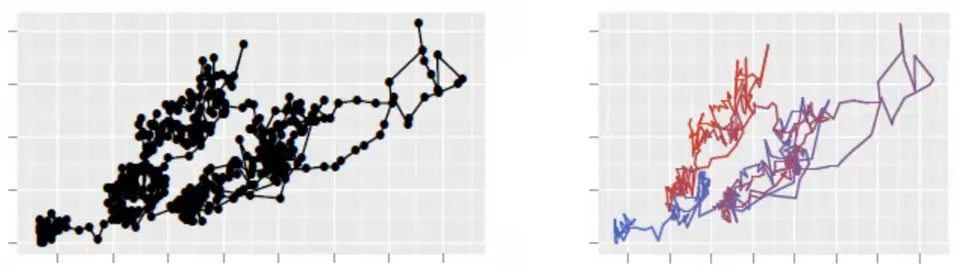
更具体地说,我正在绘制一个带有单色线的二维随机行走图。但是,由于这些点具有相关序列,因此我想查看绘图并查看数据移动的位置。渐变颜色的线条可以解决问题。或者是透明度逐渐变化的线条。
我只是想改善我的数据可视化效果。请查看R的ggplot2包生成的这张美丽的图片。我正在寻找与matplotlib相同的效果。谢谢。

请注意,如果您有许多数据点,则为每个线段调用plt.plot可能会非常慢。使用LineCollection对象更有效率。
使用colorline方法,您可以进行以下操作:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.collections as mcoll
import matplotlib.path as mpath
def colorline(
x, y, z=None, cmap=plt.get_cmap('copper'), norm=plt.Normalize(0.0, 1.0),
linewidth=3, alpha=1.0):
"""
http://nbviewer.ipython.org/github/dpsanders/matplotlib-examples/blob/master/colorline.ipynb
http://matplotlib.org/examples/pylab_examples/multicolored_line.html
Plot a colored line with coordinates x and y
Optionally specify colors in the array z
Optionally specify a colormap, a norm function and a line width
"""
# Default colors equally spaced on [0,1]:
if z is None:
z = np.linspace(0.0, 1.0, len(x))
# Special case if a single number:
if not hasattr(z, "__iter__"): # to check for numerical input -- this is a hack
z = np.array([z])
z = np.asarray(z)
segments = make_segments(x, y)
lc = mcoll.LineCollection(segments, array=z, cmap=cmap, norm=norm,
linewidth=linewidth, alpha=alpha)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.add_collection(lc)
return lc
def make_segments(x, y):
"""
Create list of line segments from x and y coordinates, in the correct format
for LineCollection: an array of the form numlines x (points per line) x 2 (x
and y) array
"""
points = np.array([x, y]).T.reshape(-1, 1, 2)
segments = np.concatenate([points[:-1], points[1:]], axis=1)
return segments
N = 10
np.random.seed(101)
x = np.random.rand(N)
y = np.random.rand(N)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
path = mpath.Path(np.column_stack([x, y]))
verts = path.interpolated(steps=3).vertices
x, y = verts[:, 0], verts[:, 1]
z = np.linspace(0, 1, len(x))
colorline(x, y, z, cmap=plt.get_cmap('jet'), linewidth=2)
plt.show()
z = np.array(z, subok=True, copy=False, ndmin=1)。这将替换掉包括z = np.asarray(z)在内的所有内容。 - Mad PhysicistLineCollection 段之间连接不好。仔细观察,每个段之间都有间隙。这在拐角处更为明显,特别是当你将 linewidth 增加到像 10 这样的值时。对于许多短线段,线条中的间隙实际上会使其看起来部分透明!将此结果与 ax.plot(x, y, lw=10) 进行比较,后者不会留下间隙,甚至会圆角处理拐角。请参见此问题 https://dev59.com/QGbWa4cB1Zd3GeqPV1gO 获取一些解决方案。 - goweon我最近回答了一个类似的问题(使用matplotlib创建超过20个唯一的图例颜色)。在那里,我展示了如何将您需要绘制线条的颜色循环映射到颜色映射中。您可以使用同样的程序为每对点获取特定的颜色。
您应该仔细选择颜色映射,因为如果颜色映射太过花哨,沿着您的线路的颜色变化可能会出现剧烈的情况。
或者,您可以更改每个线段的alpha值,范围从0到1。
下面的代码示例中包含了一个例程(highResPoints),用于扩展您的随机游走的点数,因为如果点数太少,则过渡可能看起来很剧烈。这段代码是受我最近提供的另一个答案的启发:https://dev59.com/a2sy5IYBdhLWcg3w5CBr#8253729
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def highResPoints(x,y,factor=10):
'''
Take points listed in two vectors and return them at a higher
resultion. Create at least factor*len(x) new points that include the
original points and those spaced in between.
Returns new x and y arrays as a tuple (x,y).
