我正在尝试在有障碍物(多边形)的有界矩形空间中实现重心沃罗诺伊镶嵌算法。
以下代码在没有障碍物(多边形)的边界框中提供了重心沃罗诺伊镶嵌图。蓝点是发生器,红点是重心,黄点是蓝点和红点之间的中间点。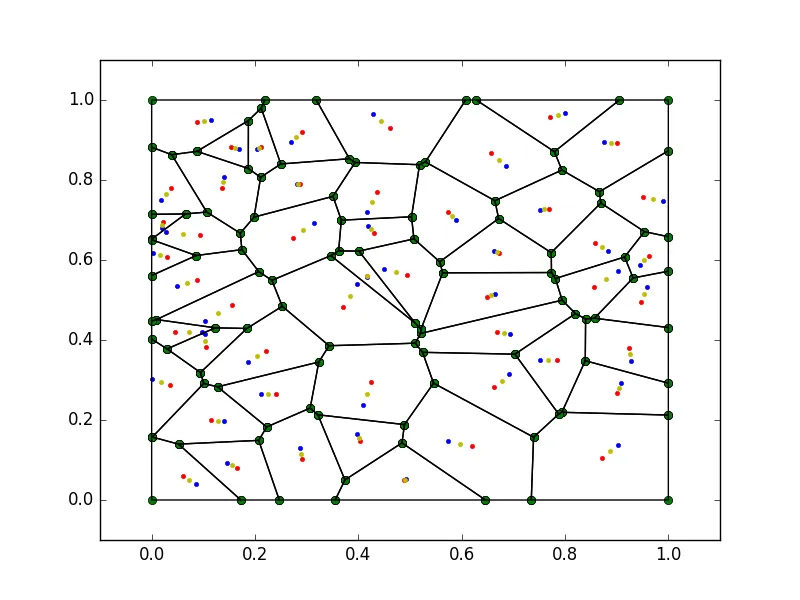
现在我想将这个特定的代码扩展到有障碍物的情况,例如我想做类似于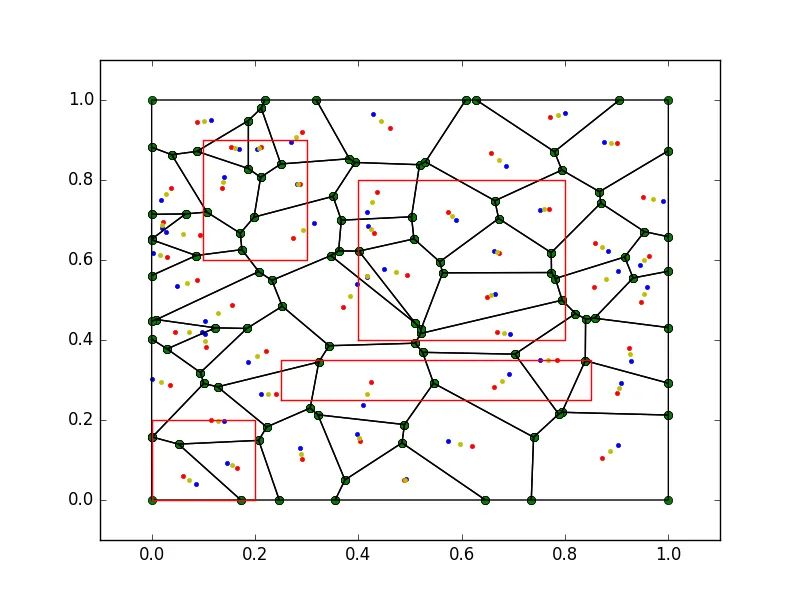 ,但是我不想有任何红色多边形中的内容。
,但是我不想有任何红色多边形中的内容。
我尝试过的一种方法是使用未占用区域划分空间,但效果不佳。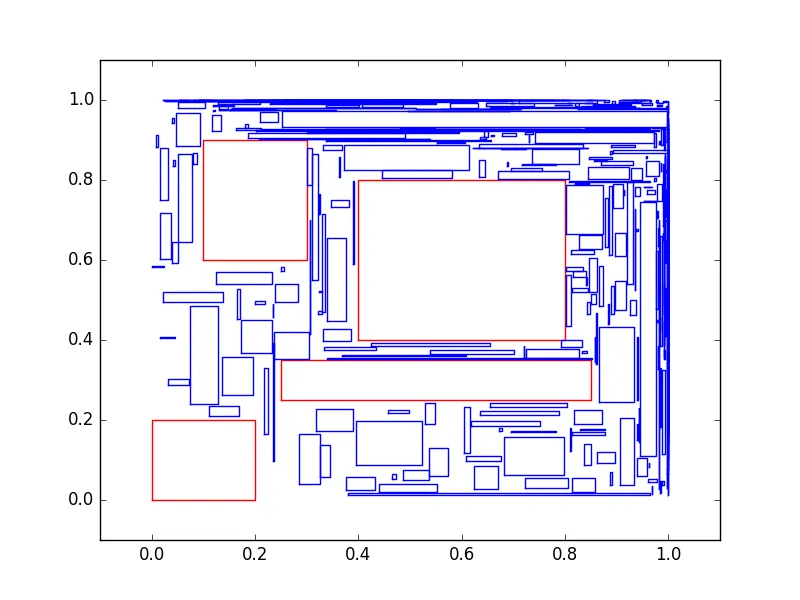 。
。
第一种方法的代码:
以下代码在没有障碍物(多边形)的边界框中提供了重心沃罗诺伊镶嵌图。蓝点是发生器,红点是重心,黄点是蓝点和红点之间的中间点。

import matplotlib.pyplot as pl
import numpy as np
import scipy as sp
import scipy.spatial
import sys
np.random.seed(1)
eps = sys.float_info.epsilon
n_robots = 10
robots = np.random.rand(n_robots, 2)
#print(robots)
bounding_box = np.array([0., 1., 0., 1.])
def in_box(robots, bounding_box):
return np.logical_and(np.logical_and(bounding_box[0] <= robots[:, 0],
robots[:, 0] <= bounding_box[1]),
np.logical_and(bounding_box[2] <= robots[:, 1],
robots[:, 1] <= bounding_box[3]))
def voronoi(robots, bounding_box):
i = in_box(robots, bounding_box)
points_center = robots[i, :]
points_left = np.copy(points_center)
points_left[:, 0] = bounding_box[0] - (points_left[:, 0] - bounding_box[0])
points_right = np.copy(points_center)
points_right[:, 0] = bounding_box[1] + (bounding_box[1] - points_right[:, 0])
points_down = np.copy(points_center)
points_down[:, 1] = bounding_box[2] - (points_down[:, 1] - bounding_box[2])
points_up = np.copy(points_center)
points_up[:, 1] = bounding_box[3] + (bounding_box[3] - points_up[:, 1])
points = np.append(points_center,
np.append(np.append(points_left,
points_right,
axis=0),
