假设有许多曲线,包括直线段和圆弧段,如何计算所有曲线的最小外接矩形(OBB)?
似乎直接合并每个单独曲线的OBB不能得到正确答案,因为它不是最小覆盖。
请看下图,如何计算红色框?
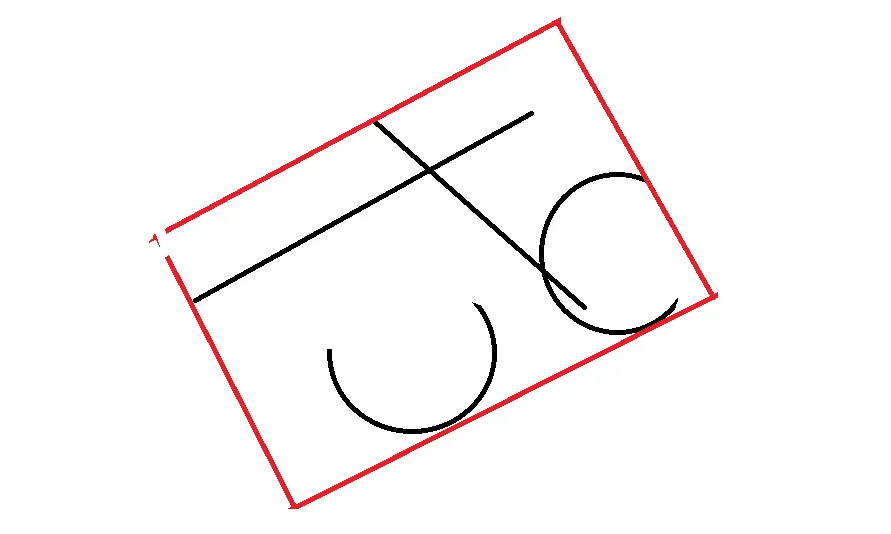
假设有许多曲线,包括直线段和圆弧段,如何计算所有曲线的最小外接矩形(OBB)?
似乎直接合并每个单独曲线的OBB不能得到正确答案,因为它不是最小覆盖。
请看下图,如何计算红色框?

您还应该将输入以向量形式添加,这样我们就可以在您的数据上进行测试... 我会这样处理:
O(n)compute max distance in each angle O(n)
just create table for enough m angles (like 5 deg step so m = 360/5) where for each angle section you remember max distant point distance only.
compute max perpendicular distance for each rotation O(m^2)
so for each angle section compute value that is:
value[actual_section] = max(distance[i]*cos(section_angle[i]-section_angle[actual_section]))
where i covers +/- 90 deg around actual section angle so now you got max perpendicular distances for each angle...
pick best solution O(m)
so look all rotations from 0 to 90 degrees and remember the one that has minimal OBB area. Just to be sure the OBB is aligned to section angle and size of axises is the value of that angle and all the 90 deg increments... around center
灰色是从您的图像中检测到的点,绿色矩形是轴对齐的BBox,红色矩形是找到的OBBox。 青色的点是每个角度间隔找到的最大距离,绿色的点是+/-90deg相邻角度间隔的最大垂直距离。我使用了400个角度,正如您所看到的结果非常接近...360/400 deg的精度,所以这种方法很有效...