'''
# r is the distance spanned between pairs of points
r = [0]
for i in range(1,len(x)):
dx = x[i]-x[i-1]
dy = y[i]-y[i-1]
r.append(np.sqrt(dx*dx+dy*dy))
r = np.array(r)
# rtot is a cumulative sum of r, it's used to save time
rtot = []
for i in range(len(r)):
rtot.append(r[0:i].sum())
rtot.append(r.sum())
dr = rtot[-1]/(NPOINTS*RESFACT-1)
xmod=[x[0]]
ymod=[y[0]]
rPos = 0 # current point on walk along data
rcount = 1
while rPos < r.sum():
x1,x2 = x[rcount-1],x[rcount]
y1,y2 = y[rcount-1],y[rcount]
dpos = rPos-rtot[rcount]
theta = np.arctan2((x2-x1),(y2-y1))
rx = np.sin(theta)*dpos+x1
ry = np.cos(theta)*dpos+y1
xmod.append(rx)
ymod.append(ry)
rPos+=dr
while rPos > rtot[rcount+1]:
rPos = rtot[rcount+1]
rcount+=1
if rcount>rtot[-1]:
break
return xmod,ymod
#CONSTANTS
NPOINTS = 10
COLOR='blue'
RESFACT=10
MAP='winter' # choose carefully, or color transitions will not appear smoooth
# create random data
np.random.seed(101)
x = np.random.rand(NPOINTS)
y = np.random.rand(NPOINTS)
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(221) # regular resolution color map
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(222) # regular resolution alpha
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(223) # high resolution color map
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(224) # high resolution alpha
# Choose a color map, loop through the colors, and assign them to the color
# cycle. You need NPOINTS-1 colors, because you'll plot that many lines
# between pairs. In other words, your line is not cyclic, so there's
# no line from end to beginning
cm = plt.get_cmap(MAP)
ax1.set_color_cycle([cm(1.*i/(NPOINTS-1)) for i in range(NPOINTS-1)])
for i in range(NPOINTS-1):
ax1.plot(x[i:i+2],y[i:i+2])
ax1.text(.05,1.05,'Reg. Res - Color Map')
ax1.set_ylim(0,1.2)
# same approach, but fixed color and
# alpha is scale from 0 to 1 in NPOINTS steps
for i in range(NPOINTS-1):
ax2.plot(x[i:i+2],y[i:i+2],alpha=float(i)/(NPOINTS-1),color=COLOR)
ax2.text(.05,1.05,'Reg. Res - alpha')
ax2.set_ylim(0,1.2)
# get higher resolution data
xHiRes,yHiRes = highResPoints(x,y,RESFACT)
npointsHiRes = len(xHiRes)
cm = plt.get_cmap(MAP)
ax3.set_color_cycle([cm(1.*i/(npointsHiRes-1))
for i in range(npointsHiRes-1)])
for i in range(npointsHiRes-1):
ax3.plot(xHiRes[i:i+2],yHiRes[i:i+2])
ax3.text(.05,1.05,'Hi Res - Color Map')
ax3.set_ylim(0,1.2)
for i in range(npointsHiRes-1):
ax4.plot(xHiRes[i:i+2],yHiRes[i:i+2],
alpha=float(i)/(npointsHiRes-1),
color=COLOR)
ax4.text(.05,1.05,'High Res - alpha')
ax4.set_ylim(0,1.2)
fig.savefig('gradColorLine.png')
plt.show()
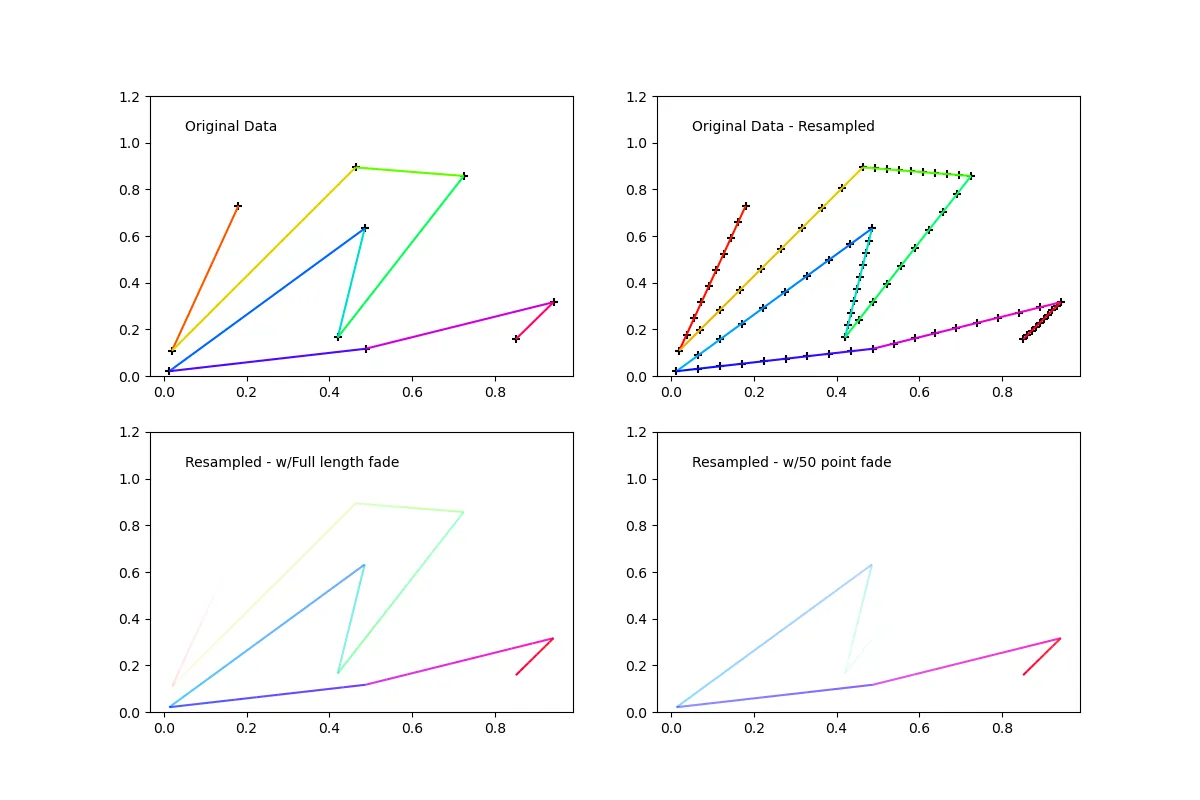
以下图片展示了四种情况:
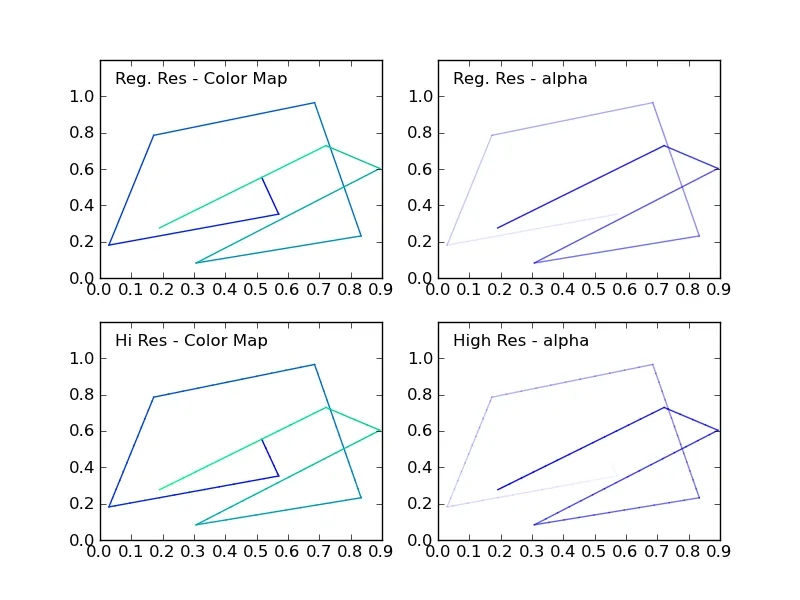
x = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0] 和 y = [1.0, 3.0, 8.0],这段代码将会失败并显示 Traceback (most recent call last): File ".../gradient", line 89, in <module>; xHiRes,yHiRes = highResPoints(x,y,RESFACT); File ".../gradient", line 67, in highResPoints; while rPos > rtot[rcount+1]: IndexError: list index out of range。如何修复这个问题? - shrxset_color_cycle自1.5版本起已被弃用,其他都运行良好。相反,您可以使用set_prop_cycle,例如ax1.set_prop_cycle(color=[cm(1.*i/(NPOINTS-1)) for i in range(NPOINTS-1)])。 - eaksan评论区无法容纳这么多内容,只想确认一下 LineCollection 比对线段子分段进行循环的速度要快得多。
就我个人而言,使用 LineCollection 方法会更快。
# Setup
x = np.linspace(0,4*np.pi,1000)
y = np.sin(x)
MAP = 'cubehelix'
NPOINTS = len(x)
我们将对迭代绘图和LineCollection方法进行测试。
%%timeit -n1 -r1
# Using IPython notebook timing magics
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111) # regular resolution color map
