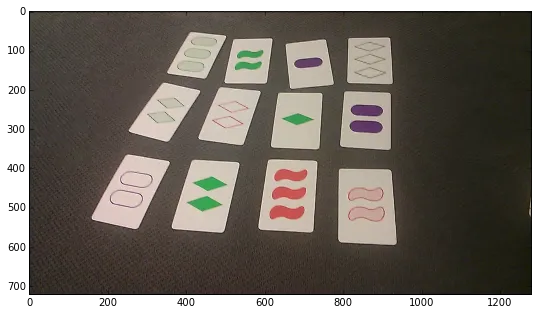
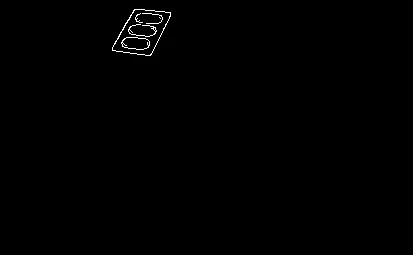
我正在尝试从照片中识别卡片。我已经在理想的照片上实现了我想要的效果,但是现在在应用相同过程时遇到了一些困难,例如光线略有不同等。因此,问题是如何使以下轮廓检测更加稳健。
我需要分享我的代码的大部分内容,以便接受者能够制作感兴趣的图像,但是我的问题仅涉及最后一个块和图像。
我需要分享我的代码的大部分内容,以便接受者能够制作感兴趣的图像,但是我的问题仅涉及最后一个块和图像。
import numpy as np
import cv2
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import ImageGrid
import math
img = cv2.imread('image.png')
img = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.imshow(img)
# Prepocess
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray,(1,1),1000)
flag, thresh = cv2.threshold(blur, 120, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# Find contours
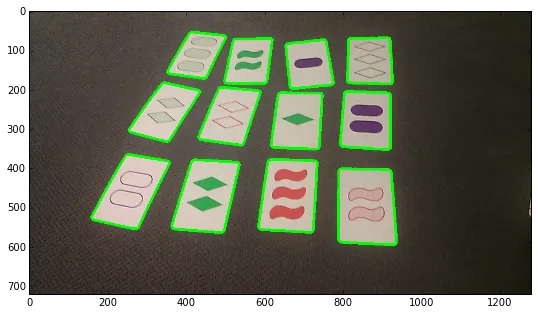
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh,cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
contours = sorted(contours, key=cv2.contourArea,reverse=True)
# Select long perimeters only
perimeters = [cv2.arcLength(contours[i],True) for i in range(len(contours))]
listindex=[i for i in range(15) if perimeters[i]>perimeters[0]/2]
numcards=len(listindex)
# Show image
imgcont = img.copy()
[cv2.drawContours(imgcont, [contours[i]], 0, (0,255,0), 5) for i in listindex]
plt.imshow(imgcont)
#plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (3.0, 3.0)
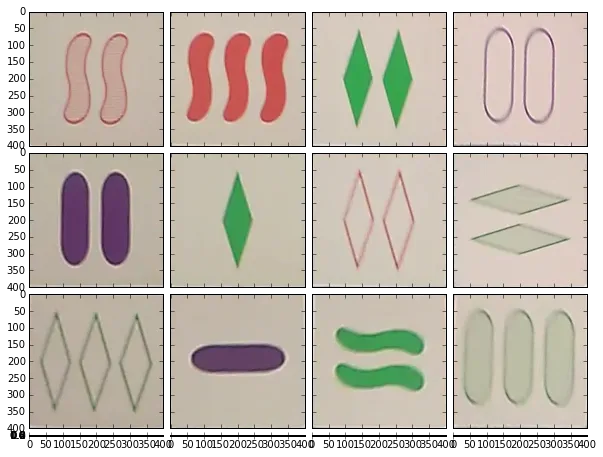
warp = range(numcards)
for i in range(numcards):
card = contours[i]
peri = cv2.arcLength(card,True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(card,0.02*peri,True)
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(contours[i])
r = cv2.cv.BoxPoints(rect)
h = np.array([ [0,0],[399,0],[399,399],[0,399] ],np.float32)
approx = np.array([item for sublist in approx for item in sublist],np.float32)
transform = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(approx,h)
warp[i] = cv2.warpPerspective(img,transform,(400,400))
# Show perspective correction
fig = plt.figure(1, (10,10))
grid = ImageGrid(fig, 111, # similar to subplot(111)
nrows_ncols = (4, 4), # creates 2x2 grid of axes
axes_pad=0.1, # pad between axes in inch.
aspect=True, # do not force aspect='equal'
)
for i in range(numcards):
grid[i].imshow(warp[i]) # The AxesGrid object work as a list of axes.
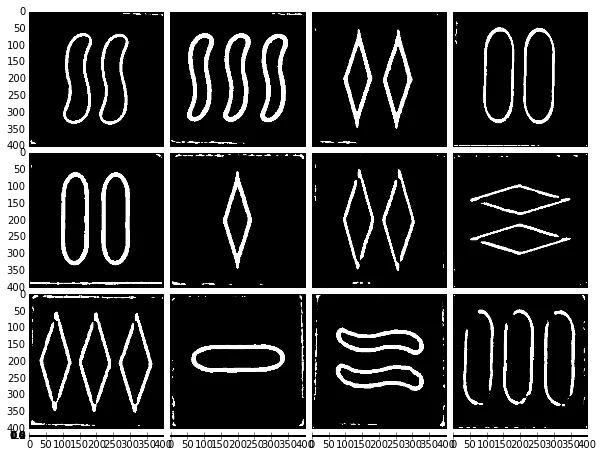
这就是我遇到的问题。我想要检测形状的轮廓。我发现最好的方法是在灰度图像上使用 bilateralFilter 和 AdaptativeThreshold 的组合:
fig = plt.figure(1, (10,10))
grid = ImageGrid(fig, 111, # similar to subplot(111)
nrows_ncols = (4, 4), # creates 2x2 grid of axes
axes_pad=0.1, # pad between axes in inch.
aspect=True, # do not force aspect='equal'
)
for i in range(numcards):
image2 = cv2.bilateralFilter(warp[i].copy(),10,100,100)
grey = cv2.cvtColor(image2,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
grey2 = cv2.cv.AdaptiveThreshold(cv2.cv.fromarray(grey), cv2.cv.fromarray(grey), 255, cv2.cv.CV_ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, cv2.cv.CV_THRESH_BINARY, blockSize=31, param1=6)
grid[i].imshow(grey,cmap=plt.cm.binary)