F, ...){
# x numeric matrix
# Rowp: phylogenetic tree (class phylo) to be used in rows
# Colp: phylogenetic tree (class phylo) to be used in columns
# ... additional arguments to be passed to image function
scale01 <- function(x, low = min(x), high = max(x)) {
x <- (x - low)/(high - low)
x
}
col.tip <- Colp$tip
n.col <- 1
if (is.null(col.tip)) {
n.col <- length(Colp)
col.tip <- unlist(lapply(Colp, function(t) t$tip))
col.lengths <- unlist(lapply(Colp, function(t) length(t$tip)))
col.fraction <- col.lengths / sum(col.lengths)
col.heights <- unlist(lapply(Colp, function(t) max(node.depth.edgelength(t))))
col.max_height <- max(col.heights)
}
row.tip <- Rowp$tip
n.row <- 1
if (is.null(row.tip)) {
n.row <- length(Rowp)
row.tip <- unlist(lapply(Rowp, function(t) t$tip))
row.lengths <- unlist(lapply(Rowp, function(t) length(t$tip)))
row.fraction <- row.lengths / sum(row.lengths)
row.heights <- unlist(lapply(Rowp, function(t) max(node.depth.edgelength(t))))
row.max_height <- max(row.heights)
}
cexRow <- min(1, 0.2 + 1/log10(n.row))
cexCol <- min(1, 0.2 + 1/log10(n.col))
x <- x[row.tip, col.tip]
xl <- c(0.5, ncol(x)+0.5)
yl <- c(0.5, nrow(x)+0.5)
screen_matrix <- matrix( c(
0,1,4,5,
1,4,4,5,
0,1,1,4,
1,4,1,4,
1,4,0,1,
4,5,1,4
) / 5, byrow=T, ncol=4 )
if (respect) {
r <- grconvertX(1, from = "inches", to = "ndc") / grconvertY(1, from = "inches", to = "ndc")
if (r < 1) {
screen_matrix <- screen_matrix * matrix( c(r,r,1,1), nrow=6, ncol=4, byrow=T)
} else {
screen_matrix <- screen_matrix * matrix( c(1,1,1/r,1/r), nrow=6, ncol=4, byrow=T)
}
}
split.screen( screen_matrix )
screen(2)
par(mar=rep(0,4))
if (n.col == 1) {
plot(Colp, direction="downwards", show.tip.label=FALSE,xaxs="i", x.lim=xl)
} else {
screens <- split.screen( as.matrix(data.frame( left=cumsum(col.fraction)-col.fraction, right=cumsum(col.fraction), bottom=0, top=1)))
for (i in 1:n.col) {
screen(screens[i])
plot(Colp[[i]], direction="downwards", show.tip.label=FALSE,xaxs="i", x.lim=c(0.5,0.5+col.lengths[i]), y.lim=-col.max_height+col.heights[i]+c(0,col.max_height))
}
}
screen(3)
par(mar=rep(0,4))
if (n.col == 1) {
plot(Rowp, direction="rightwards", show.tip.label=FALSE,yaxs="i", y.lim=yl)
} else {
screens <- split.screen( as.matrix(data.frame( left=0, right=1, bottom=cumsum(row.fraction)-row.fraction, top=cumsum(row.fraction))) )
for (i in 1:n.col) {
screen(screens[i])
plot(Rowp[[i]], direction="rightwards", show.tip.label=FALSE,yaxs="i", x.lim=c(0,row.max_height), y.lim=c(0.5,0.5+row.lengths[i]))
}
}
screen(4)
par(mar=rep(0,4), xpd=TRUE)
image((1:nrow(x))-0.5, (1:ncol(x))-0.5, x, xaxs="i", yaxs="i", axes=FALSE, xlab="",ylab="", breaks=breaks, col=col, ...)