cm = plt.get_cmap(MAP)
for i in range(10):
ax1.set_color_cycle([cm(1.*i/(NPOINTS-1)) for i in range(NPOINTS-1)])
for i in range(NPOINTS-1):
plt.plot(x[i:i+2],y[i:i+2])
1循环,最佳时间为1次:每次13.4秒
%%timeit -n1 -r1
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111) # regular resolution color map
for i in range(10):
colorline(x,y,cmap='cubehelix', linewidth=1)
1 循环,最佳为 1: 每个循环532毫秒
如果你想要一个平滑的渐变并且只有少量点时,通过上采样线条可以得到更好的颜色渐变,正如当前所选答案提供的一样,这仍然是一个好主意。
cm(np.linspace(0, 1, NPOINTS-1, endpoint=False))替换[cm(1.*i/(NPOINTS-1)) for i in range(NPOINTS-1)]。 - Guimoute这里是我的另一种解决方案,使用pcolormesh。每条线段都是用四边形绘制的,它在每个端点之间插值颜色。因此,它可以真正地插值颜色而不添加额外的线段。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def _get_perp_line(current_seg, out_of_page, linewidth):
perp = np.cross(current_seg, out_of_page)[0:2]
perp_unit = _get_unit_vector(perp)
current_seg_perp_line = perp_unit*linewidth
return current_seg_perp_line
def _get_unit_vector(vector):
vector_size = (vector[0]**2 + vector[1]**2)**0.5
vector_unit = vector / vector_size
return vector_unit[0:2]
def colored_line(x, y, z=None, line_width=1, MAP='jet'):
# use pcolormesh to make interpolated rectangles
num_pts = len(x)
[xs, ys, zs] = [
np.zeros((num_pts,2)),
np.zeros((num_pts,2)),
np.zeros((num_pts,2))
]
dist = 0
out_of_page = [0, 0, 1]
for i in range(num_pts):
# set the colors and the x,y locations of the source line
xs[i][0] = x[i]
ys[i][0] = y[i]
if i > 0:
x_delta = x[i] - x[i-1]
y_delta = y[i] - y[i-1]
seg_length = (x_delta**2 + y_delta**2)**0.5
dist += seg_length
zs[i] = [dist, dist]
# define the offset perpendicular points
if i == num_pts - 1:
current_seg = [x[i]-x[i-1], y[i]-y[i-1], 0]
else:
current_seg = [x[i+1]-x[i], y[i+1]-y[i], 0]
current_seg_perp = _get_perp_line(
current_seg, out_of_page, line_width)
if i == 0 or i == num_pts - 1:
xs[i][1] = xs[i][0] + current_seg_perp[0]
ys[i][1] = ys[i][0] + current_seg_perp[1]
continue
current_pt = [x[i], y[i]]
current_seg_unit = _get_unit_vector(current_seg)
previous_seg = [x[i]-x[i-1], y[i]-y[i-1], 0]
previous_seg_perp = _get_perp_line(
previous_seg, out_of_page, line_width)
previous_seg_unit = _get_unit_vector(previous_seg)
# current_pt + previous_seg_perp + scalar * previous_seg_unit =
# current_pt + current_seg_perp - scalar * current_seg_unit =
scalar = (
(current_seg_perp - previous_seg_perp) /
(previous_seg_unit + current_seg_unit)
)
new_pt = current_pt + previous_seg_perp + scalar[0] * previous_seg_unit
xs[i][1] = new_pt[0]
ys[i][1] = new_pt[1]
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
cm = plt.get_cmap(MAP)
ax.pcolormesh(xs, ys, zs, shading='gouraud', cmap=cm)
plt.axis('scaled')
plt.show()
# create random data
N = 10
np.random.seed(101)
x = np.random.rand(N)
y = np.random.rand(N)
colored_line(x, y, line_width = .01)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import collections as mc
from scipy.interpolate import interp1d
from matplotlib.colors import colorConverter
def colored_line_segments(xs,ys,color):
if isinstance(color,str):
color = colorConverter.to_rgba(color)[:-1]
color = np.array([color for i in range(len(xs))])
segs = []
seg_colors = []
lastColor = [color[0][0],color[0][1],color[0][2]]
start = [xs[0],ys[0]]
end = [xs[0],ys[0]]
for x,y,c in zip(xs,ys,color):
seg_colors.append([(chan+lastChan)*.5 for chan,lastChan in zip(c,lastColor)])
lastColor = [c[0],c[1],c[2]]
start = [end[0],end[1]]
end = [x,y]
segs.append([start,end])
colors = [(*color,1) for color in seg_colors]
