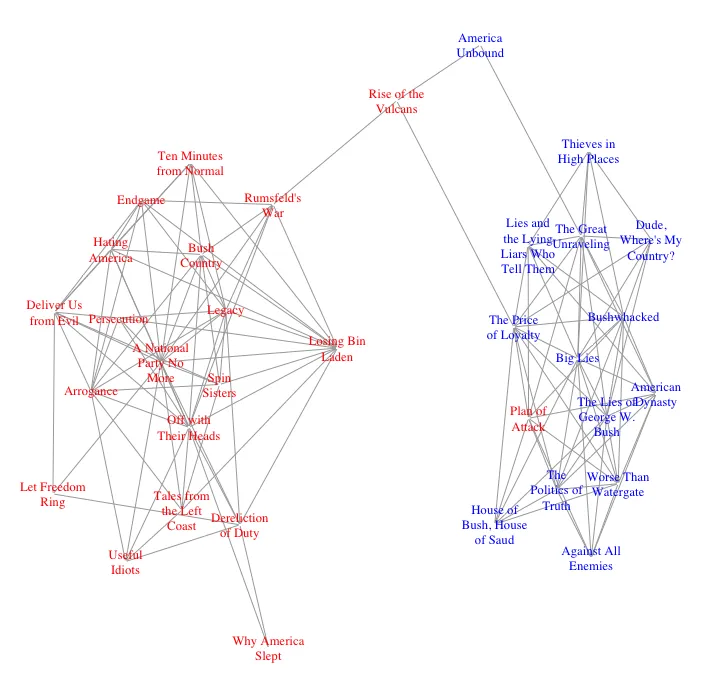
我正在使用R和igraph可视化亚马逊上一些政治书籍的购买情况。我已经得到了一个网络图,显示了某些书籍的位置,表明它们不仅被与相同政治观点的其他书籍一起购买。下面是这张图:

g<-read.graph("data/polbooks/polbooks.gml", format=c("gml"))
V(g)$degree <- degree(g, mode="all")
cut.off <- mean(V(g)$degree)
sub <- induced_subgraph(g, which(V(g)$degree>cut.off))
plot(sub, vertex.shape="none", vertex.size=1,
vertex.label.color=ifelse(V(sub)$value=="l", "blue", "red"),
layout=layout_with_fr)
我尝试了几种内置布局,但没有一种能真正产生所需的效果。
Error in text.default(x, y, labels = labels, col = label.color, family = label.family, : zero-length 'labels' specified。我不确定问题是在我的端还是你的代码中有些东西丢失了。如果你启动一个干净的会话,你发布的代码是否能在你的系统上无误地运行? - eipi10