np.append(points_down,
points_up,
axis=0),
axis=0),
axis=0)
# Compute Voronoi
vor = sp.spatial.Voronoi(points)
# Filter regions and select corresponding points
regions = []
points_to_filter = [] # we'll need to gather points too
ind = np.arange(points.shape[0])
ind = np.expand_dims(ind,axis= 1)
for i,region in enumerate(vor.regions): # enumerate the regions
if not region: # nicer to skip the empty region altogether
continue
flag = True
for index in region:
if index == -1:
flag = False
break
else:
x = vor.vertices[index, 0]
y = vor.vertices[index, 1]
if not(bounding_box[0] - eps <= x and x <= bounding_box[1] + eps and
bounding_box[2] - eps <= y and y <= bounding_box[3] + eps):
flag = False
break
if flag:
regions.append(region)
# find the point which lies inside
points_to_filter.append(vor.points[vor.point_region == i][0,:])
vor.filtered_points = np.array(points_to_filter)
vor.filtered_regions = regions
return vor
def centroid_region(vertices):
A = 0
C_x = 0
C_y = 0
for i in range(0, len(vertices) - 1):
s = (vertices[i, 0] * vertices[i + 1, 1] - vertices[i + 1, 0] * vertices[i, 1])
A = A + s
C_x = C_x + (vertices[i, 0] + vertices[i + 1, 0]) * s
C_y = C_y + (vertices[i, 1] + vertices[i + 1, 1]) * s
A = 0.5 * A
C_x = (1.0 / (6.0 * A)) * C_x
C_y = (1.0 / (6.0 * A)) * C_y
return np.array([[C_x, C_y]])
def plot(r,index):
vor = voronoi(r, bounding_box)
fig = pl.figure()
ax = fig.gca()
#ax.plot(pol2[:,0],pol2[:,1],'k-')
# Plot initial points
ax.plot(vor.filtered_points[:, 0], vor.filtered_points[:, 1], 'b.')