lc = mc.LineCollection(segs, colors=colors)
return lc, segs, colors
def segmented_resample(xs,ys,color,n_resample=100):
n_points = len(xs)
if isinstance(color,str):
color = colorConverter.to_rgba(color)[:-1]
color = np.array([color for i in range(n_points)])
n_segs = (n_points-1)*(n_resample-1)
xsInterp = np.linspace(0,1,n_resample)
segs = []
seg_colors = []
hiResXs = [xs[0]]
hiResYs = [ys[0]]
RGB = color.swapaxes(0,1)
for i in range(n_points-1):
fit_xHiRes = interp1d([0,1],xs[i:i+2])
fit_yHiRes = interp1d(xs[i:i+2],ys[i:i+2])
xHiRes = fit_xHiRes(xsInterp)
yHiRes = fit_yHiRes(xHiRes)
hiResXs = hiResXs+list(xHiRes[1:])
hiResYs = hiResYs+list(yHiRes[1:])
R_HiRes = interp1d([0,1],RGB[0][i:i+2])(xHiRes)
G_HiRes = interp1d([0,1],RGB[1][i:i+2])(xHiRes)
B_HiRes = interp1d([0,1],RGB[2][i:i+2])(xHiRes)
lastColor = [R_HiRes[0],G_HiRes[0],B_HiRes[0]]
start = [xHiRes[0],yHiRes[0]]
end = [xHiRes[0],yHiRes[0]]
for x,y,r,g,b in zip(xHiRes[1:],yHiRes[1:],R_HiRes[1:],G_HiRes[1:],B_HiRes[1:]):
seg_colors.append([(chan+lastChan)*.5 for chan,lastChan in zip((r,g,b),lastColor)])
lastColor = [r,g,b]
start = [end[0],end[1]]
end = [x,y]
segs.append([start,end])
colors = [(*color,1) for color in seg_colors]
return segs, colors, [hiResXs,hiResYs]
def fadeCollection(xs,ys,color,fade_len=20,n_resample=100,direction='Head'):
segs, colors, hiResData = segmented_resample(xs,ys,color,n_resample)
n_segs = len(segs)
if fade_len>len(segs):
fade_len=n_segs
if direction=='Head':
#Head fade
alphas = np.concatenate((np.zeros(n_segs-fade_len),np.linspace(0,1,fade_len)))
else:
#Tail fade
alphas = np.concatenate((np.linspace(1,0,fade_len),np.zeros(n_segs-fade_len)))
colors = [(*color[:-1],alpha) for color,alpha in zip(colors,alphas)]
lc = mc.LineCollection(segs, colors=colors)
return segs, colors, hiResData
if __name__ == "__main__":
NPOINTS = 10
RESAMPLE = 10
N_FADE = int(RESAMPLE*NPOINTS*0.5)
N_SEGS = (NPOINTS-1)*(RESAMPLE-1)
SHOW_POINTS_AXI_12 = True
SHOW_POINTS_AXI_34 = False
np.random.seed(11)
xs = np.random.rand(NPOINTS)
ys = np.random.rand(NPOINTS)
COLOR='b'
MARKER_COLOR = 'k'
MARKER = '+'
CMAP = plt.get_cmap('hsv')
COLORS = np.array([CMAP(i)[:-1] for i in np.linspace(0,1,NPOINTS)])
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,8),dpi=100)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(221) # original data
lc, segs, colors = colored_line_segments(xs,ys,COLORS)
if SHOW_POINTS_AXI_12: ax1.scatter(xs,ys,marker=MARKER,color=MARKER_COLOR)
ax1.add_collection(lc)
ax1.text(.05,1.05,'Original Data')
ax1.set_ylim(0,1.2)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(222, sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1) # resampled data
segs, colors, hiResData = segmented_resample(xs,ys,COLORS,RESAMPLE)
if SHOW_POINTS_AXI_12: ax2.scatter(hiResData[0],hiResData[1],marker=MARKER,color=MARKER_COLOR)
ax2.add_collection(mc.LineCollection(segs, colors=colors))
ax2.text(.05,1.05,'Original Data - Resampled')
ax2.set_ylim(0,1.2)
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(223, sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1) # resampled with linear alpha fade start to finish
segs, colors, hiResData = fadeCollection(xs,ys,COLORS,fade_len=RESAMPLE*NPOINTS,n_resample=RESAMPLE,direction='Head')
if SHOW_POINTS_AXI_34: ax3.scatter(hiResData[0],hiResData[1],marker=MARKER,color=MARKER_COLOR)
ax3.add_collection(mc.LineCollection(segs, colors=colors))
ax3.text(.05,1.05,'Resampled - w/Full length fade')
ax3.set_ylim(0,1.2)
