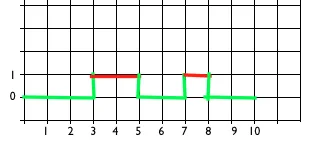
当y值改变时,我该如何更改线条颜色?
4
- The Dude
6
相关链接:https://dev59.com/R2sz5IYBdhLWcg3weHkA - Chris Mueller
@ChrisMueller 我不能完全理解scatter,它看起来像是随机更改颜色? - The Dude
还有相关内容:http://matplotlib.org/examples/pylab_examples/multicolored_line.html - tmdavison
@tom 这看起来很有前途。谢谢。 - The Dude
你期望的结果是什么?对于“y=1,改变线条的颜色”不太清楚。 - SparkAndShine
1@sparkandshine 添加了一个草图以更好地解释。 - The Dude
2个回答
2
受这个答案的启发:
from matplotlib import collections as mc
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
x = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
y = [0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,0]
def getLines(points):
lines = []
lastX, lastY = points[0]
for x,y in points[1:]:
lines.append([(lastX,lastY), (lastX+1,lastY)])
if y!=lastY:
lines.append( [(x, lastY), (x,y)] )
lastX, lastY = (x,y)
return lines
def getColor(point0, point1):
x0,y0 = point0
x1,y1 = point1
return "r" if (y1==y0) and (y1==1) else "g"
points = [(i,j) for i,j in zip(x,y)]
lines = getLines(points)
colors = [getColor(*line) for line in lines]
lc = mc.LineCollection(lines, colors=colors, linewidths=2)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.add_collection(lc)
ax.autoscale()
ax.margins(0.1)
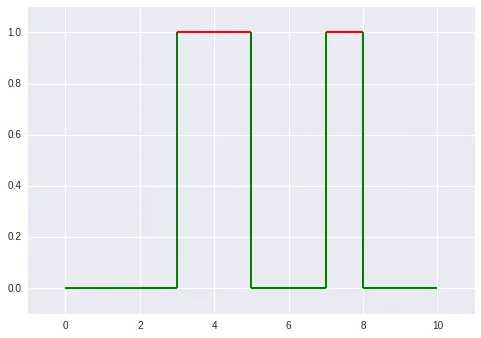
输出:
注意:本文中的“Outputs”已被翻译为“输出”。
- michael_j_ward
0
@michael_j_ward 给出了很好的答案 (+1)。只是为了给出使用普通绘图命令的替代方案,这也是一种可能的解决方法。
首先需要考虑的是,您需要将数据从现有格式进行转换:
x = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
y = [0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0]
你想绘制什么:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
y = [0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0]
nx, ny = [x[0]], [y[0]]
for i in range(0, len(y)-1):
nx.append(x[i])
ny.append(y[i])
if y[i] == 0 and y[i+1] == 1:
nx.append(x[i])
ny.append(y[i+1])
elif y[i] == 1 and y[i+1] == 0:
nx.append(x[i+1])
ny.append(y[i])
nx.append(x[-1])
ny.append(y[-1])
plt.plot(x, y, c='blue', label='Your data')
plt.plot(nx, ny, c='black', linestyle='--', label='New data')
plt.ylim(-1, 2)
plt.yticks([0, 1], ['0', '1'])
plt.legend()
plt.show()
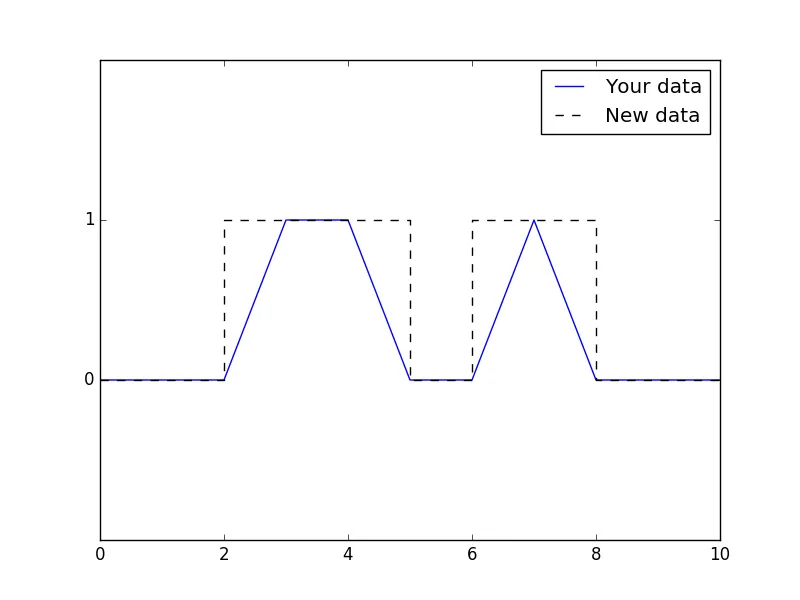
其比较如下:
使用新数据,您只需执行以下操作:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
y = [0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0]
nx, ny = [x[0]], [y[0]]
for i in range(0, len(y)-1):
nx.append(x[i])
ny.append(y[i])
if y[i] == 0 and y[i+1] == 1:
nx.append(x[i])
ny.append(y[i+1])
elif y[i] == 1 and y[i+1] == 0:
nx.append(x[i+1])
ny.append(y[i])
nx.append(x[-1])
ny.append(y[-1])
for i in range(1,len(ny)):
if ny[i] == 1 and ny[i-1] == 1:
choice = 'r'
else:
choice = 'g'
plt.plot([nx[i-1], nx[i]], [ny[i-1], ny[i]], c=choice)
plt.ylim(-1, 2)
plt.yticks([0, 1], ['0', '1'])
plt.grid()
plt.show()
会产生这个结果:
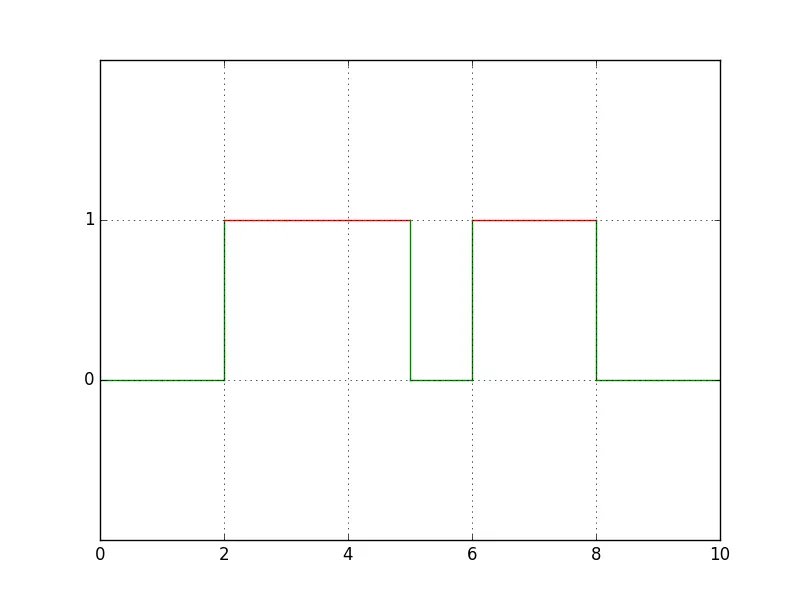
- armatita
网页内容由stack overflow 提供, 点击上面的可以查看英文原文,
原文链接
原文链接