print("initial",vor.filtered_points)
# Plot ridges points
for region in vor.filtered_regions:
vertices = vor.vertices[region, :]
ax.plot(vertices[:, 0], vertices[:, 1], 'go')
# Plot ridges
for region in vor.filtered_regions:
vertices = vor.vertices[region + [region[0]], :]
ax.plot(vertices[:, 0], vertices[:, 1], 'k-')
# Compute and plot centroids
centroids = []
for region in vor.filtered_regions:
vertices = vor.vertices[region + [region[0]], :]
centroid = centroid_region(vertices)
centroids.append(list(centroid[0, :]))
ax.plot(centroid[:, 0], centroid[:, 1], 'r.')
centroids = np.asarray(centroids)
rob = np.copy(vor.filtered_points)
# the below code is for the plotting purpose the update happens in the update function
interim_x = np.asarray(centroids[:,0] - rob[:,0])
interim_y = np.asarray(centroids[:,1] - rob[:,1])
magn = [np.linalg.norm(centroids[i,:] - rob[i,:]) for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
x = np.copy(interim_x)
x = np.asarray([interim_x[i]/magn[i] for i in range(interim_x.shape[0])])
y = np.copy(interim_y)
y = np.asarray([interim_y[i]/magn[i] for i in range(interim_y.shape[0])])
nor = np.copy(rob)
for i in range(x.shape[0]):
nor[i,0] = x[i]
nor[i,1] = y[i]
temp = np.copy(rob)
temp[:,0] = [rob[i,0] + 0.5*interim_x[i] for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
temp[:,1] = [rob[i,1] + 0.5*interim_y[i] for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
pol = [[]]
ax.plot(temp[:,0] ,temp[:,1], 'y.' )
ax.set_xlim([-0.1, 1.1])
ax.set_ylim([-0.1, 1.1])
pl.savefig("voronoi" + str(index) + ".png")
return centroids
def update(rob,centroids):
interim_x = np.asarray(centroids[:,0] - rob[:,0])
interim_y = np.asarray(centroids[:,1] - rob[:,1])
magn = [np.linalg.norm(centroids[i,:] - rob[i,:]) for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
x = np.copy(interim_x)
x = np.asarray([interim_x[i]/magn[i] for i in range(interim_x.shape[0])])
y = np.copy(interim_y)
y = np.asarray([interim_y[i]/magn[i] for i in range(interim_y.shape[0])])
nor = [np.linalg.norm([x[i],y[i]]) for i in range(x.shape[0])]