以下是C++源代码:
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
struct _pnt2D
{
double x,y;
// inline
_pnt2D() {}
_pnt2D(_pnt2D& a) { *this=a; }
~_pnt2D() {}
_pnt2D* operator = (const _pnt2D *a) { *this=*a; return this; }
//_pnt2D* operator = (const _pnt2D &a) { ...copy... return this; }
};
struct _ang
{
double ang; // center angle of section
double dis; // max distance of ang section
double pdis; // max perpendicular distance of +/-90deg section
// inline
_ang() {}
_ang(_ang& a) { *this=a; }
~_ang() {}
_ang* operator = (const _ang *a) { *this=*a; return this; }
//_ang* operator = (const _ang &a) { ...copy... return this; }
};
const int angs=400; // must be divisible by 4
const int angs4=angs>>2;
const double dang=2.0*M_PI/double(angs);
const double dang2=0.5*dang;
_ang ang[angs];
List<_pnt2D> pnt;
_pnt2D bbox[2],obb[4],center;
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void compute_OBB()
{
_pnt2D ppp[4];
int i,j; double a,b,dx,dy;
_ang *aa,*bb;
_pnt2D p,*pp; DWORD *q;
// convert bmp -> pnt[]
pnt.num=0;
Graphics::TBitmap *bmp=new Graphics::TBitmap;
bmp->LoadFromFile("in.bmp");
bmp->HandleType=bmDIB;
bmp->PixelFormat=pf32bit;
for (p.y=0;p.y<bmp->Height;p.y++)
for (q=(DWORD*)bmp->ScanLine[int(p.y)],p.x=0;p.x<bmp->Width;p.x++)
if ((q[int(p.x)]&255)<20)
pnt.add(p);
delete bmp;
// axis aligned bbox
bbox[0]=pnt[0];
bbox[1]=pnt[0];
for (pp=pnt.dat,i=0;i<pnt.num;i++,pp++)
{
if (bbox[0].x>pp->x) bbox[0].x=pp->x;
if (bbox[0].y>pp->y) bbox[0].y=pp->y;
if (bbox[1].x<pp->x) bbox[1].x=pp->x;
if (bbox[1].y<pp->y) bbox[1].y=pp->y;
}
center.x=(bbox[0].x+bbox[1].x)*0.5;
center.y=(bbox[0].y+bbox[1].y)*0.5;
// ang[] table init
for (aa=ang,a=0.0,i=0;i<angs;i++,aa++,a+=dang)
{
aa->ang=a;
aa-> dis=0.0;
aa->pdis=0.0;
}
// ang[].dis
for (pp=pnt.dat,i=0;i<pnt.num;i++,pp++)
{
dx=pp->x-center.x;
dy=pp->y-center.y;
a=atan2(dy,dx);
j=floor((a/dang)+0.5); if (j<0) j+=angs; j%=angs;
a=(dx*dx)+(dy*dy);
if (ang[j].dis<a) ang[j].dis=a;
}
for (aa=ang,i=0;i<angs;i++,aa++) aa->dis=sqrt(aa->dis);
// ang[].adis
for (aa=ang,i=0;i<angs;i++,aa++)
for (bb=ang,j=0;j<angs;j++,bb++)
{
a=fabs(aa->ang-bb->ang);
if (a>M_PI) a=(2.0*M_PI)-a;
if (a<=0.5*M_PI)
{
a=bb->dis*cos(a);
if (aa->pdis<a) aa->pdis=a;
}
}
// find best oriented bbox (the best angle is ang[j].ang)
for (b=0,j=0,i=0;i<angs;i++)
{
dx =ang[i].pdis; i+=angs4; i%=angs;
dy =ang[i].pdis; i+=angs4; i%=angs;
dx+=ang[i].pdis; i+=angs4; i%=angs;
dy+=ang[i].pdis; i+=angs4; i%=angs;
a=dx*dy; if ((b>a)||(i==0)) { b=a; j=i; }
}
// compute endpoints for OBB
i=j;
ppp[0].x=ang[i].pdis*cos(ang[i].ang);
ppp[0].y=ang[i].pdis*sin(ang[i].ang); i+=angs4; i%=angs;
ppp[1].x=ang[i].pdis*cos(ang[i].ang);
ppp[1].y=ang[i].pdis*sin(ang[i].ang); i+=angs4; i%=angs;
ppp[2].x=ang[i].pdis*cos(ang[i].ang);
ppp[2].y=ang[i].pdis*sin(ang[i].ang); i+=angs4; i%=angs;
ppp[3].x=ang[i].pdis*cos(ang[i].ang);
ppp[3].y=ang[i].pdis*sin(ang[i].ang); i+=angs4; i%=angs;
obb[0].x=center.x+ppp[0].x+ppp[3].x;
obb[0].y=center.y+ppp[0].y+ppp[3].y;
obb[1].x=center.x+ppp[1].x+ppp[0].x;
obb[1].y=center.y+ppp[1].y+ppp[0].y;
obb[2].x=center.x+ppp[2].x+ppp[1].x;
obb[2].y=center.y+ppp[2].y+ppp[1].y;
obb[3].x=center.x+ppp[3].x+ppp[2].x;
obb[3].y=center.y+ppp[3].y+ppp[2].y;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
List<double> xxx; 相当于 double xxx[];
xxx.add(5); 将 5 添加到列表末尾
xxx[7] 访问数组元素(安全)
xxx.dat[7] 访问数组元素(不安全但直接访问速度快)
xxx.num 是数组的实际使用大小
xxx.reset() 清除数组并设置 xxx.num=0
xxx.allocate(100) 为 100 个项目预分配空间// convert bmp -> pnt[]。