性能基准测试
鉴于Divakar提出了几种解决方案,我在想应该选择哪种方案,在此提供性能基准测试结果。还添加了这篇答案。
结果
简而言之 - 只需使用:np.concatenate(([x[0]], x_diff)).cumsum()。
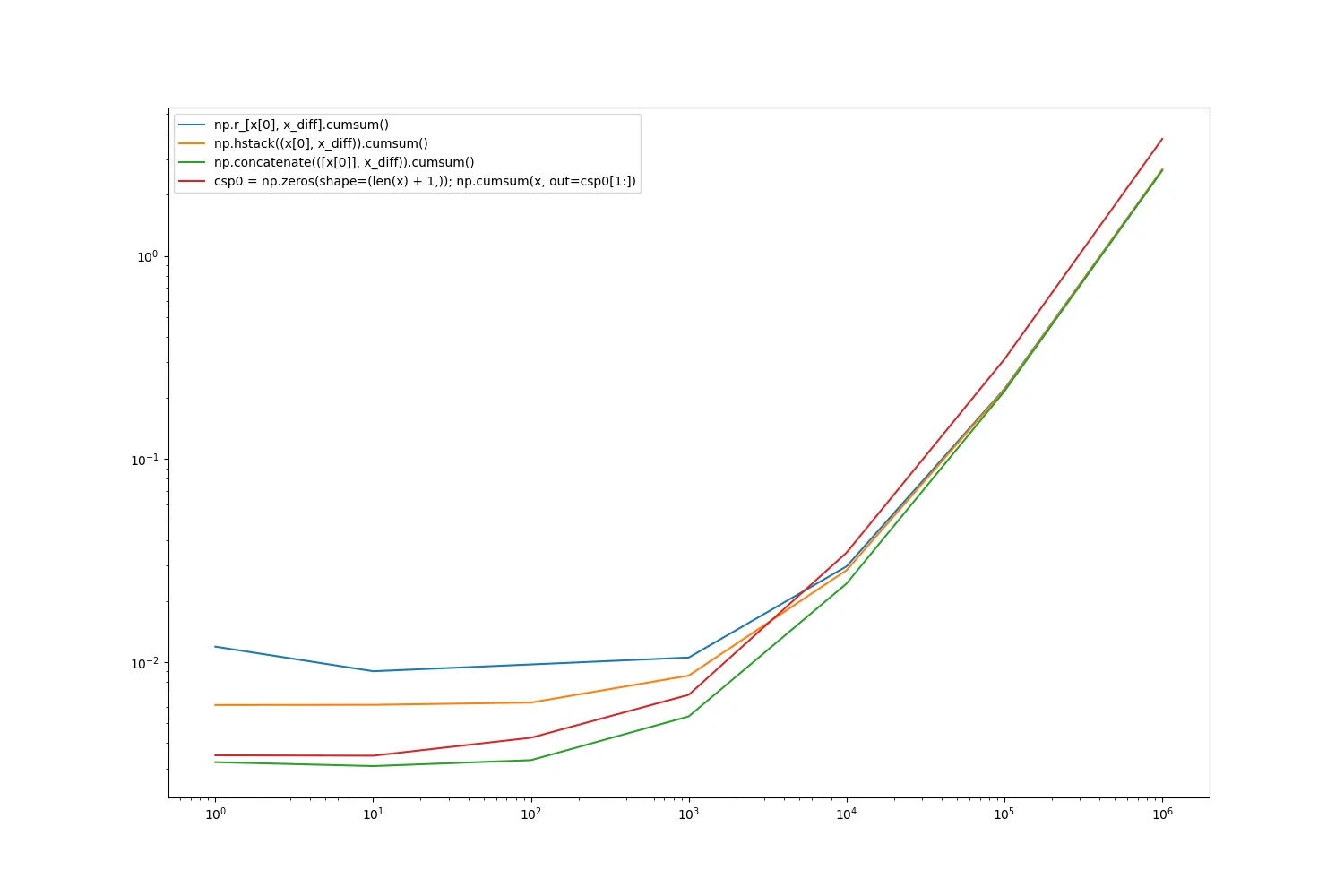
x: 问题规模, y: 每1000次运行的计算时间
代码
import timeit
import random
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
cmds = [
'np.r_[x[0], x_diff].cumsum()',
'np.hstack((x[0], x_diff)).cumsum()',
'np.concatenate(([x[0]], x_diff)).cumsum()',
'csp0 = np.zeros(shape=(len(x) + 1,)); np.cumsum(x, out=csp0[1:])',
]
test_range = [1e0, 1e1, 1e2, 1e3, 1e4, 1e5, 1e6]
ts = np.empty((len(cmds), len(test_range)), dtype=float)
for tt, size_float in enumerate(test_range):
size = round(size_float)
print('array size:', size)
x = np.random.randint(low=0, high=100, size=size)
x_diff = np.diff(x)
n_trials = 1000
for cc, cmd in enumerate(cmds):
t = timeit.Timer(cmd, globals={**globals(), **locals()})
t = t.timeit(n_trials)
ts[cc, tt] = t
print('time for {:d}x \"{:}\": {:.6f}'.format(n_trials, cmd, t))
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(15, 10))
for cc, cmd in enumerate(cmds):
ax.plot(test_range, ts[cc, :], label=cmd)
print(cmd)
ax.legend()
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_yscale('log')
输出
array size: 1
time for 1000x "np.r_[x[0], x_diff].cumsum()": 0.011935
time for 1000x "np.hstack((x[0], x_diff)).cumsum()": 0.006159
time for 1000x "np.concatenate(([x[0]], x_diff)).cumsum()": 0.003221
time for 1000x "csp0 = np.zeros(shape=(len(x) + 1,)); np.cumsum(x, out=csp0[1:])": 0.003482
array size: 10
time for 1000x "np.r_[x[0], x_diff].cumsum()": 0.009031
time for 1000x "np.hstack((x[0], x_diff)).cumsum()": 0.006170
time for 1000x "np.concatenate(([x[0]], x_diff)).cumsum()": 0.003082
