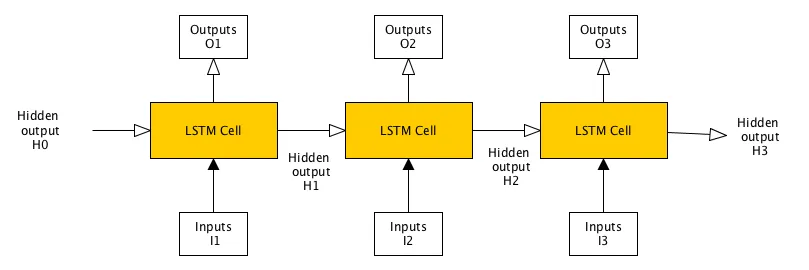
我正在尝试使用Tensorflow学习LSTM模型进行情感分析,我已经阅读了LSTM模型。
下面的代码(create_sentiment_featuresets.py)从5000个正向句子和5000个负向句子中生成词汇表。
import nltk
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
import numpy as np
import random
from collections import Counter
from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer
lemmatizer = WordNetLemmatizer()
def create_lexicon(pos, neg):
lexicon = []
with open(pos, 'r') as f:
contents = f.readlines()
for l in contents[:len(contents)]:
l= l.decode('utf-8')
all_words = word_tokenize(l)
lexicon += list(all_words)
f.close()
with open(neg, 'r') as f:
contents = f.readlines()
for l in contents[:len(contents)]:
l= l.decode('utf-8')
all_words = word_tokenize(l)
lexicon += list(all_words)
f.close()
lexicon = [lemmatizer.lemmatize(i) for i in lexicon]
w_counts = Counter(lexicon)
l2 = []
for w in w_counts:
if 1000 > w_counts[w] > 50:
l2.append(w)
print("Lexicon length create_lexicon: ",len(lexicon))
return l2
def sample_handling(sample, lexicon, classification):
featureset = []
print("Lexicon length Sample handling: ",len(lexicon))
with open(sample, 'r') as f:
contents = f.readlines()
for l in contents[:len(contents)]:
l= l.decode('utf-8')
current_words = word_tokenize(l.lower())
current_words= [lemmatizer.lemmatize(i) for i in current_words]
features = np.zeros(len(lexicon))
for word in current_words:
if word.lower() in lexicon:
index_value = lexicon.index(word.lower())
features[index_value] +=1
features = list(features)
featureset.append([features, classification])
f.close()
print("Feature SET------")
print(len(featureset))
return featureset
def create_feature_sets_and_labels(pos, neg, test_size = 0.1):
global m_lexicon
m_lexicon = create_lexicon(pos, neg)
features = []
features += sample_handling(pos, m_lexicon, [1,0])
features += sample_handling(neg, m_lexicon, [0,1])
random.shuffle(features)
features = np.array(features)
testing_size = int(test_size * len(features))
train_x = list(features[:,0][:-testing_size])
train_y = list(features[:,1][:-testing_size])
test_x = list(features[:,0][-testing_size:])
test_y = list(features[:,1][-testing_size:])
return train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y
def get_lexicon():
global m_lexicon
return m_lexicon
以下代码 (sentiment_analysis.py) 用于使用简单神经网络模型进行情感分析,并且工作正常。
from create_sentiment_featuresets import create_feature_sets_and_labels
from create_sentiment_featuresets import get_lexicon
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# extras for testing
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer
lemmatizer = WordNetLemmatizer()
#- end extras
train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y = create_feature_sets_and_labels('pos.txt', 'neg.txt')
# pt A-------------
n_nodes_hl1 = 1500
n_nodes_hl2 = 1500
n_nodes_hl3 = 1500
n_classes = 2
batch_size = 100
hm_epochs = 10
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
hidden_1_layer = {'f_fum': n_nodes_hl1,
'weight': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([len(train_x[0]), n_nodes_hl1])),
'bias': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_nodes_hl1]))}
hidden_2_layer = {'f_fum': n_nodes_hl2,
'weight': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_nodes_hl1, n_nodes_hl2])),
'bias': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_nodes_hl2]))}
hidden_3_layer = {'f_fum': n_nodes_hl3,
'weight': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_nodes_hl2, n_nodes_hl3])),
'bias': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_nodes_hl3]))}
output_layer = {'f_fum': None,
'weight': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_nodes_hl3, n_classes])),