temp = np.copy(rob)
temp[:,0] = [rob[i,0] + 0.5*interim_x[i] for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
temp[:,1] = [rob[i,1] + 0.5*interim_y[i] for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
return np.asarray(temp)
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(1):
centroids = plot(robots,i)
robots = update(robots,centroids)
现在我想将这个特定的代码扩展到有障碍物的情况,例如我想做类似于
 ,但是我不想有任何红色多边形中的内容。
,但是我不想有任何红色多边形中的内容。我尝试过的一种方法是使用未占用区域划分空间,但效果不佳。
 。
。第一种方法的代码:
import random
from shapely.geometry import Polygon, Point
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pl
def get_random_point_in_polygon(poly,polygons,num):
(minx, miny, maxx, maxy) = poly.bounds
points =[]
while num != 0:
p = Point(random.uniform(minx, maxx), random.uniform(miny, maxy))
if any(poly.contains(p) for poly in polygons):
continue
else:
num = num-1
#print(num)
points.append([p.x,p.y])
return np.asarray(points)
def polysplit(poly,polygons):
(minx, miny, maxx, maxy) = poly.bounds
pols =[]
return pols
def randomRects(p,poly):
(minx, miny, maxx, maxy) = poly.bounds
rect = []
while True:
w = round(random.uniform(0, 1),3)
h = round(random.uniform(0, 1),3)
if (((p[:,0]+w) < maxx) and ((p[:,1]+h) < maxy)):
rect.append(np.squeeze([np.squeeze(p[:,0]),np.squeeze(p[:,1])]))
rect.append(np.squeeze([np.squeeze(p[:,0]+w),np.squeeze(p[:,1])]))
rect.append(np.squeeze([np.squeeze(p[:,0]+w),np.squeeze(p[:,1]+h)]))
rect.append(np.squeeze([np.squeeze(p[:,0]),np.squeeze(p[:,1]+h)]))
rect.append(np.squeeze([np.squeeze(p[:,0]),np.squeeze(p[:,1])]))
break
else:
continue
return np.asarray(rect)
def rect(poly,polygons):
rec =[]
area = poly.area
areas = 0
for i in polygons:
areas = areas+i.area
#print(area - areas)
flag = False
while (area - areas) > 0.4:
p = get_random_point_in_polygon(poly,polygons,1)
#print(p)
rect = randomRects(p,poly)
if any(poly.intersects(Polygon(rect)) for poly in polygons):
continue
#elif any(poly.intersects(Polygon(rect)) for poly in rec):
#continue
else:
if rec == []:
rec.append(Polygon(rect))