screen(6)
par(mar=rep(0,4))
plot(NA, axes=FALSE, ylab="", xlab="", yaxs="i", xlim=c(0,2), ylim=yl)
text(rep(0,nrow(x)),1:nrow(x),row.tip, pos=4, cex=cexCol)
screen(5)
par(mar=rep(0,4))
plot(NA, axes=FALSE, ylab="", xlab="", xaxs="i", ylim=c(0,2), xlim=xl)
text(1:ncol(x),rep(2,ncol(x)),col.tip, srt=90, adj=c(1,0.5), cex=cexRow)
screen(1)
par(mar = c(2, 2, 1, 1), cex = 0.75)
symkey <- T
tmpbreaks <- breaks
if (symkey) {
max.raw <- max(abs(c(x, breaks)), na.rm = TRUE)
min.raw <- -max.raw
tmpbreaks[1] <- -max(abs(x), na.rm = TRUE)
tmpbreaks[length(tmpbreaks)] <- max(abs(x), na.rm = TRUE)
} else {
min.raw <- min(x, na.rm = TRUE)
max.raw <- max(x, na.rm = TRUE)
}
z <- seq(min.raw, max.raw, length = length(col))
image(z = matrix(z, ncol = 1), col = col, breaks = tmpbreaks,
xaxt = "n", yaxt = "n")
par(usr = c(0, 1, 0, 1))
lv <- pretty(breaks)
xv <- scale01(as.numeric(lv), min.raw, max.raw)
axis(1, at = xv, labels = lv)
h <- hist(x, plot = FALSE, breaks = breaks)
hx <- scale01(breaks, min.raw, max.raw)
hy <- c(h$counts, h$counts[length(h$counts)])
lines(hx, hy/max(hy) * 0.95, lwd = 1, type = "s",
col = denscol)
axis(2, at = pretty(hy)/max(hy) * 0.95, pretty(hy))
par(cex = 0.5)
mtext(side = 2, "Count", line = 2)
close.screen(all.screens = T)
}
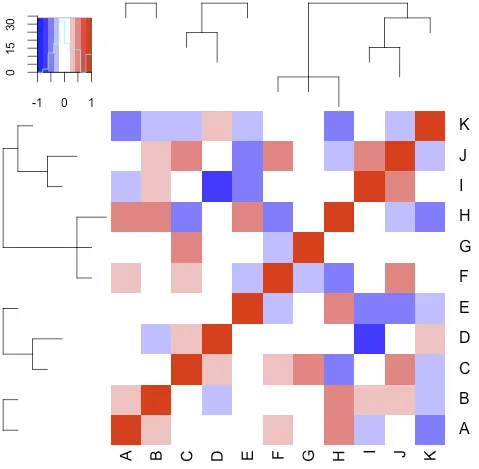
tree <- read.tree(text = "(A:1,B:1);((C:1,D:2):2,E:1);((F:1,G:1,H:2):5,((I:1,J:2):2,K:1):1);", comment.char="")
N <- sum(unlist(lapply(tree, function(t) length(t$tip))))
set.seed(42)
m <- cor(matrix(rnorm(N*N), nrow=N))
rownames(m) <- colnames(m) <- LETTERS[1:N]
heatmap.phylo(m, tree, tree, col=bluered(10), breaks=seq(-1,1,length.out=11), respect=T)
1
tree对象时:tree <- read.tree(text = "(A:1,B:1);((C:1,D:2):2,E:1);((F:1,G:1,H:2):5,((I:1,J:2):2,K:1):1);", comment.char=""),我遇到了这个错误消息Error in if (z[i]) { : missing value where TRUE/FALSE needed。有什么想法吗? - Antonio Canepahttp://joey711.github.io/phyloseq/plot_heatmap-examples
有一个需要注意的地方,虽然不是你明确要求的,但是phyloseq::plot_heatmap不会为任何轴叠加分层树。有一个很好的理由不基于分层聚类来排序轴,这是因为在节点旋转时,长枝末端的索引仍然可以任意相邻。关于这一点,以及基于非度量多维缩放的替代方法在NeatMap软件包文章中有进一步解释,该软件包也是用R编写的,并使用ggplot2。这种降维(排序)方法适用于phyloseq::plot_heatmap中的系统发育丰度数据。
3