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(224, sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1) # resampled with linear alpha fade N_FADE long
segs, colors, hiResData = fadeCollection(xs,ys,COLORS,fade_len=N_FADE,n_resample=RESAMPLE,direction='Head')
if SHOW_POINTS_AXI_34: ax4.scatter(hiResData[0],hiResData[1],marker=MARKER,color=MARKER_COLOR)
ax4.add_collection(mc.LineCollection(segs, colors=colors))
ax4.text(.05,1.05,'Resampled - w/{} point fade'.format(N_FADE))
ax4.set_ylim(0,1.2)
fig.savefig('fadeSegmentedColorLine.png')
plt.show()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import collections as mc
from scipy.interpolate import interp1d
from matplotlib.colors import colorConverter
def colored_line_segments(xs,ys,color,mid_colors=False):
if isinstance(color,str):
color = colorConverter.to_rgba(color)[:-1]
color = np.array([color for i in range(len(xs))])
segs = []
seg_colors = []
lastColor = [color[0][0],color[0][1],color[0][2]]
start = [xs[0],ys[0]]
end = [xs[0],ys[0]]
for x,y,c in zip(xs,ys,color):
if mid_colors:
seg_colors.append([(chan+lastChan)*.5 for chan,lastChan in zip(c,lastColor)])
else:
seg_colors.append(c)
lastColor = [c[0],c[1],c[2]]
start = [end[0],end[1]]
end = [x,y]
segs.append([start,end])
colors = [(*color,1) for color in seg_colors]
lc = mc.LineCollection(segs, colors=colors)
return lc, segs, colors
def segmented_resample(xs,ys,color,n_resample=100,mid_colors=False):
n_points = len(xs)
if isinstance(color,str):
color = colorConverter.to_rgba(color)[:-1]
color = np.array([color for i in range(n_points)])
n_segs = (n_points-1)*(n_resample-1)
xsInterp = np.linspace(0,1,n_resample)
segs = []
seg_colors = []
hiResXs = [xs[0]]
hiResYs = [ys[0]]
RGB = color.swapaxes(0,1)
for i in range(n_points-1):
fit_xHiRes = interp1d([0,1],xs[i:i+2])
fit_yHiRes = interp1d(xs[i:i+2],ys[i:i+2])
xHiRes = fit_xHiRes(xsInterp)
yHiRes = fit_yHiRes(xHiRes)
hiResXs = hiResXs+list(xHiRes[1:])
hiResYs = hiResYs+list(yHiRes[1:])
R_HiRes = interp1d([0,1],RGB[0][i:i+2])(xHiRes)
G_HiRes = interp1d([0,1],RGB[1][i:i+2])(xHiRes)
B_HiRes = interp1d([0,1],RGB[2][i:i+2])(xHiRes)
lastColor = [R_HiRes[0],G_HiRes[0],B_HiRes[0]]
start = [xHiRes[0],yHiRes[0]]
end = [xHiRes[0],yHiRes[0]]
if mid_colors: seg_colors.append([R_HiRes[0],G_HiRes[0],B_HiRes[0]])
for x,y,r,g,b in zip(xHiRes[1:],yHiRes[1:],R_HiRes[1:],G_HiRes[1:],B_HiRes[1:]):
if mid_colors:
seg_colors.append([(chan+lastChan)*.5 for chan,lastChan in zip((r,g,b),lastColor)])
else:
seg_colors.append([r,g,b])
lastColor = [r,g,b]
start = [end[0],end[1]]
end = [x,y]
segs.append([start,end])
colors = [(*color,1) for color in seg_colors]
return segs, colors, [hiResXs,hiResYs]
def faded_segment_resample(xs,ys,color,fade_len=20,n_resample=100,direction='Head'):
segs, colors, hiResData = segmented_resample(xs,ys,color,n_resample)
n_segs = len(segs)
if fade_len>len(segs):
fade_len=n_segs
if direction=='Head':
#Head fade
alphas = np.concatenate((np.zeros(n_segs-fade_len),np.linspace(0,1,fade_len)))
else:
#Tail fade
alphas = np.concatenate((np.linspace(1,0,fade_len),np.zeros(n_segs-fade_len)))
colors = [(*color[:-1],alpha) for color,alpha in zip(colors,alphas)]
lc = mc.LineCollection(segs, colors=colors)
return segs, colors, hiResData
if __name__ == "__main__":
NPOINTS = 10
RESAMPLE = 10
N_FADE = int(RESAMPLE*NPOINTS*0.5)
N_SEGS = (NPOINTS-1)*(RESAMPLE-1)
SHOW_POINTS_AXI_12 = True
SHOW_POINTS_AXI_34 = True
np.random.seed(11)
xs = np.random.rand(NPOINTS)
ys = np.random.rand(NPOINTS)
COLOR='b'
MARKER = '.'
