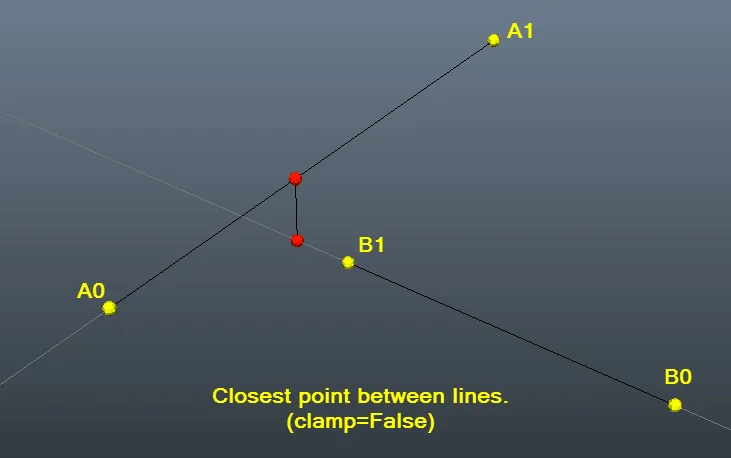
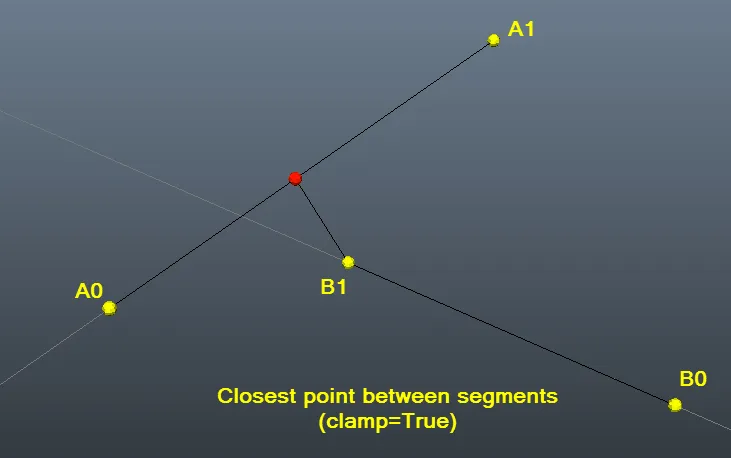
我的解决方案是Fnord解决方案的翻译。我用Javascript和C语言实现。
在Javascript中,您需要包含mathjs。
var closestDistanceBetweenLines = function(a0, a1, b0, b1, clampAll, clampA0, clampA1, clampB0, clampB1){
clampA0 = clampA0 || false;
clampA1 = clampA1 || false;
clampB0 = clampB0 || false;
clampB1 = clampB1 || false;
clampAll = clampAll || false;
if(clampAll){
clampA0 = true;
clampA1 = true;
clampB0 = true;
clampB1 = true;
}
var A = math.subtract(a1, a0);
var B = math.subtract(b1, b0);
var _A = math.divide(A, math.norm(A))
var _B = math.divide(B, math.norm(B))
var cross = math.cross(_A, _B);
var denom = math.pow(math.norm(cross), 2);
if (denom == 0){
var d0 = math.dot(_A, math.subtract(b0, a0));
var d = math.norm(math.subtract(math.add(math.multiply(d0, _A), a0), b0));
if(clampA0 || clampA1 || clampB0 || clampB1){
var d1 = math.dot(_A, math.subtract(b1, a0));
if(d0 <= 0 && 0 >= d1){
if(clampA0 == true && clampB1 == true){
if(math.absolute(d0) < math.absolute(d1)){
return [b0, a0, math.norm(math.subtract(b0, a0))];
}
return [b1, a0, math.norm(math.subtract(b1, a0))];
}
}
else if(d0 >= math.norm(A) && math.norm(A) <= d1){
if(clampA1 == true && clampB0 == true){
if(math.absolute(d0) < math.absolute(d1)){
return [b0, a1, math.norm(math.subtract(b0, a1))];
}
return [b1, a1, math.norm(math.subtract(b1,a1))];
}
}
}
return [null, null, d];
}
var t = math.subtract(b0, a0);
var det0 = math.det([t, _B, cross]);
var det1 = math.det([t, _A, cross]);
var t0 = math.divide(det0, denom);
var t1 = math.divide(det1, denom);
var pA = math.add(a0, math.multiply(_A, t0));
var pB = math.add(b0, math.multiply(_B, t1));
if(clampA0 || clampA1 || clampB0 || clampB1){
if(t0 < 0 && clampA0)
pA = a0;
else if(t0 > math.norm(A) && clampA1)
pA = a1;
if(t1 < 0 && clampB0)
pB = b0;
else if(t1 > math.norm(B) && clampB1)
pB = b1;
}
var d = math.norm(math.subtract(pA, pB))
return [pA, pB, d];
}
var a1=[13.43, 21.77, 46.81];
var a0=[27.83, 31.74, -26.60];
var b0=[77.54, 7.53, 6.22];
var b1=[26.99, 12.39, 11.18];
closestDistanceBetweenLines(a0,a1,b0,b1,true);
在纯C语言中
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
double determinante3(double* a, double* v1, double* v2){
return a[0] * (v1[1] * v2[2] - v1[2] * v2[1]) + a[1] * (v1[2] * v2[0] - v1[0] * v2[2]) + a[2] * (v1[0] * v2[1] - v1[1] * v2[0]);
}
double* cross3(double* v1, double* v2){
double* v = (double*)malloc(3 * sizeof(double));
v[0] = v1[1] * v2[2] - v1[2] * v2[1];
v[1] = v1[2] * v2[0] - v1[0] * v2[2];
v[2] = v1[0] * v2[1] - v1[1] * v2[0];
return v;
}
double dot3(double* v1, double* v2){
return v1[0] * v2[0] + v1[1] * v2[1] + v1[2] * v2[2];
}
double norma3(double* v1){
double soma = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
