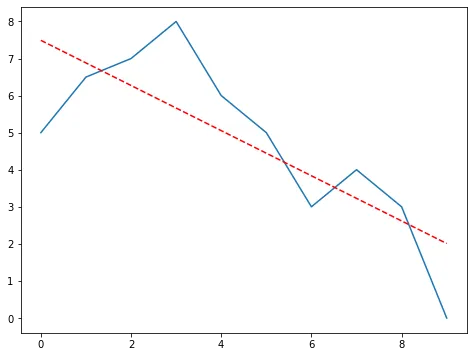
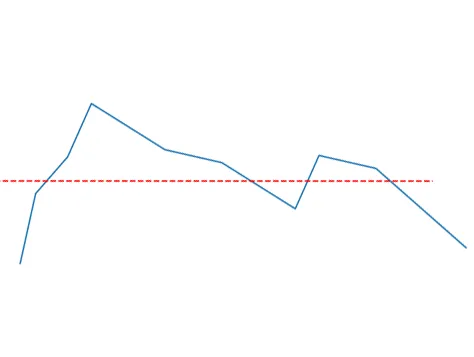
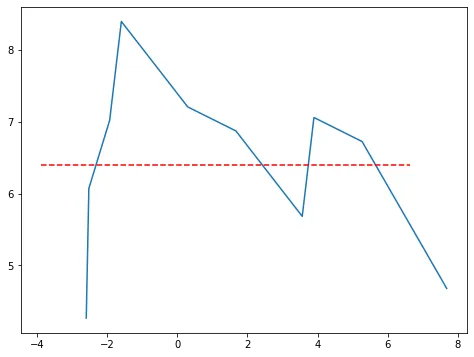
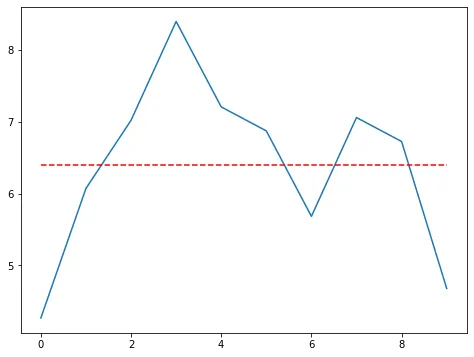
我想将一条折线图水平旋转。目前,我已经有了目标角度,但是我无法旋转图形数组(在图表中的蓝色图形)。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = [5, 6.5, 7, 8, 6, 5, 3, 4, 3, 0]
y = range(len(x))
best_fit_line = np.poly1d(np.polyfit(y, x, 1))(y)
angle = np.rad2deg(np.arctan2(y[-1] - y[0], best_fit_line[-1] - best_fit_line[0]))
print("angle: " + str(angle))
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(x)
plt.plot(best_fit_line, "--", color="r")
plt.show()