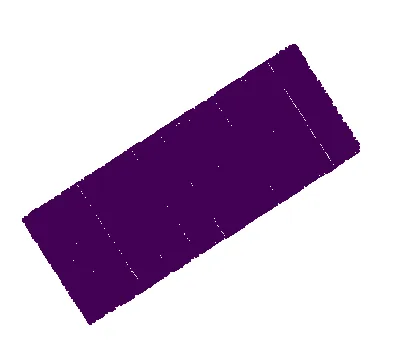
如何使用二进制掩码进行图像遮罩?
8
- Sibh
4
将它们相乘? - Paul Panzer
2这些不是灰度图像。 - Marcin Orlowski
我正在使用带有viridis色图的matplotlib,因此它们不会呈现灰色,但它们不是RGB。 - Sibh
您的图片尺寸不相同。另外,请始终发布不带彩色映射的适当图像;否则会使人们感到困惑,并且还会使演示灰度图像的解决方案变得困难。 - fmw42
3个回答
12
使用
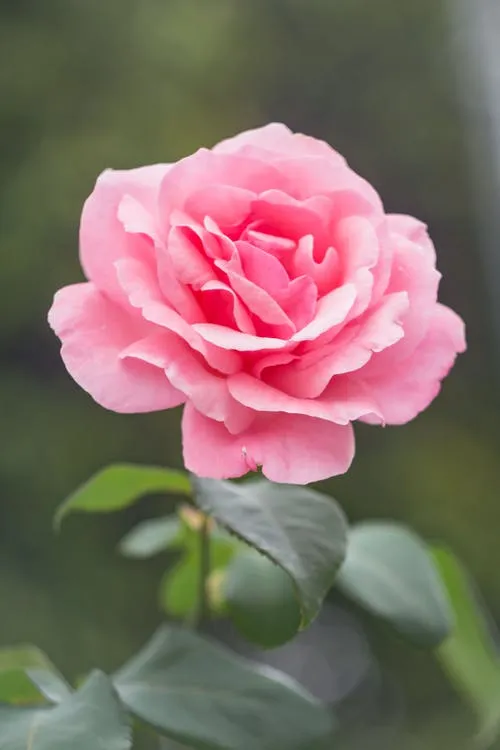
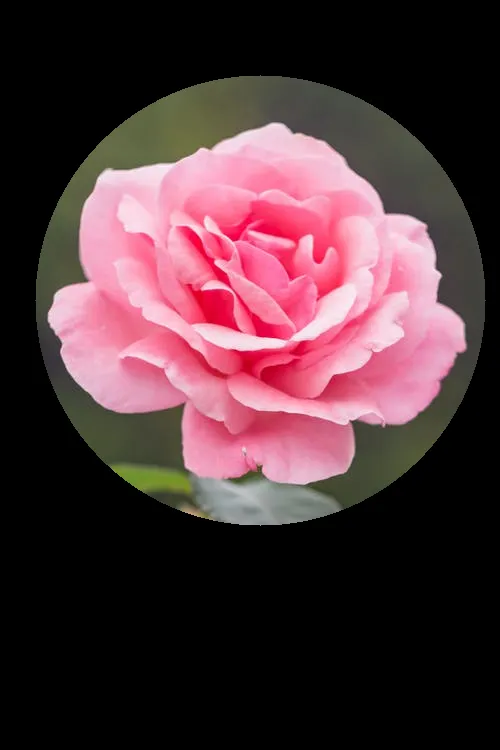
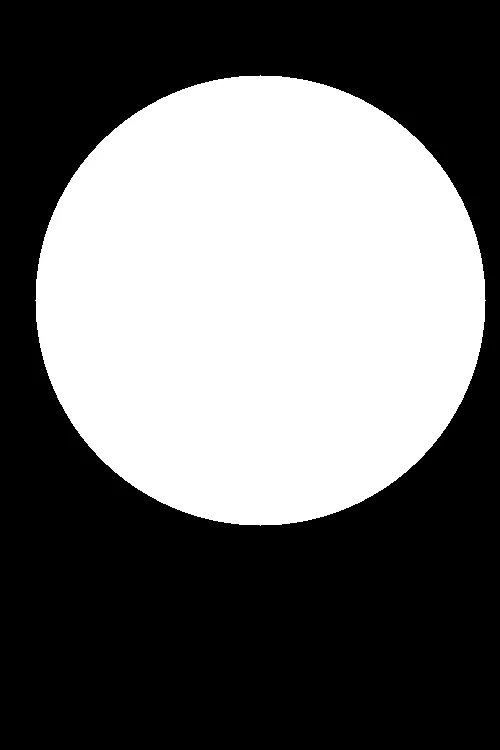
输入图像(左),掩膜(右)
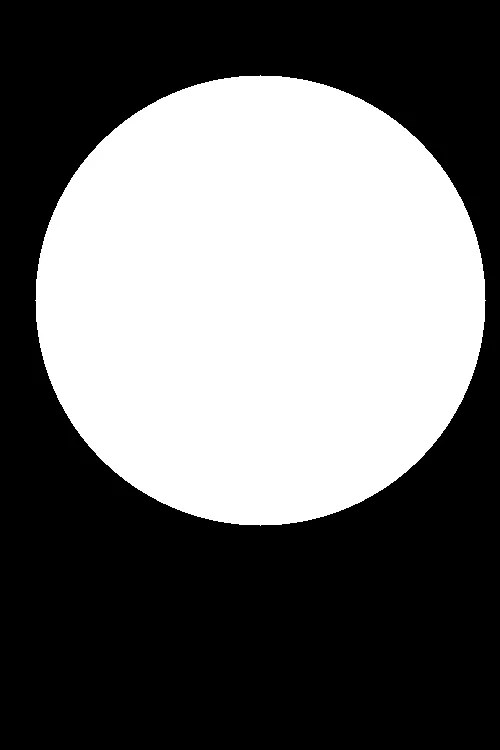 掩模后的结果
掩模后的结果
 代码
代码
cv2.bitwise_and函数对图像进行二值掩膜。掩膜中所有白色像素(值为1)将保留,而黑色像素(值为0)将被忽略。以下是一个例子:输入图像(左),掩膜(右)

 掩模后的结果
掩模后的结果
 代码
代码import cv2
import numpy as np
# Load image, create mask, and draw white circle on mask
image = cv2.imread('1.jpeg')
mask = np.zeros(image.shape, dtype=np.uint8)
mask = cv2.circle(mask, (260, 300), 225, (255,255,255), -1)
# Mask input image with binary mask
result = cv2.bitwise_and(image, mask)
# Color background white
result[mask==0] = 255 # Optional
cv2.imshow('image', image)
cv2.imshow('mask', mask)
cv2.imshow('result', result)
cv2.waitKey()
- nathancy
2
这里有另外两种使用Python Opencv的方法。第一种类似于@nathancy的方法。第二种使用乘法来进行掩膜处理。
我使用了与@nathancy提供的相同的图像。
两种方法的结果相同:
import cv2
import numpy as np
# read image
img = cv2.imread('pink_flower.png')
#mask it - method 1:
# read mask as grayscale in range 0 to 255
mask1 = cv2.imread('pink_flower_mask.png',0)
result1 = img.copy()
result1[mask1 == 0] = 0
result1[mask1 != 0] = img[mask1 != 0]
