我正在使用scipy.spatial中的Delaunay或ConvexHull(来自qhull库)从一组点中获取凸包。现在,我想获取一个在凸包外部的点到凸包上的投影(即来自点外最小距离的凸包上的点)。
这是我目前的代码:
from scipy.spatial import Delaunay, ConvexHull
import numpy as np
hu = np.random.rand(10, 2) ## the set of points to get the hull from
pt = np.array([1.1, 0.5]) ## a point outside
pt2 = np.array([0.4, 0.4]) ## a point inside
hull = ConvexHull(hu) ## get only the convex hull
#hull2 = Delaunay(hu) ## or get the full Delaunay triangulation
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(hu[:,0], hu[:,1], "ro") ## plot all points
#plt.triplot(hu[:,0], hu[:,1], hull2.simplices.copy()) ## plot the Delaunay triangulation
## Plot the convexhull
for simplex in hull.simplices:
plt.plot(hu[simplex,0], hu[simplex,1], "ro-")
## Plot the points inside and outside the convex hull
plt.plot(pt[0], pt[1], "bs")
plt.plot(pt2[0], pt2[1], "bs")
plt.show()
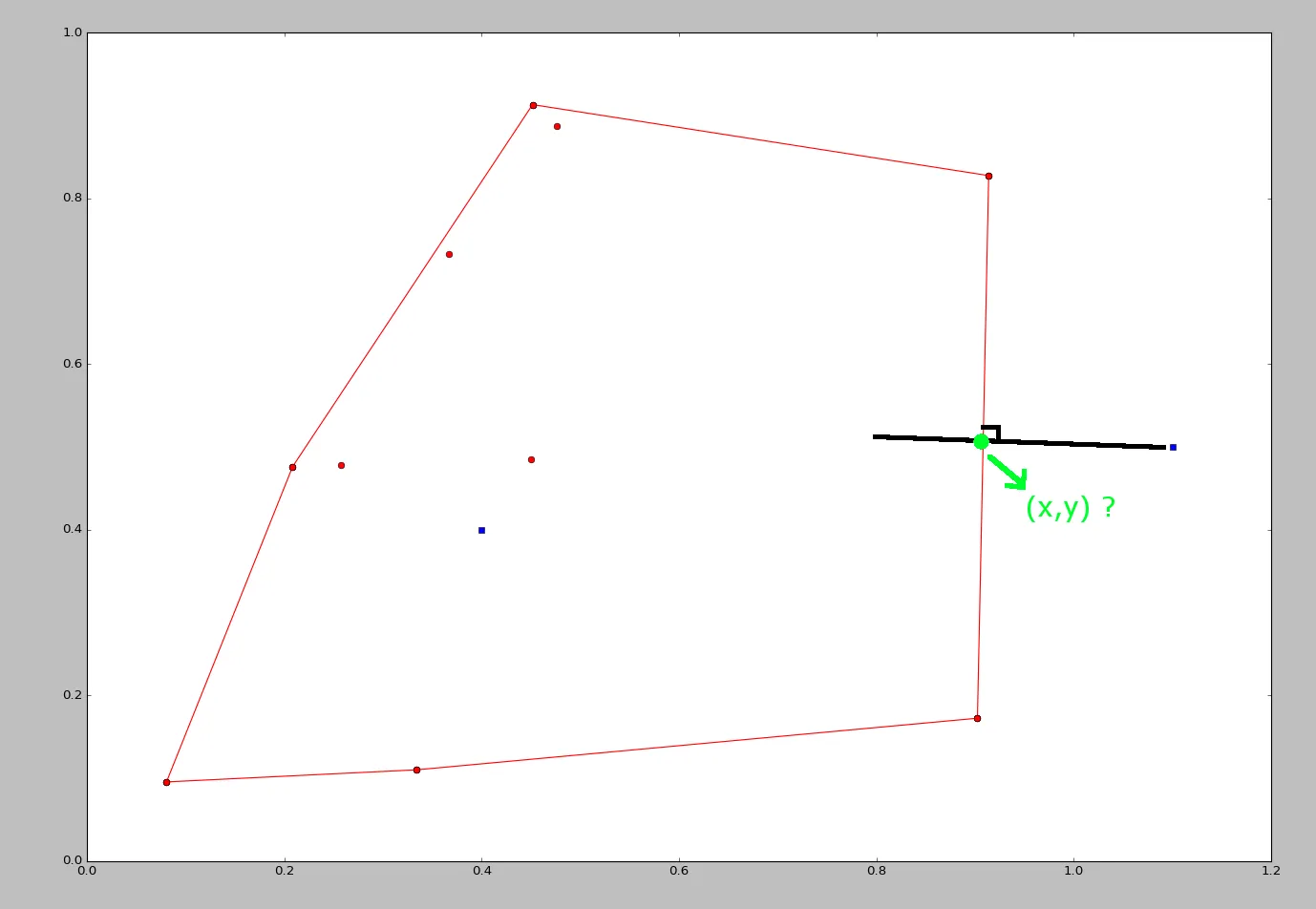
有一张图片可能会更容易,我想获取凸包外的蓝点中绿色坐标的x和y值。这个例子是2D的,但我也需要在更高的维度中应用它。 感谢您的帮助。
编辑:这个问题在这里得到了解决,但我在实现时遇到了麻烦:https://mathoverflow.net/questions/118088/projection-of-a-point-to-a-convex-hull-in-d-dimensions
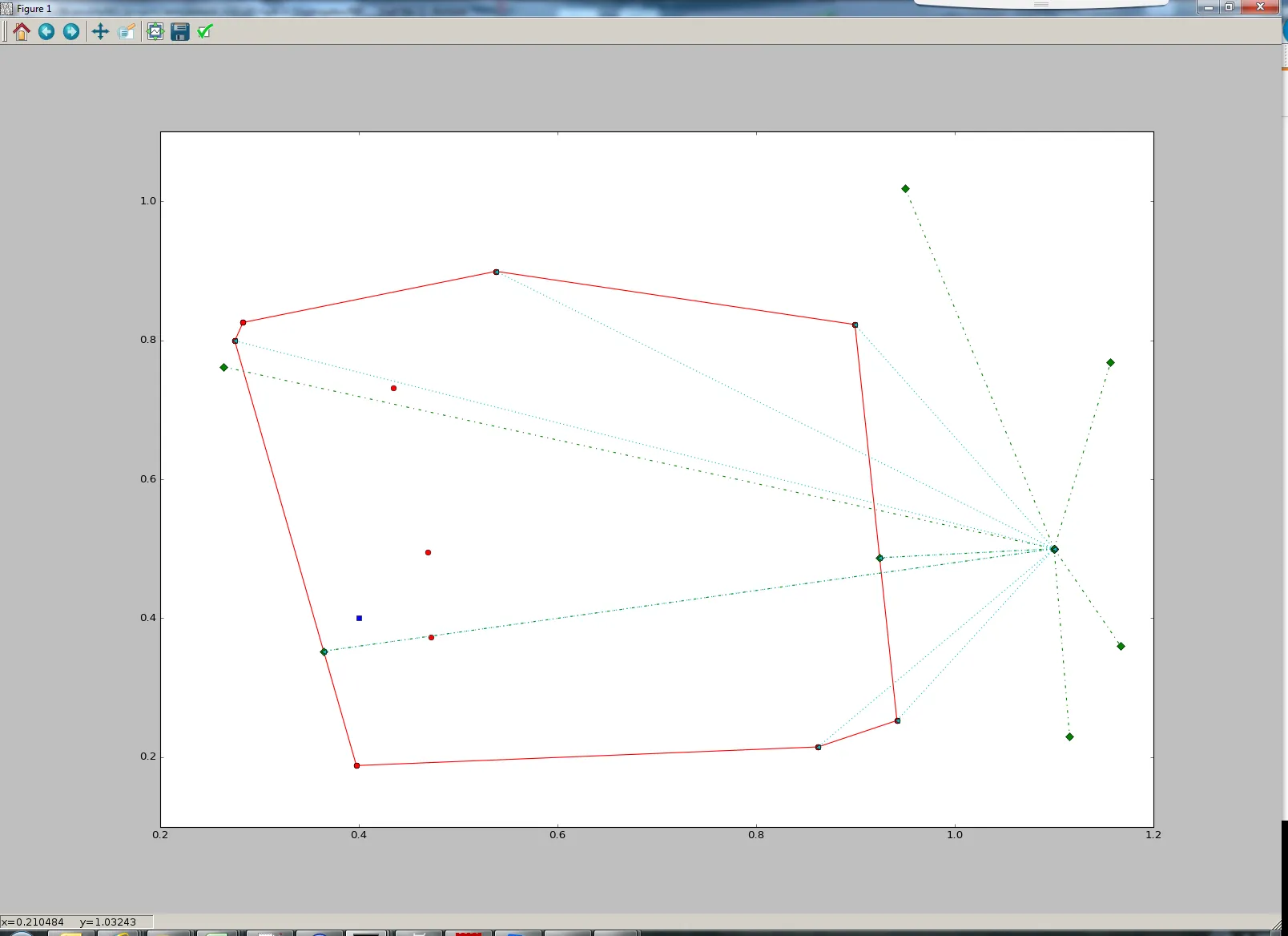
ConvexHull.equations获取凸包的超平面,因此您可以计算点与每个超平面之间的距离。然后,您可以使用这些距离找到最近的超平面。但是,您应该按照自己的方式_定义_坐标,因为您只有法向量。 - 0Tech