#MARKER_COLOR = 'k'
CMAP = plt.get_cmap('hsv')
COLORS = np.array([CMAP(i)[:-1] for i in np.linspace(0,1,NPOINTS)])
MARKER_COLOR = COLORS
N_SCATTER = (NPOINTS-1)*(RESAMPLE-1)+1
COLORS_LONG = np.array([CMAP(i)[:-1] for i in np.linspace(1/N_SCATTER,1,N_SCATTER)])
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,8),dpi=100)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(221) # original data
lc, segs, colors = colored_line_segments(xs,ys,COLORS,True)
if SHOW_POINTS_AXI_12: ax1.scatter(xs,ys,marker=MARKER,color=COLORS)
ax1.add_collection(lc)
ax1.text(.05,1.05,'Original Data')
ax1.set_ylim(0,1.2)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(222, sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1) # resampled data
segs, colors, hiResData = segmented_resample(xs,ys,COLORS,RESAMPLE)
if SHOW_POINTS_AXI_12: ax2.scatter(hiResData[0],hiResData[1],marker=MARKER,color=COLORS_LONG)
ax2.add_collection(mc.LineCollection(segs, colors=colors))
ax2.text(.05,1.05,'Original Data - Resampled')
ax2.set_ylim(0,1.2)
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(223, sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1) # resampled with linear alpha fade start to finish
segs, colors, hiResData = faded_segment_resample(xs,ys,COLORS,fade_len=RESAMPLE*NPOINTS,n_resample=RESAMPLE,direction='Head')
if SHOW_POINTS_AXI_34: ax3.scatter(hiResData[0],hiResData[1],marker=MARKER,color=COLORS_LONG)
ax3.add_collection(mc.LineCollection(segs, colors=colors))
ax3.text(.05,1.05,'Resampled - w/Full length fade')
ax3.set_ylim(0,1.2)
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(224, sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1) # resampled with linear alpha fade N_FADE long
segs, colors, hiResData = faded_segment_resample(xs,ys,COLORS,fade_len=N_FADE,n_resample=RESAMPLE,direction='Head')
if SHOW_POINTS_AXI_34: ax4.scatter(hiResData[0],hiResData[1],marker=MARKER,color=COLORS_LONG)
ax4.add_collection(mc.LineCollection(segs, colors=colors))
ax4.text(.05,1.05,'Resampled - w/{} point fade'.format(N_FADE))
ax4.set_ylim(0,1.2)
fig.savefig('fadeSegmentedColorLine.png')
plt.show()
更新2: 保证这是最后一次更新..但我将其扩展到了3D,并更正了一些之前由于测试数据在0,1范围内而未能发现的错误。
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.collections import LineCollection as lc
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.art3d import Line3DCollection as lc3d
from scipy.interpolate import interp1d
from matplotlib.colors import colorConverter
def colored_line_segments(xs,ys,zs=None,color='k',mid_colors=False):
if isinstance(color,str):
color = colorConverter.to_rgba(color)[:-1]
color = np.array([color for i in range(len(xs))])
segs = []
seg_colors = []
lastColor = [color[0][0],color[0][1],color[0][2]]
start = [xs[0],ys[0]]
end = [xs[0],ys[0]]
if not zs is None:
start.append(zs[0])
end.append(zs[0])
else:
zs = [zs]*len(xs)
for x,y,z,c in zip(xs,ys,zs,color):
if mid_colors:
seg_colors.append([(chan+lastChan)*.5 for chan,lastChan in zip(c,lastColor)])
else:
seg_colors.append(c)
lastColor = c[:-1]
if not z is None:
start = [end[0],end[1],end[2]]
end = [x,y,z]
else:
start = [end[0],end[1]]
end = [x,y]
segs.append([start,end])
colors = [(*color,1) for color in seg_colors]
return segs, colors
def segmented_resample(xs,ys,zs=None,color='k',n_resample=100,mid_colors=False):
n_points = len(xs)
if isinstance(color,str):
color = colorConverter.to_rgba(color)[:-1]
color = np.array([color for i in range(n_points)])
n_segs = (n_points-1)*(n_resample-1)
xsInterp = np.linspace(0,1,n_resample)
segs = []
seg_colors = []
hiResXs = [xs[0]]
hiResYs = [ys[0]]
if not zs is None:
hiResZs = [zs[0]]
RGB = color.swapaxes(0,1)
for i in range(n_points-1):
fit_xHiRes = interp1d([0,1],xs[i:i+2])
fit_yHiRes = interp1d([0,1],ys[i:i+2])
xHiRes = fit_xHiRes(xsInterp)
yHiRes = fit_yHiRes(xsInterp)
hiResXs = hiResXs+list(xHiRes[1:])
hiResYs = hiResYs+list(yHiRes[1:])
R_HiRes = interp1d([0,1],RGB[0][i:i+2])(xsInterp)
G_HiRes = interp1d([0,1],RGB[1][i:i+2])(xsInterp)
B_HiRes = interp1d([0,1],RGB[2][i:i+2])(xsInterp)
lastColor = [R_HiRes[0],G_HiRes[0],B_HiRes[0]]
start = [xHiRes[0],yHiRes[0]]
end = [xHiRes[0],yHiRes[0]]
if not zs is None:
fit_zHiRes = interp1d([0,1],zs[i:i+2])
zHiRes = fit_zHiRes(xsInterp)
hiResZs = hiResZs+list(zHiRes[1:])
start.append(zHiRes[0])
end.append(zHiRes[0])
else:
zHiRes = [zs]*len(xHiRes)
if mid_colors: seg_colors.append([R_HiRes[0],G_HiRes[0],B_HiRes[0]])
for x,y,z,r,g,b in zip(xHiRes[1:],yHiRes[1:],zHiRes[1:],R_HiRes[1:],G_HiRes[1:],B_HiRes[1:]):
if mid_colors:
seg_colors.append([(chan+lastChan)*.5 for chan,lastChan in zip((r,g,b),lastColor)])
else:
seg_colors.append([r,g,b])
lastColor = [r,g,b]
if not z is None:
start = [end[0],end[1],end[2]]
end = [x,y,z]
else:
start = [end[0],end[1]]
end = [x,y]
segs.append([start,end])
colors = [(*color,1) for color in seg_colors]
data = [hiResXs,hiResYs]
if not zs is None:
data = [hiResXs,hiResYs,hiResZs]
return segs, colors, data
def faded_segment_resample(xs,ys,zs=None,color='k',fade_len=20,n_resample=100,direction='Head'):
segs, colors, hiResData = segmented_resample(xs,ys,zs,color,n_resample)
n_segs = len(segs)
if fade_len>len(segs):
fade_len=n_segs
if direction=='Head':
#Head fade
alphas = np.concatenate((np.zeros(n_segs-fade_len),np.linspace(0,1,fade_len)))
else:
#Tail fade
alphas = np.concatenate((np.linspace(1,0,fade_len),np.zeros(n_segs-fade_len)))
colors = [(*color[:-1],alpha) for color,alpha in zip(colors,alphas)]
return segs, colors, hiResData
def test2d():
NPOINTS = 10
RESAMPLE = 10
N_FADE = int(RESAMPLE*NPOINTS*0.5)
N_SEGS = (NPOINTS-1)*(RESAMPLE-1)
SHOW_POINTS_AXI_12 = True
SHOW_POINTS_AXI_34 = True
np.random.seed(11)
xs = np.random.rand(NPOINTS)
ys = np.random.rand(NPOINTS)
MARKER = '.'