plot_heatmap 可以制作一个没有层次聚类树的热图,但无法(如 OP 所请求)按系统发生学进行聚类(或在图旁放置系统发生学树以指示系统发生学)。这样说对吗?还是我漏掉了什么? - ohnoplusphyloseq::plot_heatmap可以根据树中的顺序对热图中的分类单元进行排序。这是通过taxa.order命令实现的,该命令可以采用分类阶层来聚类索引,或者采用索引本身的任意顺序。https://www.rdocumentation.org/packages/phyloseq/versions/1.16.2/topics/plot_heatmap https://github.com/joey711/phyloseq/issues/230 - Paul 'Joey' McMurdie虽然我对phlyoseq::plot_heatmap的建议可以让你完成部分工作,但是强大的"ggtree"包可以做更多,如果你真的想要在树上表示数据。
以下是一些示例,显示在下面的ggtree文档页面的顶部:
http://www.bioconductor.org/packages/3.7/bioc/vignettes/ggtree/inst/doc/advanceTreeAnnotation.html
请注意,我与ggtree dev没有任何关联。我只是该项目的粉丝,并且了解其已经能够实现的功能。与@plannapus沟通后,我修改了代码(只是一些)以删除上面代码中的一些额外的xlab = ""信息。
在这里,您将找到代码。您可以看到有注释的行具有额外的代码,现在新行只是擦除它们。
希望这能帮助像我这样的新用户! :)
heatmap.phylo <- function(x, Rowp, Colp, ...){
# x numeric matrix
# Rowp: phylogenetic tree (class phylo) to be used in rows
# Colp: phylogenetic tree (class phylo) to be used in columns
# ... additional arguments to be passed to image function
x <- x[Rowp$tip, Colp$tip]
xl <- c(0.5, ncol(x) + 0.5)
yl <- c(0.5, nrow(x) + 0.5)
layout(matrix(c(0,1,0,2,3,4,0,5,0),nrow = 3, byrow = TRUE),
width = c(1,3,1), height = c(1,3,1))
par(mar = rep(0,4))
# plot(Colp, direction = "downwards", show.tip.label = FALSE,
# xlab = "", ylab = "", xaxs = "i", x.lim = xl)
plot(Colp, direction = "downwards", show.tip.label = FALSE,
xaxs = "i", x.lim = xl)
par(mar = rep(0,4))
# plot(Rowp, direction = "rightwards", show.tip.label = FALSE,
# xlab = "", ylab = "", yaxs = "i", y.lim = yl)
plot(Rowp, direction = "rightwards", show.tip.label = FALSE,
yaxs = "i", y.lim = yl)
par(mar = rep(0,4), xpd = TRUE)
image((1:nrow(x)) - 0.5, (1:ncol(x)) - 0.5, x,
#xaxs = "i", yaxs = "i", axes = FALSE, xlab = "", ylab = "", ...)
xaxs = "i", yaxs = "i", axes = FALSE, ...)
par(mar = rep(0,4))
plot(NA, axes = FALSE, ylab = "", xlab = "", yaxs = "i", xlim = c(0,2), ylim = yl)
text(rep(0, nrow(x)), 1:nrow(x), Rowp$tip, pos = 4)
par(mar = rep(0,4))
plot(NA, axes = FALSE, ylab = "", xlab = "", xaxs = "i", ylim = c(0,2), xlim = xl)
text(1:ncol(x), rep(2, ncol(x)), Colp$tip, srt = 90, pos = 2)
}
原文链接
dput(head(mymatrixdata))的输出粘贴到文本中,可以让其他人轻松重建您数据的一部分,并且更容易为您提供帮助。 - Simon O'Hanlon(A:0.1,B:0.2,(C:0.3,D:0.4):0.5);。 - RNA