print("hi")
elif any(pol.intersects(Polygon(rect)) for pol in rec):
continue
else:
areas = areas+Polygon(rect).area
print(area-areas)
rec.append(Polygon(rect))
return rec
p = Polygon([(0, 0), (1, 0), (1, 1), (0, 1), (0, 0)])
p2 = Polygon([(0, 0), (.2,0), (.2,.2), (0, 0.2), (0,0)])
p3 = Polygon([(0.4, 0.4), (0.8,0.4), (.8,.8), (0.4, 0.8), (0.4,0.4)])
p4 = Polygon([(0.1,0.6),(0.3,.6),(0.3,0.9),(0.1,0.9),(0.1,0.6)])
p5 = Polygon([(0.25,0.25),(0.85,.25),(0.85,0.35),(0.25,0.35),(0.25,0.25)])
polygons = []
polygons.append(p2)
polygons.append(p3)
polygons.append(p4)
polygons.append(p5)
point_in_poly = get_random_point_in_polygon(p,polygons,10000)
fig = pl.figure()
ax = fig.gca()
#ax.plot(point_in_poly[:,0],point_in_poly[:,1],'b.')
area = 0
for po in polygons:
#area = area +po.area
x,y = po.exterior.xy
#print [x,y]
ax.plot(x,y,'r-')
#print(p.area - area)
r = rect(p,polygons)
for rr in r:
#area = area +po.area
x,y = rr.exterior.xy
#print [x,y]
ax.plot(x,y,'b-')
ax.set_xlim([-0.1, 1.1])
ax.set_ylim([-0.1, 1.1])
pl.savefig("test1.png")
第二种方法是我考虑使用二进制空间分割来将自由区域划分为矩形,并对每个自由区域矩形应用上述代码。但我不确定如何在Python中实现。
第三种方法:我使用了Python的triangle库来计算自由空间的符合约束的Delaunay三角剖分,并尝试将其转换回Voronoi图。结果并不如预期。
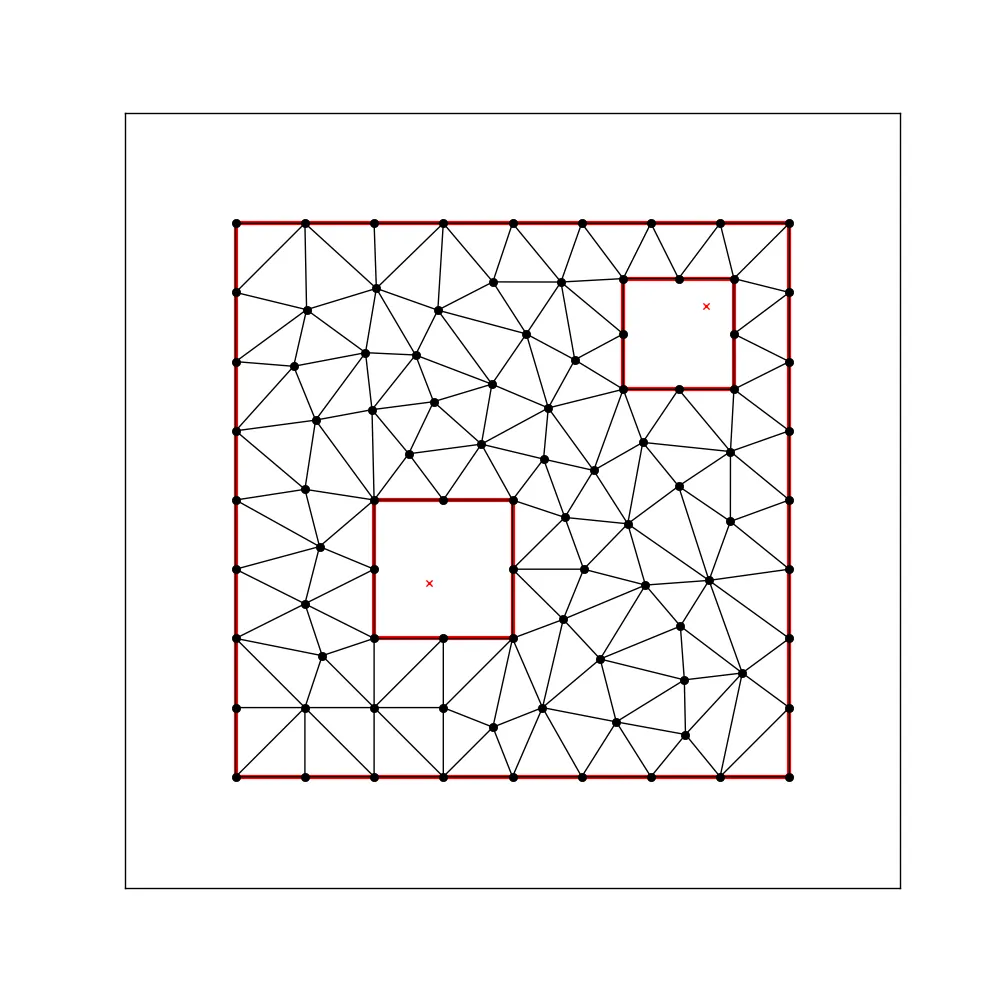 以及它的
以及它的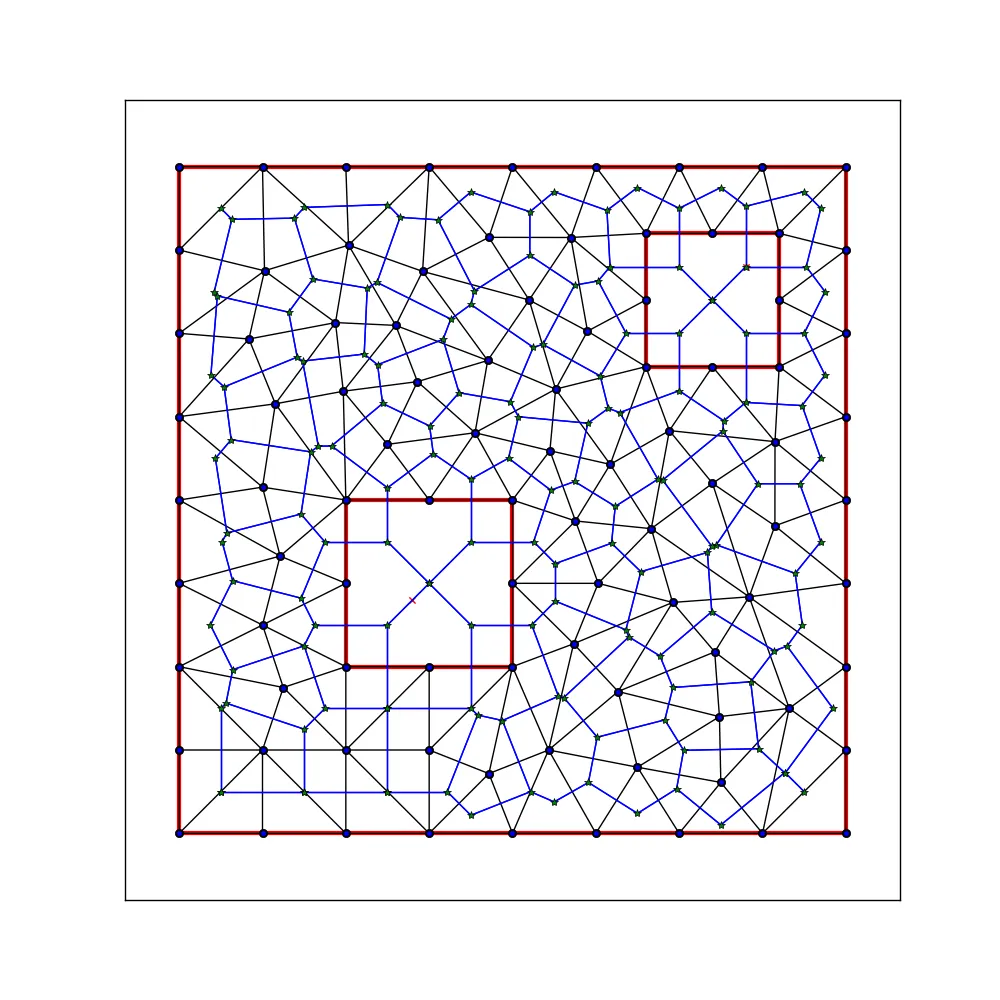
下面的代码是我尝试的所有方法的编译,所以可能有点凌乱。我尝试使用Scipy、Triangle库中的Voronoi函数,并尝试使用自定义方法将三角剖分转换为Voronoi。但这些代码不太好用,而且还存在一些错误。
from numpy import array
import numpy as np
def read_poly(file_name):
"""
Simple poly-file reader, that creates a python dictionary
with information about vertices, edges and holes.
It assumes that vertices have no attributes or boundary markers.
It assumes that edges have no boundary markers.
No regional attributes or area constraints are parsed.
"""
output = {'vertices': None, 'holes': None, 'segments': None}
# open file and store lines in a list
file = open(file_name, 'r')
lines = file.readlines()
file.close()
lines = [x.strip('\n').split() for x in lines]
# Store vertices
vertices= []
N_vertices, dimension, attr, bdry_markers = [int(x) for x in lines[0]]