time for 1000x "csp0 = np.zeros(shape=(len(x) + 1,)); np.cumsum(x, out=csp0[1:])": 0.003467
array size: 100
time for 1000x "np.r_[x[0], x_diff].cumsum()": 0.009754
time for 1000x "np.hstack((x[0], x_diff)).cumsum()": 0.006332
time for 1000x "np.concatenate(([x[0]], x_diff)).cumsum()": 0.003296
time for 1000x "csp0 = np.zeros(shape=(len(x) + 1,)); np.cumsum(x, out=csp0[1:])": 0.004249
array size: 1000
time for 1000x "np.r_[x[0], x_diff].cumsum()": 0.010550
time for 1000x "np.hstack((x[0], x_diff)).cumsum()": 0.008595
time for 1000x "np.concatenate(([x[0]], x_diff)).cumsum()": 0.005414
time for 1000x "csp0 = np.zeros(shape=(len(x) + 1,)); np.cumsum(x, out=csp0[1:])": 0.006916
array size: 10000
time for 1000x "np.r_[x[0], x_diff].cumsum()": 0.029658
time for 1000x "np.hstack((x[0], x_diff)).cumsum()": 0.028389
time for 1000x "np.concatenate(([x[0]], x_diff)).cumsum()": 0.024410
time for 1000x "csp0 = np.zeros(shape=(len(x) + 1,)); np.cumsum(x, out=csp0[1:])": 0.034652
array size: 100000
time for 1000x "np.r_[x[0], x_diff].cumsum()": 0.221405
time for 1000x "np.hstack((x[0], x_diff)).cumsum()": 0.219564
time for 1000x "np.concatenate(([x[0]], x_diff)).cumsum()": 0.215796
time for 1000x "csp0 = np.zeros(shape=(len(x) + 1,)); np.cumsum(x, out=csp0[1:])": 0.310225
array size: 1000000
time for 1000x "np.r_[x[0], x_diff].cumsum()": 2.660822
time for 1000x "np.hstack((x[0], x_diff)).cumsum()": 2.664244
time for 1000x "np.concatenate(([x[0]], x_diff)).cumsum()": 2.636382
time for 1000x "csp0 = np.zeros(shape=(len(x) + 1,)); np.cumsum(x, out=csp0[1:])": 3.770557
np.r_[x[0], x_diff].cumsum()
np.hstack((x[0], x_diff)).cumsum()
np.concatenate(([x[0]], x_diff)).cumsum()
csp0 = np.zeros(shape=(len(x) + 1,)); np.cumsum(x, out=csp0[1:])