soma += pow(v1[i], 2);
}
return sqrt(soma);
}
double* multiplica3(double* v1, double v){
double* v2 = (double*)malloc(3 * sizeof(double));
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
v2[i] = v1[i] * v;
}
return v2;
}
double* soma3(double* v1, double* v2, int sinal){
double* v = (double*)malloc(3 * sizeof(double));
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
v[i] = v1[i] + sinal * v2[i];
}
return v;
}
Result_distance* closestDistanceBetweenLines(double* a0, double* a1, double* b0, double* b1, int clampAll, int clampA0, int clampA1, int clampB0, int clampB1){
double denom, det0, det1, t0, t1, d;
double *A, *B, *_A, *_B, *cross, *t, *pA, *pB;
Result_distance *rd = (Result_distance *)malloc(sizeof(Result_distance));
if (clampAll){
clampA0 = 1;
clampA1 = 1;
clampB0 = 1;
clampB1 = 1;
}
A = soma3(a1, a0, -1);
B = soma3(b1, b0, -1);
_A = multiplica3(A, 1 / norma3(A));
_B = multiplica3(B, 1 / norma3(B));
cross = cross3(_A, _B);
denom = pow(norma3(cross), 2);
if (denom == 0){
double d0 = dot3(_A, soma3(b0, a0, -1));
d = norma3(soma3(soma3(multiplica3(_A, d0), a0, 1), b0, -1));
if (clampA0 || clampA1 || clampB0 || clampB1){
double d1 = dot3(_A, soma3(b1, a0, -1));
if (d0 <= 0 && 0 >= d1){
if (clampA0 && clampB1){
if (abs(d0) < abs(d1)){
rd->pA = b0;
rd->pB = a0;
rd->d = norma3(soma3(b0, a0, -1));
}
else{
rd->pA = b1;
rd->pB = a0;
rd->d = norma3(soma3(b1, a0, -1));
}
}
}
else if (d0 >= norma3(A) && norma3(A) <= d1){
if (clampA1 && clampB0){
if (abs(d0) <abs(d1)){
rd->pA = b0;
rd->pB = a1;
rd->d = norma3(soma3(b0, a1, -1));
}
else{
rd->pA = b1;
rd->pB = a1;
rd->d = norma3(soma3(b1, a1, -1));
}
}
}
}
else{
rd->pA = NULL;
rd->pB = NULL;
rd->d = d;
}
}
else{
t = soma3(b0, a0, -1);
det0 = determinante3(t, _B, cross);
det1 = determinante3(t, _A, cross);
t0 = det0 / denom;
t1 = det1 / denom;
pA = soma3(a0, multiplica3(_A, t0), 1);
pB = soma3(b0, multiplica3(_B, t1), 1);
if (clampA0 || clampA1 || clampB0 || clampB1){
if (t0 < 0 && clampA0)
pA = a0;
else if (t0 > norma3(A) && clampA1)
pA = a1;
if (t1 < 0 && clampB0)
pB = b0;
else if (t1 > norma3(B) && clampB1)
pB = b1;
}
d = norma3(soma3(pA, pB, -1));
rd->pA = pA;
rd->pB = pB;
rd->d = d;
}
free(A);
free(B);
free(cross);
free(t);
return rd;
}
int main(void){
double a1[] = { 13.43, 21.77, 46.81 };
double a0[] = { 27.83, 31.74, -26.60 };
double b0[] = { 77.54, 7.53, 6.22 };
double b1[] = { 26.99, 12.39, 11.18 };
Result_distance* rd = closestDistanceBetweenLines(a0, a1, b0, b1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0);
printf("pA = [%f, %f, %f]\n", rd->pA[0], rd->pA[1], rd->pA[2]);
printf("pB = [%f, %f, %f]\n", rd->pB[0], rd->pB[1], rd->pB[2]);
printf("d = %f\n", rd->d);
return 0;
}