# We assume attr = bdrt_markers = 0
for k in range(N_vertices):
label, x, y = [items for items in lines[k+1]]
vertices.append([float(x), float(y)])
output['vertices']=array(vertices)
# Store segments
segments = []
N_segments, bdry_markers = [int(x) for x in lines[N_vertices+1]]
for k in range(N_segments):
label, pointer_1, pointer_2 = [items for items in lines[N_vertices+k+2]]
segments.append([int(pointer_1)-1, int(pointer_2)-1])
output['segments'] = array(segments)
# Store holes
N_holes = int(lines[N_segments+N_vertices+2][0])
holes = []
for k in range(N_holes):
label, x, y = [items for items in lines[N_segments + N_vertices + 3 + k]]
holes.append([float(x), float(y)])
output['holes'] = array(holes)
print(holes)
return output
from triangle import triangulate,voronoi, plot as tplot
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
image = read_poly("/home/pranav/catkin_ws/src/beginner_tutorials/scripts/test.poly")
cncfq20adt = triangulate(image, 'pq20a.01D')
#print(cncfq20adt['vertices'])
#print(cncfq20adt['triangles'])
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = plt.subplot(111, aspect='equal')
tplot.plot(ax, **cncfq20adt)
plt.savefig("image.png")
import triangle
from scipy.spatial import Delaunay
pts = cncfq20adt['vertices']
tri = Delaunay(pts)
p = tri.points[tri.vertices]
#print(pts)
# Triangle vertices
A = p[:,0,:].T
B = p[:,1,:].T
C = p[:,2,:].T
print(C)
# See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circumscribed_circle#Circumscribed_circles_of_triangles
# The following is just a direct transcription of the formula there
a = A - C
b = B - C
def dot2(u, v):
return u[0]*v[0] + u[1]*v[1]
def cross2(u, v, w):
"""u x (v x w)"""
return dot2(u, w)*v - dot2(u, v)*w
def ncross2(u, v):
"""|| u x v ||^2"""
return sq2(u)*sq2(v) - dot2(u, v)**2
def sq2(u):
return dot2(u, u)
cc = cross2(sq2(a) * b - sq2(b) * a, a, b) / (2*ncross2(a, b)) + C
# Grab the Voronoi edges
vc = cc[:,tri.neighbors]
vc[:,tri.neighbors == -1] = np.nan # edges at infinity, plotting those would need more work...
