我的问题是如何构建一个简单的程序来检测图像中的数字,我做了一些研究,发现了这个主题 Simple OCR digits 在stack上,我觉得它非常有教育意义,所以我想用它来满足我的需求。
我的训练数据图像如下: 我用的代码来构建数据集是:(我对Abid Rahman的代码进行了一些修改,以便处理我的情况)
结果如下所示:
我的训练数据图像如下: 我用的代码来构建数据集是:(我对Abid Rahman的代码进行了一些修改,以便处理我的情况)
import sys
import numpy as np
import cv2
im = cv2.imread('data_set_trans.png')
im3 = im.copy()
gray = cv2.cvtColor(im,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray,(5,5),0)
thresh = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(blur,255,1,1,11,2)
################# Now finding Contours ###################
contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh,cv2.RETR_LIST,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
samples = np.empty((0,100))
responses = []
keys = [i for i in range(48,58)]
for cnt in contours:
if cv2.contourArea(cnt)>20:
[x,y,w,h] = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
if h>=10:
cv2.rectangle(im,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,0,255),2)
roi = thresh[y:y+h,x:x+w]
roismall = cv2.resize(roi,(10,10))
cv2.imshow('norm',im)
print "Begin wait"
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
key = raw_input('What is the number ?') #cv2.waitKey didnt work for me so i add this line
if key == -1: # (-1 to quit)
sys.exit()
else:
responses.append(int(key))
sample = roismall.reshape((1,100))
samples = np.append(samples,sample,0)
responses = np.array(responses,np.float32)
responses = responses.reshape((responses.size,1))
print "training complete"
np.savetxt('generalsamples.data',samples)
np.savetxt('generalresponses.data',responses)
我使用相同的训练数据图像作为测试部分,以获得最佳结果的准确性,并查看是否正确:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import collections
####### training part ###############
samples = np.loadtxt('generalsamples.data',np.float32)
responses = np.loadtxt('generalresponses.data',np.float32)
responses = responses.reshape((responses.size,1))
model = cv2.KNearest()
model.train(samples,responses)
############################# testing part #########################
im = cv2.imread('one_white_1.png')
out = np.zeros(im.shape,np.uint8)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(im,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
thresh = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(gray,255,1,1,11,2)
contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh,cv2.RETR_LIST,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for cnt in contours:
if cv2.contourArea(cnt)>20:
[x,y,w,h] = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
if h>=10:
cv2.rectangle(im,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,255,0),2)
roi = thresh[y:y+h,x:x+w]
roismall = cv2.resize(roi,(10,10))
roismall = roismall.reshape((1,100))
roismall = np.float32(roismall)
retval, results, neigh_resp, dists = model.find_nearest(roismall, k = 1)
string = str(int((results[0][0])))
cv2.putText(out,string,(x,y+h),1,1,(0,255,0))
cv2.imshow('im',im)
cv2.imshow('out',out)
#cv2.waitKey(0)
raw_input('Tape to exit')
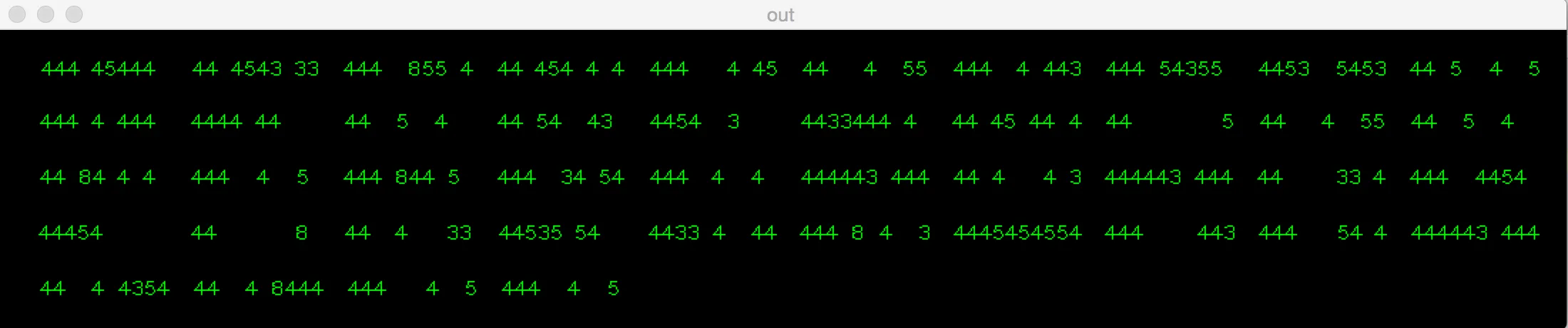
结果如下所示:
结果如下:
正如您所看到的,完全错误。
我不知道我缺少了什么或者我的情况是否更为特殊,无法被这个数字OCR系统处理???
如果有人能够提供任何想法帮助我
我注意到我正在使用Python 2.7,OpenCV 2.4.11,NumPy 1.9和Mac OS 10.10.4
谢谢