'bias': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes]))}
def nueral_network_model(data):
l1 = tf.add(tf.matmul(data, hidden_1_layer['weight']), hidden_1_layer['bias'])
l1 = tf.nn.relu(l1)
l2 = tf.add(tf.matmul(l1, hidden_2_layer['weight']), hidden_2_layer['bias'])
l2 = tf.nn.relu(l2)
l3 = tf.add(tf.matmul(l2, hidden_3_layer['weight']), hidden_3_layer['bias'])
l3 = tf.nn.relu(l3)
output = tf.matmul(l3, output_layer['weight']) + output_layer['bias']
return output
# pt B--------------
def train_neural_network(x):
prediction = nueral_network_model(x)
cost = tf.reduce_mean( tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits= prediction, labels= y))
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate= 0.001).minimize(cost)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for epoch in range(hm_epochs):
epoch_loss = 0
i = 0
while i < len(train_x):
start = i
end = i+ batch_size
batch_x = np.array(train_x[start: end])
batch_y = np.array(train_y[start: end])
_, c = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict= {x: batch_x, y: batch_y})
epoch_loss += c
i+= batch_size
print('Epoch', epoch+ 1, 'completed out of ', hm_epochs, 'loss:', epoch_loss)
correct= tf.equal(tf.argmax(prediction, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct, 'float'))
print('Accuracy:', accuracy.eval({x:test_x, y:test_y}))
# testing --------------
m_lexicon= get_lexicon()
print('Lexicon length: ',len(m_lexicon))
input_data= "David likes to go out with Kary"
current_words= word_tokenize(input_data.lower())
current_words = [lemmatizer.lemmatize(i) for i in current_words]
features = np.zeros(len(m_lexicon))
for word in current_words:
if word.lower() in m_lexicon:
index_value = m_lexicon.index(word.lower())
features[index_value] +=1
features = np.array(list(features)).reshape(1,-1)
print('features length: ',len(features))
result = sess.run(tf.argmax(prediction.eval(feed_dict={x:features}), 1))
print(prediction.eval(feed_dict={x:features}))
if result[0] == 0:
print('Positive: ', input_data)
elif result[0] == 1:
print('Negative: ', input_data)
train_neural_network(x)
我正在尝试修改上述(sentiment_analysis.py)的LSTM模型。在阅读了TensorFlow和Python中LSTM单元的RNN示例,该示例是针对mnist图像数据集的:
在经过多次尝试后,我终于得到了下面运行的代码(sentiment_demo_lstm.py):
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib import rnn
from create_sentiment_featuresets import create_feature_sets_and_labels
from create_sentiment_featuresets import get_lexicon
import numpy as np
# extras for testing
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer
lemmatizer = WordNetLemmatizer()
#- end extras
train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y = create_feature_sets_and_labels('pos.txt', 'neg.txt')
n_steps= 100
input_vec_size= len(train_x[0])
hm_epochs = 8
n_classes = 2
batch_size = 128
n_hidden = 128
x = tf.placeholder('float', [None, input_vec_size, 1])
y = tf.placeholder('float')
def recurrent_neural_network(x):
layer = {'weights': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden, n_classes])), # hidden_layer, n_classes
'biases': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes]))}
h_layer = {'weights': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1, n_hidden])), # hidden_layer, n_classes
'biases': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden], mean = 1.0))}
x = tf.transpose(x, [1,0,2])
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 1])
x= tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(x, h_layer['weights']) + h_layer['biases'])
x = tf.split(x, input_vec_size, 0)
lstm_cell = rnn.BasicLSTMCell(n_hidden, state_is_tuple=True)
outputs, states = rnn.static_rnn(lstm_cell, x, dtype= tf.float32)