lines = []
lines.extend(zip(cc.T, vc[:,:,0].T))
lines.extend(zip(cc.T, vc[:,:,1].T))
lines.extend(zip(cc.T, vc[:,:,2].T))
# Plot it
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.collections import LineCollection
lines = LineCollection(lines, edgecolor='b')
#plt.hold(1)
plt.plot(pts[:,0], pts[:,1], '.')
plt.plot(cc[0], cc[1], '*')
plt.gca().add_collection(lines)
plt.axis('equal')
plt.xlim(-0.1, 1.1)
plt.ylim(-0.1, 1.1)
plt.savefig("vor2.png")
ax1 = plt.subplot(121, aspect='equal')
triangle.plot.plot(ax1, vertices=pts)
lim = ax1.axis()
points, edges, ray_origin, ray_direct = triangle.voronoi(pts)
d = dict(vertices=points, edges=edges, ray_origins=ray_origin, ray_directions=ray_direct)
ax2 = plt.subplot(111, aspect='equal')
triangle.plot.plot(ax2, **d)
ax2.axis(lim)
plt.savefig("vor.png")
import matplotlib.pyplot as pl
import scipy as sp
import scipy.spatial
import sys
from shapely.geometry import Polygon,Point
import random
np.random.seed(1)
eps = sys.float_info.epsilon
"""
n_robots = 50
#robots = np.random.rand(n_robots, 2)
def get_random_point_in_polygon(poly,polygons,num):
(minx, miny, maxx, maxy) = poly.bounds
points =[]
while num != 0:
p = Point(random.uniform(minx, maxx), random.uniform(miny, maxy))
if any(poly.contains(p) for poly in polygons):
continue
else:
num = num-1
print(num)
points.append([p.x,p.y])
return np.asarray(points)
def polysplit(poly,polygons):
rectangles = []
return rectangles
p = Polygon([(0, 0), (1, 0), (1, 1), (0, 1), (0, 0)])
p2 = Polygon([(0, 0), (.2,0), (.2,.2), (0, 0.2), (0,0)])
p3 = Polygon([(0.4, 0.4), (0.7,0.4), (.7,.7), (0.4, 0.7), (0.4,0.4)])
polygons = []
polygons.append(p2)
polygons.append(p3)
#point_in_poly = get_random_point_in_polygon(p,polygons,10)
robots = get_random_point_in_polygon(p,polygons,n_robots)
#print(sampl)
print(robots)
bounding_box = np.array([0., 1, 0., 1])
box = np.array([0.2, 0.6, 0, 0.6])
box2 = np.array([0, 0.6, 0.2, 0.6])
boxes =[]
boxes.append(box)
boxes.append(box2)
"""
robots = cncfq20adt['vertices']
print("length",len(robots))
bounding_box = np.array([0., 1., 0., 1.])
def in_box(robots, bounding_box):
return np.logical_and(np.logical_and(bounding_box[0] <= robots[:, 0],
robots[:, 0] <= bounding_box[1]),
np.logical_and(bounding_box[2] <= robots[:, 1],
robots[:, 1] <= bounding_box[3]))
def voronoi(robots, bounding_box):
i = in_box(robots, bounding_box)
points_center = robots[i, :]
points_left = np.copy(points_center)
points_left[:, 0] = bounding_box[0] - (points_left[:, 0] - bounding_box[0])
points_right = np.copy(points_center)
points_right[:, 0] = bounding_box[1] + (bounding_box[1] - points_right[:, 0])
points_down = np.copy(points_center)
points_down[:, 1] = bounding_box[2] - (points_down[:, 1] - bounding_box[2])
points_up = np.copy(points_center)
points_up[:, 1] = bounding_box[3] + (bounding_box[3] - points_up[:, 1])
points = np.append(points_center,
np.append(np.append(points_left,
points_right,
axis=0),
np.append(points_down,
points_up,
axis=0),
axis=0),
axis=0)
# Compute Voronoi
vor = sp.spatial.Voronoi(points)
# Filter regions and select corresponding points
regions = []
points_to_filter = [] # we'll need to gather points too
ind = np.arange(points.shape[0])
ind = np.expand_dims(ind,axis= 1)
for i,region in enumerate(vor.regions): # enumerate the regions
if not region: # nicer to skip the empty region altogether
continue
flag = True
for index in region:
if index == -1:
flag = False
break
else:
x = vor.vertices[index, 0]