# mask it - method 2:
# read mask normally, but divide by 255.0, so range is 0 to 1 as float
mask2 = cv2.imread('pink_flower_mask.png') / 255.0
# mask by multiplication, clip to range 0 to 255 and make integer
result2 = (img * mask2).clip(0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
cv2.imshow('image', img)
cv2.imshow('mask1', mask1)
cv2.imshow('masked image1', result1)
cv2.imshow('masked image2', result2)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# save results
cv2.imwrite('pink_flower_masked1.png', result1)
cv2.imwrite('pink_flower_masked2.png', result2)
两种方法的结果相同:
- fmw42
1
其他答案对我没有用。当时,我花了很多时间寻找一个好的掩码函数。这里有两个只用numpy的简单答案。
import numpy as np
arr = np.arange(27).reshape(3,3,3) #3 channel image
mask = np.zeros(shape=(3,3))
mask[1,1] = 1 # binary mask
mask_3d = np.stack((mask,mask,mask),axis=0) #3 channel mask
## Answer 1
# Simply multiply the image array with the mask
masked_arr = arr*mask_3d
## Answer 2
# Use the where function in numpy
masked_arr = np.where(mask_3d==1,arr,mask_3d)
#Both answer gives
print(masked_arr)
array([[[ 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 4., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0.]],
[[ 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 13., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0.]],
[[ 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 22., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0.]]])
- Prefect
网页内容由stack overflow 提供, 点击上面的可以查看英文原文,
原文链接
原文链接