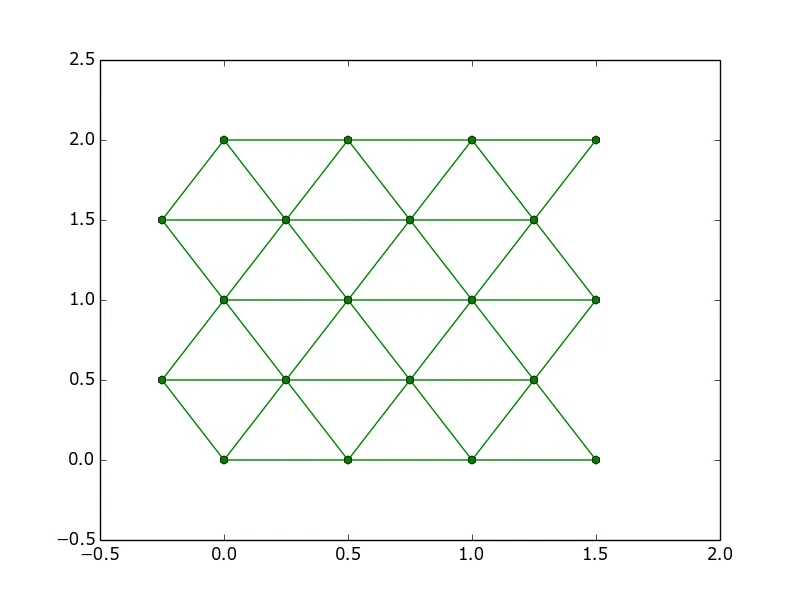
我是Python的新手,我想绘制一个类似于这样的三角形网格:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
r = 0.25
d = 2*r
s = 0
l1 = np.array([[s,0], [s+d,0], [s+2*d,0], [s+3*d,0]])
l2 = np.array([[s-r,d], [s+r,d], [s+r+d,d], [s+r+2*d,d]])
l3 = np.array([[s,2*d], [s+d,2*d], [s+2*d,2*d], [s+3*d,2*d]])
l4 = np.array([[s-r,3*d], [s+r,3*d], [s+r+d,3*d], [s+r+2*d,3*d]])
l5 = np.array([[s,4*d], [s+d,4*d], [s+2*d,4*d], [s+3*d,4*d]])
plt.scatter(*zip(*l1))
plt.scatter(*zip(*l2))
plt.scatter(*zip(*l3))
plt.scatter(*zip(*l4))
plt.scatter(*zip(*l5))
plt.show
我的问题是,我不知道如何连接所有的点。我已经使用plt.plot(*zip(*l1))为所有的l添加了水平线,但是我不知道如何画出“垂直”的之字形线条...有没有人有一个“简单”的解决方案?
非常感谢您提前的帮助!