2个回答
2
为了避免使用Box2D,您可以将形状定义为多边形并使用polygon.contains(x,y)方法或使用Intersector。
以下是同时使用两者的示例:
以下是同时使用两者的示例:
import com.badlogic.gdx.ApplicationAdapter;
import com.badlogic.gdx.Gdx;
import com.badlogic.gdx.InputProcessor;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.Color;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.GL20;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.glutils.ShapeRenderer;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.Circle;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.Intersector;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.Polygon;
public class Test extends ApplicationAdapter implements InputProcessor{
private ShapeRenderer sr;
private Polygon polya;
private boolean isColliding = false;
private Circle mp;
@Override
public void create () {
//define arc as polygon
// the more points used to define the shape will
// increase both required computation and collision precision
polya = new Polygon();
// create vertices
float section = 15f;
float[] newVerts = new float[200];
for(int i = 0; i < 50; i++){
newVerts[i*2] = (float)Math.sin(i/section); //x 0 to 98 even
newVerts[i*2+1] = (float)Math.cos(i/section); //y 1 to 99 odd
newVerts[199-i*2] = (float)Math.cos(i/section); //x 100 to 108
newVerts[198-i*2] = (float)Math.sin(i/section) + 0.2f; //y 101 to 199
}
polya.setVertices(newVerts);
polya.scale(50);
polya.setOrigin(1, 1);
polya.rotate(60);
//define circle to act as point for checking intersections
mp = new Circle(Gdx.graphics.getWidth()/2,Gdx.graphics.getHeight()/2,4);
// setup batchers
sr = new ShapeRenderer();
sr.setAutoShapeType(true);
Gdx.input.setInputProcessor(this);
}
@Override
public void render () {
Gdx.gl.glClearColor(0f, 0f, 0f, 0f);
Gdx.gl.glClear(GL20.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// check collision with polygon
isColliding = polya.contains(mp.x,mp.y);
//check collision using Intersector
isColliding = Intersector.isPointInPolygon(polya.getTransformedVertices(),0,polya.getVertices().length,mp.x,mp.y);
sr.begin();
sr.setColor(Color.WHITE);
if(isColliding){
sr.setColor(Color.RED);
}
sr.polygon(polya.getTransformedVertices());
sr.circle(mp.x,mp.y,mp.radius);
sr.end();
}
@Override
public void dispose () {
}
@Override
public boolean mouseMoved(int screenX, int screenY) {
int newy = Gdx.graphics.getHeight() - screenY;
polya.setPosition(screenX, newy);
return false;
}
(... removed unused input processor methods for clarity ...)
}
- dfour
2
好的,我运行了你的代码,所以我能看到你做了什么,我发现你用弧线制作了多边形,这很酷哦 :) 但我的问题是,我正在旋转我的弧线,所以我也需要旋转我的多边形,我该怎么做呢? - Sagar Balyan
2您可以使用polya.rotate(degrees)旋转多边形;您可能还需要设置原点,以便它围绕正确的点旋转,polya.setOrigin(originX, originY)。我已将它们添加到示例中。 - dfour
0
在我的情况下,弧正在运动中,我需要计算它的碰撞,因此我随着渲染更新了多边形。基本上,我以与
他是如何工作的?