CMAP = plt.get_cmap('hsv')
COLORS = np.array([CMAP(i)[:-1] for i in np.linspace(0,1,NPOINTS)])
MARKER_COLOR = COLORS
N_SCATTER = (NPOINTS-1)*(RESAMPLE-1)+1
COLORS_LONG = np.array([CMAP(i)[:-1] for i in np.linspace(1/N_SCATTER,1,N_SCATTER)])
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,8),dpi=100)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(221) # original data
segs, colors = colored_line_segments(xs,ys,color=COLORS,mid_colors=True)
if SHOW_POINTS_AXI_12: ax1.scatter(xs,ys,marker=MARKER,color=COLORS)
ax1.add_collection(lc(segs, colors=colors))
ax1.text(.05,1.05,'Original Data')
ax1.set_ylim(0,1.2)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(222, sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1) # resampled data
segs, colors, hiResData = segmented_resample(xs,ys,color=COLORS,n_resample=RESAMPLE)
if SHOW_POINTS_AXI_12: ax2.scatter(hiResData[0],hiResData[1],marker=MARKER,color=COLORS_LONG)
ax2.add_collection(lc(segs, colors=colors))
ax2.text(.05,1.05,'Original Data - Resampled')
ax2.set_ylim(0,1.2)
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(223, sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1) # resampled with linear alpha fade start to finish
segs, colors, hiResData = faded_segment_resample(xs,ys,color=COLORS,fade_len=RESAMPLE*NPOINTS,n_resample=RESAMPLE,direction='Head')
if SHOW_POINTS_AXI_34: ax3.scatter(hiResData[0],hiResData[1],marker=MARKER,color=COLORS_LONG)
ax3.add_collection(lc(segs, colors=colors))
ax3.text(.05,1.05,'Resampled - w/Full length fade')
ax3.set_ylim(0,1.2)
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(224, sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1) # resampled with linear alpha fade N_FADE long
segs, colors, hiResData = faded_segment_resample(xs,ys,color=COLORS,fade_len=N_FADE,n_resample=RESAMPLE,direction='Head')
if SHOW_POINTS_AXI_34: ax4.scatter(hiResData[0],hiResData[1],marker=MARKER,color=COLORS_LONG)
ax4.add_collection(lc(segs, colors=colors))
ax4.text(.05,1.05,'Resampled - w/{} point fade'.format(N_FADE))
ax4.set_ylim(0,1.2)
fig.savefig('2d_fadeSegmentedColorLine.png')
plt.show()
def test3d():
def set_view(axi):
axi.set_xlim(-.65,.65)
axi.set_ylim(-.65,.75)
axi.set_zlim(-.65,.65)
axi.view_init(elev=45, azim= 45)
NPOINTS = 40
RESAMPLE = 2
N_FADE = int(RESAMPLE*NPOINTS*0.5)
N_FADE = 20
N_SEGS = (NPOINTS-1)*(RESAMPLE-1)
SHOW_POINTS_AXI_12 = True
SHOW_POINTS_AXI_34 = False
alpha = np.linspace(.5,1.5,NPOINTS)*np.pi
theta = np.linspace(.25,1.5,NPOINTS)*np.pi
rad = np.linspace(0,1,NPOINTS)
xs = rad*np.sin(theta)*np.cos(alpha)
ys = rad*np.sin(theta)*np.sin(alpha)
zs = rad*np.cos(theta)
MARKER = '.'
CMAP = plt.get_cmap('hsv')
COLORS = np.array([CMAP(i)[:-1] for i in np.linspace(0,1,NPOINTS)])
MARKER_COLOR = COLORS
N_SCATTER = (NPOINTS-1)*(RESAMPLE-1)+1
COLORS_LONG = np.array([CMAP(i)[:-1] for i in np.linspace(1/N_SCATTER,1,N_SCATTER)])
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,8),dpi=100)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(221,projection='3d') # original data
segs, colors = colored_line_segments(xs,ys,zs,color=COLORS,mid_colors=True)
if SHOW_POINTS_AXI_12: ax1.scatter(xs,ys,zs,marker=MARKER,color=COLORS)
ax1.add_collection(lc3d(segs, colors=colors))
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(222, projection='3d', sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1) # resampled data