y = vor.vertices[index, 1]
if not(bounding_box[0] - eps <= x and x <= bounding_box[1] + eps and
bounding_box[2] - eps <= y and y <= bounding_box[3] + eps):
flag = False
break
if flag:
regions.append(region)
# find the point which lies inside
points_to_filter.append(vor.points[vor.point_region == i][0,:])
vor.filtered_points = np.array(points_to_filter)
vor.filtered_regions = regions
return vor
def centroid_region(vertices):
A = 0
C_x = 0
C_y = 0
for i in range(0, len(vertices) - 1):
s = (vertices[i, 0] * vertices[i + 1, 1] - vertices[i + 1, 0] * vertices[i, 1])
A = A + s
C_x = C_x + (vertices[i, 0] + vertices[i + 1, 0]) * s
C_y = C_y + (vertices[i, 1] + vertices[i + 1, 1]) * s
A = 0.5 * A
C_x = (1.0 / (6.0 * A)) * C_x
C_y = (1.0 / (6.0 * A)) * C_y
return np.array([[C_x, C_y]])
def plot(r,index):
vor = voronoi(r, bounding_box)
fig = pl.figure()
ax = fig.gca()
#ax.plot(pol2[:,0],pol2[:,1],'k-')
# Plot initial points
ax.plot(vor.filtered_points[:, 0], vor.filtered_points[:, 1], 'b.')
print("initial",vor.filtered_points)
# Plot ridges points
for region in vor.filtered_regions:
vertices = vor.vertices[region, :]
ax.plot(vertices[:, 0], vertices[:, 1], 'go')
# Plot ridges
for region in vor.filtered_regions:
vertices = vor.vertices[region + [region[0]], :]
ax.plot(vertices[:, 0], vertices[:, 1], 'k-')
# Compute and plot centroids
centroids = []
for region in vor.filtered_regions:
vertices = vor.vertices[region + [region[0]], :]
centroid = centroid_region(vertices)
centroids.append(list(centroid[0, :]))
ax.plot(centroid[:, 0], centroid[:, 1], 'r.')
centroids = np.asarray(centroids)
rob = np.copy(vor.filtered_points)
# the below code is for the plotting purpose the update happens in the update function
interim_x = np.asarray(centroids[:,0] - rob[:,0])
interim_y = np.asarray(centroids[:,1] - rob[:,1])
magn = [np.linalg.norm(centroids[i,:] - rob[i,:]) for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
x = np.copy(interim_x)
x = np.asarray([interim_x[i]/magn[i] for i in range(interim_x.shape[0])])
y = np.copy(interim_y)
y = np.asarray([interim_y[i]/magn[i] for i in range(interim_y.shape[0])])
nor = np.copy(rob)
for i in range(x.shape[0]):
nor[i,0] = x[i]
nor[i,1] = y[i]
temp = np.copy(rob)
temp[:,0] = [rob[i,0] + 0.5*interim_x[i] for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
temp[:,1] = [rob[i,1] + 0.5*interim_y[i] for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
pol = [[]]
ax.plot(temp[:,0] ,temp[:,1], 'y.' )
ax.set_xlim([-0.1, 1.1])
ax.set_ylim([-0.1, 1.1])
pl.savefig("voronoi" + str(index) + ".png")
return centroids
def update(rob,centroids):
interim_x = np.asarray(centroids[:,0] - rob[:,0])
interim_y = np.asarray(centroids[:,1] - rob[:,1])
magn = [np.linalg.norm(centroids[i,:] - rob[i,:]) for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
x = np.copy(interim_x)
x = np.asarray([interim_x[i]/magn[i] for i in range(interim_x.shape[0])])
y = np.copy(interim_y)
y = np.asarray([interim_y[i]/magn[i] for i in range(interim_y.shape[0])])
nor = [np.linalg.norm([x[i],y[i]]) for i in range(x.shape[0])]
temp = np.copy(rob)
temp[:,0] = [rob[i,0] + 0.5*interim_x[i] for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
temp[:,1] = [rob[i,1] + 0.5*interim_y[i] for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
return np.asarray(temp)
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(1):
centroids = plot(robots,i)
robots = update(robots,centroids)
如果有人能帮我,我会非常非常感激。