它以多边形作为参数,用于写入弧形顶点和获取弧形的形状所需的参数。这些参数与您传递给绘制弧形的方法(
然后,它以与
我只是看了一下
使用案例:
最终,您可以检查某个点是否在所需的多边形内:
LibGDX 渲染弧相同的方式获取顶点。
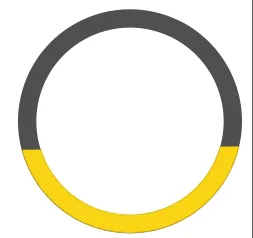
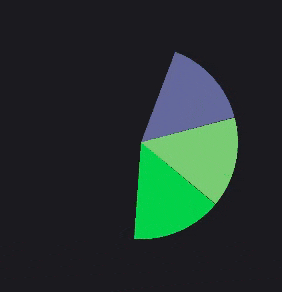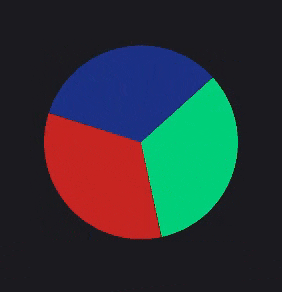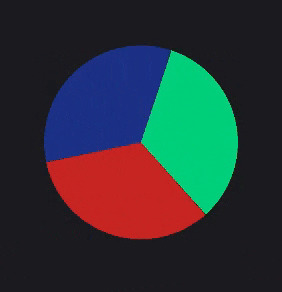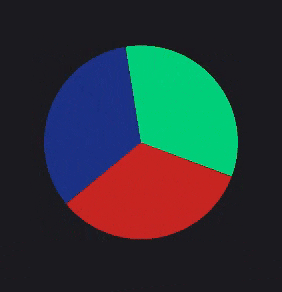
在左侧,您可以看到我绘制的弧线的外观。在右侧,您可以看到如果我必须绘制它们,从相应的弧线形状计算的多边形将会是怎样的。
忽略不同颜色和部分数量,它们是随机生成的。
为了实现这个结果,我编写了这个方法:
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.MathUtils;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.Polygon;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.Vector2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
// ...
public void fillPolygonWithArc(Polygon polygon, float x, float y, float radius, float start, float degrees, int segments) {
float theta = (2 * MathUtils.PI * (degrees / 360.0f)) / segments;
float cos = MathUtils.cos(theta);
float sin = MathUtils.sin(theta);
float cx = radius * MathUtils.cos(start * MathUtils.degreesToRadians);
float cy = radius * MathUtils.sin(start * MathUtils.degreesToRadians);
ArrayList<Vector2> vertices = new ArrayList<>();
vertices.add(new Vector2(x, y));
vertices.add(new Vector2(x + cx, y + cy));
for (int i = 0; i < segments; i++) {
vertices.add(new Vector2(x + cx, y + cy));
float temp = cx;
cx = cos * cx - sin * cy;
cy = sin * temp + cos * cy;
vertices.add(new Vector2(x + cx, y + cy));
}
vertices.add(new Vector2(x + cx, y + cy));
cx = 0;
cy = 0;
vertices.add(new Vector2(x + cx, y + cy));
polygon.setVertices(new float[vertices.size() * 2 + 4]);
for (int i = 0; i < vertices.size(); i++) {
polygon.setVertex(i, vertices.get(i).x, vertices.get(i).y);
}
}
// ...
他是如何工作的?
它以多边形作为参数,用于写入弧形顶点和获取弧形的形状所需的参数。这些参数与您传递给绘制弧形的方法(
shapeRenderer.arc)相同。然后,它以与
LibGDX相同的方式计算弧形的顶点,并用它们填充多边形。我只是看了一下
LibGDX的源代码。使用案例:
fillPolygonWithArc(polygon, getPosition().x, getPosition().y, getRadius(), start, finalStep, getSegments());
shapeRenderer.setColor(color);
shapeRenderer.begin(ShapeRenderer.ShapeType.Filled);
shapeRenderer.arc(getPosition().x, getPosition().y, getRadius(), start, finalStep, getSegments());
shapeRenderer.end();
另外,如果你愿意,你可以绘制一个多边形:
fillPolygonWithArc(polygon, getPosition().x, getPosition().y, getRadius(), start, finalStep, getSegments());
shapeRenderer.setColor(color);
shapeRenderer.begin(ShapeRenderer.ShapeType.Line);
shapeRenderer.polygon(polygon.getVertices());
shapeRenderer.end();
最终,您可以检查某个点是否在所需的多边形内:
polygon.contains(new Vector2(4, 20));
- wowandy
网页内容由stack overflow 提供, 点击上面的可以查看英文原文,
原文链接
原文链接
- 相关问题
- 6 JavaScript 碰撞检测
- 4 间歇性碰撞检测
- 4 Android 2D 圆弧碰撞检测
- 3 优化碰撞检测
- 3 碰撞检测
- 5 花栗鼠碰撞检测
- 4 圆形的碰撞检测
- 3 高效的碰撞检测
- 3 多边形的碰撞检测
- 3 圆弧和线段的碰撞检测