segs, colors, hiResData = segmented_resample(xs,ys,zs,color=COLORS,n_resample=RESAMPLE)
if SHOW_POINTS_AXI_12: ax2.scatter(hiResData[0],hiResData[1],hiResData[2],marker=MARKER,color=COLORS_LONG)
ax2.add_collection(lc3d(segs, colors=colors))
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(223,projection='3d', sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1) # resampled with linear alpha fade start to finish
segs, colors, hiResData = faded_segment_resample(xs,ys,zs,color=COLORS,fade_len=RESAMPLE*NPOINTS,n_resample=RESAMPLE,direction='Head')
if SHOW_POINTS_AXI_34: ax3.scatter(hiResData[0],hiResData[1],hiResData[2],marker=MARKER,color=COLORS_LONG)
ax3.add_collection(lc3d(segs, colors=colors))
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(224,projection='3d', sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1) # resampled with linear alpha fade N_FADE long
segs, colors, hiResData = faded_segment_resample(xs,ys,zs,color=COLORS,fade_len=N_FADE,n_resample=RESAMPLE,direction='Head')
if SHOW_POINTS_AXI_34: ax4.scatter(hiResData[0],hiResData[1],hiResData[2],marker=MARKER,color=COLORS_LONG)
ax4.add_collection(lc3d(segs, colors=colors))
labels = ('Original Data',
'Original Data - Resampled',
'Resampled - w/Full length fade',
'Resampled - w/{} point fade'.format(N_FADE) )
for ax,label in zip((ax1,ax2,ax3,ax4),labels):
set_view(ax)
ax.text(.6,-.6,1.55,label)
fig.savefig('3d_fadeSegmentedColorLine.png')
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
test2d()
test3d()
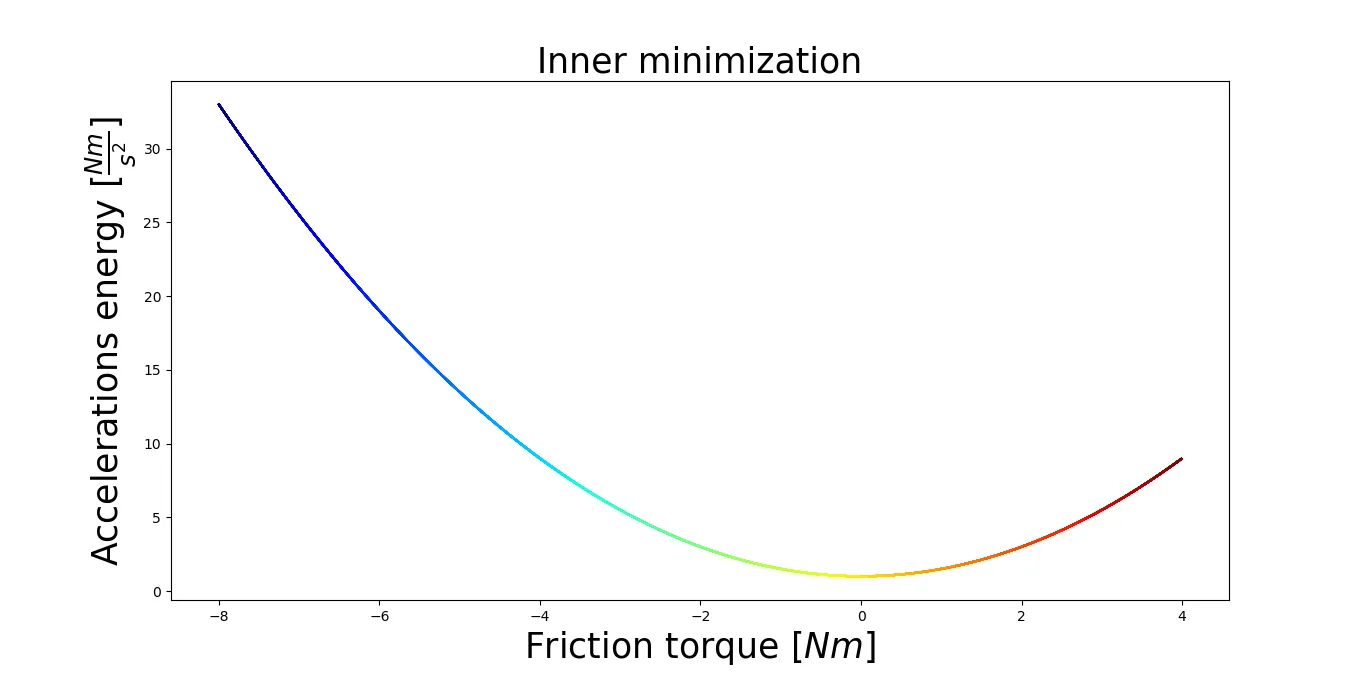
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
import matplotlib.collections as mcoll
import matplotlib.path as mpath
x = np.arange(-8, 4, 0.01)
y = 1 + 0.5 * x**2
MAP = 'jet'
NPOINTS = len(x)
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111)
cm = plt.get_cmap(MAP)
for i in range(10):
ax1.set_color_cycle([cm(1.0*i/(NPOINTS-1)) for i in range(NPOINTS-1)])
for i in range(NPOINTS-1):
plt.plot(x[i:i+2],y[i:i+2])
plt.title('Inner minimization', fontsize=25)
plt.xlabel(r'Friction torque $[Nm]$', fontsize=25)
plt.ylabel(r'Accelerations energy $[\frac{Nm}{s^2}]$', fontsize=25)
plt.show() # Show the figure
[cm(1.0*i/(NPOINTS-1)) for i in range(NPOINTS-1)]替换为cm(np.linspace(0, 1, NPOINTS-1, endpoint=False))。 - Guimoutesliding_window配方。from collections import deque
from itertools import islice
from matplotlib import collections as mc
from matplotlib.colors import colorConverter
import numpy as np
def sliding_window(iterable, n):
"""
sliding_window('ABCDEFG', 4) -> ABCD BCDE CDEF DEFG
recipe from python docs
"""
it = iter(iterable)
window = deque(islice(it, n), maxlen=n)
if len(window) == n:
yield tuple(window)
for x in it:
window.append(x)
yield tuple(window)
def color_gradient(x, y, c1, c2):
"""
Creates a line collection with a gradient from colors c1 to c2,
from data x and y.
"""
n = len(x)
if len(y) != n:
raise ValueError('x and y data lengths differ')
return mc.LineCollection(sliding_window(zip(x, y), 2),
colors=np.linspace(colorConverter.to_rgb(c1),
colorConverter.to_rgb(c2), n - 1))
这个函数只在两种颜色(c1和c2)之间线性插值RGB值。它们可以像通常使用matplotlib一样指定,并且该函数使用colorConverter将它们转换为RGB,然后使用np.linspace进行插值。每个段都是单一颜色,因此如果有许多小段,则效果最佳。我参考了Dizzixx's answer,但简化了很多。对于我的目的来说很有效,也适用于随机漫步。
示例用法:
plt.gca().add_collection(color_gradient(x_data, y_data,
'black', 'red'))