output = tf.matmul(outputs[-1], layer['weights']) + layer['biases']
return output
def train_neural_network(x):
prediction = recurrent_neural_network(x)
cost = tf.reduce_mean( tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits= prediction, labels= y))
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate= 0.001).minimize(cost)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for epoch in range(hm_epochs):
epoch_loss = 0
i = 0
while (i+ batch_size) < len(train_x):
start = i
end = i+ batch_size
batch_x = np.array(train_x[start: end])
batch_y = np.array(train_y[start: end])
batch_x = batch_x.reshape(batch_size ,input_vec_size, 1)
_, c = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict= {x: batch_x, y: batch_y})
epoch_loss += c
i+= batch_size
print('--------Epoch', epoch+ 1, 'completed out of ', hm_epochs, 'loss:', epoch_loss)
correct= tf.equal(tf.argmax(prediction, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct, 'float'))
print('Accuracy:', accuracy.eval({x:np.array(test_x).reshape(-1, input_vec_size, 1), y:test_y}))
# testing --------------
m_lexicon= get_lexicon()
print('Lexicon length: ',len(m_lexicon))
input_data= "Mary does not like pizza" #"he seems to to be healthy today" #"David likes to go out with Kary"
current_words= word_tokenize(input_data.lower())
current_words = [lemmatizer.lemmatize(i) for i in current_words]
features = np.zeros(len(m_lexicon))
for word in current_words:
if word.lower() in m_lexicon:
index_value = m_lexicon.index(word.lower())
features[index_value] +=1
features = np.array(list(features)).reshape(-1, input_vec_size, 1)
print('features length: ',len(features))
result = sess.run(tf.argmax(prediction.eval(feed_dict={x:features}), 1))
print('RESULT: ', result)
print(prediction.eval(feed_dict={x:features}))
if result[0] == 0:
print('Positive: ', input_data)
elif result[0] == 1:
print('Negative: ', input_data)
train_neural_network(x)
输出
print(train_x[0])
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
print(train_y[0])
[0, 1]
len(train_x)= 9596, len(train_x[0]) = 423 意味着train_x是一个9596x423的列表?
In sentiment_demo_lstm, I am not able to understand the following part
x = tf.transpose(x, [1,0,2]) x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 1]) x = tf.split(x, input_vec_size, 0)I have print the following shapes:
x = tf.placeholder('float', [None, input_vec_size, 1]) ==> TensorShape([Dimension(None), Dimension(423), Dimension(1)])) x = tf.transpose(x, [1,0,2]) ==> TensorShape([Dimension(423), Dimension(None), Dimension(1)])) x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 1]) ==> TensorShape([Dimension(None), Dimension(1)])) x = tf.split(x, input_vec_size, 0) ==> ?Here I took the number of hidden layers as 128, does it need to be same as the number of inputs i.e.
len(train_x)= 9596The value 1 in
x = tf.placeholder('float', [None, input_vec_size, 1])and
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 1])is because
train_x[0]is 428x1 ?The following is in order to match the placeholder
batch_x = np.array(train_x[start: end]) ==> (128, 423) batch_x = batch_x.reshape(batch_size ,input_vec_size, 1) ==> (128, 423, 1)x = tf.placeholder('float', [None, input_vec_size, 1])dimensions, right?If I modified the code:
while (i+ batch_size) < len(train_x):as
while i < len(train_x):I get the following error:
Traceback (most recent call last): File "sentiment_demo_lstm.py", line 131, in <module> train_neural_network(x) File "sentiment_demo_lstm.py", line 86, in train_neural_network batch_x = batch_x.reshape(batch_size ,input_vec_size, 1) ValueError: cannot reshape array of size 52452 into shape (128,423,1)
=> 我不能在训练时包括最后124个记录/特征集吗?