是否有可能使用声明性 XML 将小部件宽度分配给可用屏幕宽度的一半?
6个回答
285
如果你的小部件是一个按钮:
<LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:weightSum="2"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="somebutton"/>
<TextView android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
</LinearLayout>
我假设您想让您的小部件占用一半,另一个小部件占用另一半。窍门是使用LinearLayout,在两个小部件上设置layout_width="fill_parent",并在两个小部件上设置layout_weight为相同的值。如果有两个小部件,权重相同,LinearLayout将在两个小部件之间分配宽度。
- synic
7
16建议使用android:layout_width="0dp"来设置两个子元素的宽度,避免重复设置大小。 - tomash
2我从来没有明白为什么你要声明layout_width="0dp"。 - Andrew
在后期的 Android 版本中,您也可以使用 <Space /> 作为填充。如果您只想将其用作填充物,则我认为 View 比 TextView 轻一些。根据 Android 文档,layout_width="0dp" 实际上是推荐的方法。 - Muz
1@Andrew:因为这样布局渲染器就不会尝试使用组件的layout_width,而是直接根据权重共享额外的宽度。 - njzk2
顺便提一下,我刚试过在tableview中使用layout_weight,效果也非常好!! - FujiRoyale
显示剩余2条评论
61
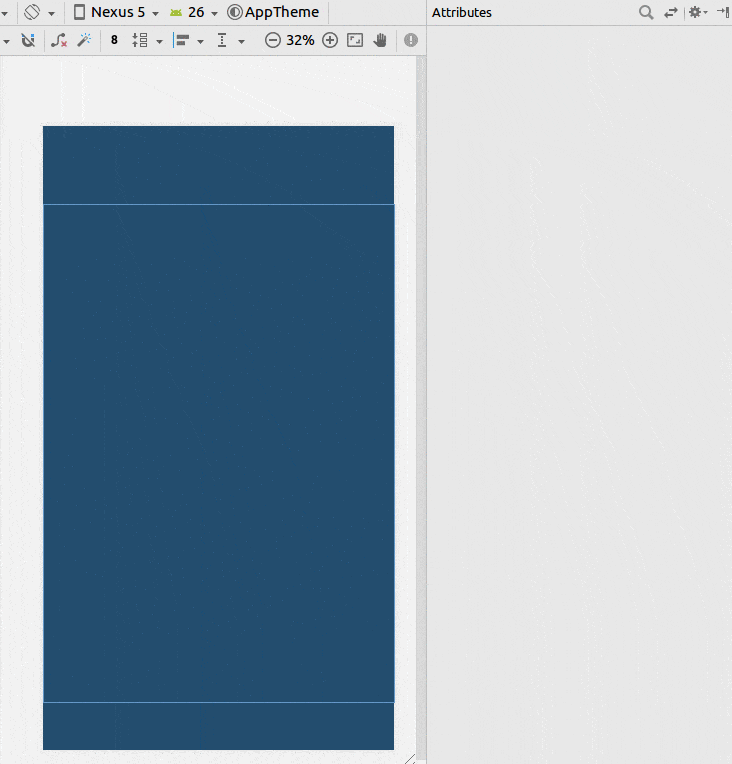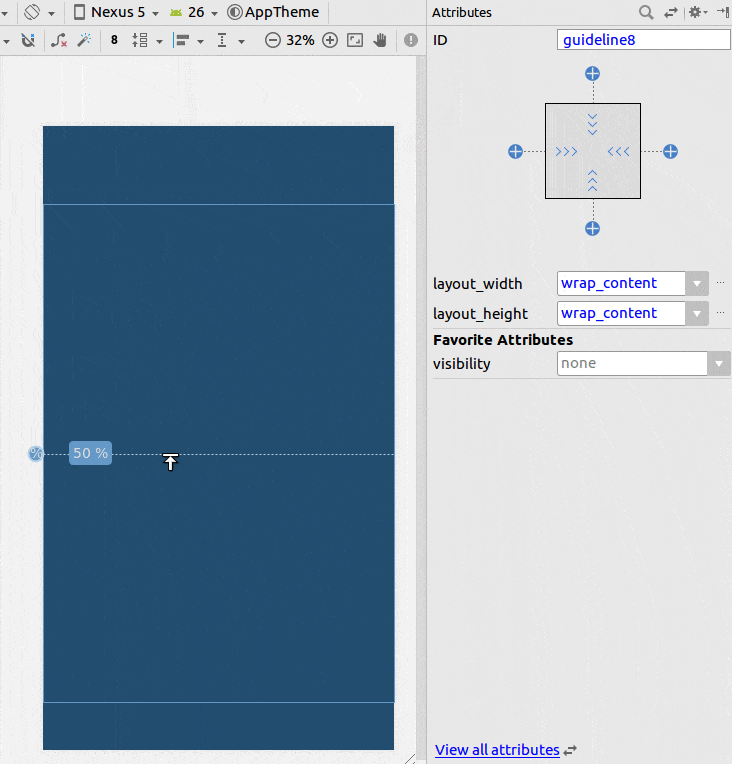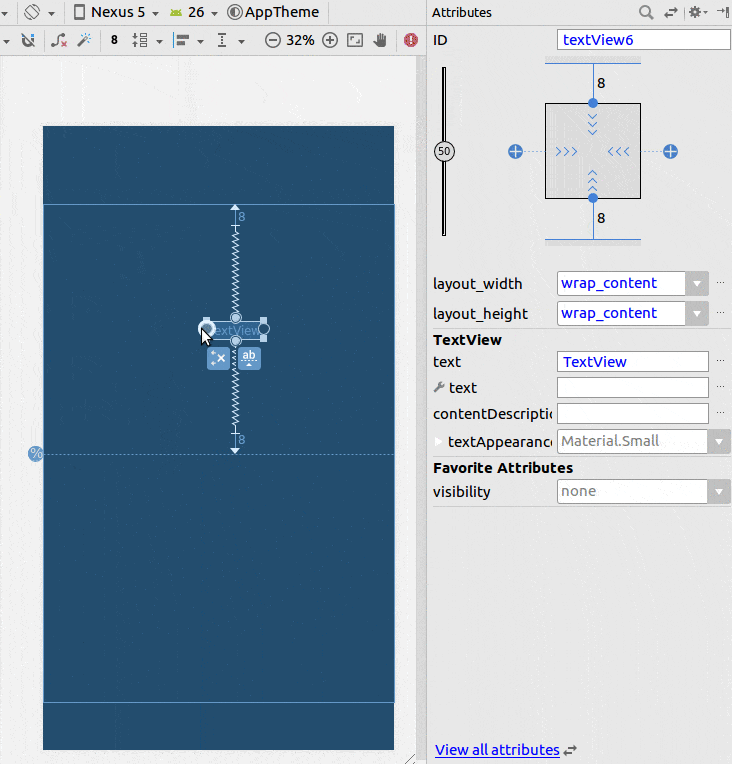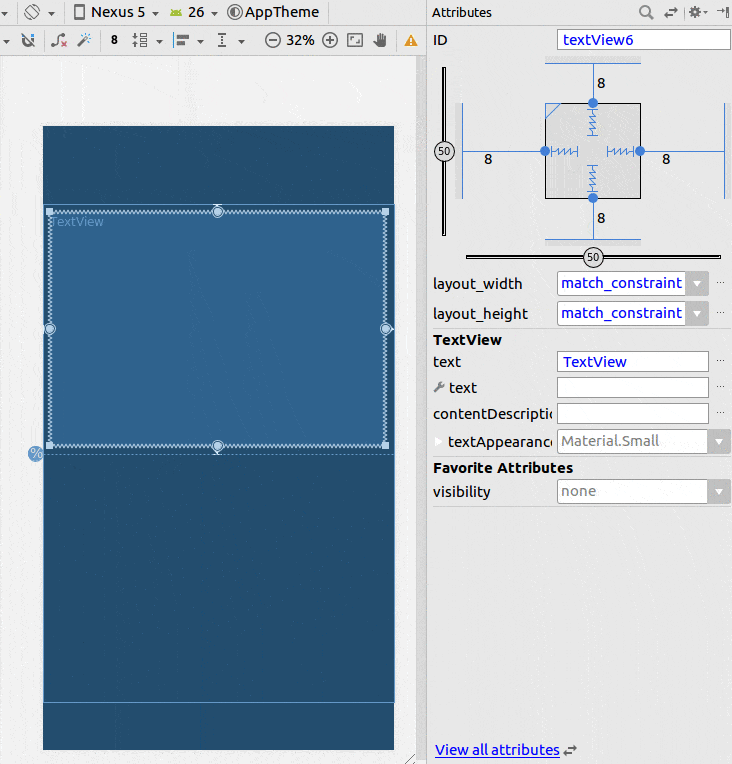
使用约束布局
- 添加一个辅助线
- 将百分比设置为50%
- 将您的视图限制在辅助线和父级上。
如果您无法将其更改为百分比,请参见此答案。
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteX="0dp"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="81dp">
<android.support.constraint.Guideline
android:id="@+id/guideline8"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
app:layout_constraintGuide_percent="0.5"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView6"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="8dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginTop="8dp"
android:text="TextView"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/guideline8"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"/>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
- Suragch
2
3这应该是最佳答案。 - Jean Eric
我是Android的新手,几乎每个关于Spinner的问题的答案都使用RelativeLayout,而我在Android Studio的Legacy部分中看到了它。您的答案简单、快速且非常用户友好。非常感谢您。 - Claudiu Razlet
19
将宽度设置为0dp,以确保其大小与其权重一致。这将确保即使子视图的内容变得更大,它们仍将被限制在正好一半的位置(根据其权重)。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:weightSum="1"
>
<Button
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="click me"
android:layout_weight="0.5"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello World"
android:layout_weight="0.5"/>
</LinearLayout>
- Rajesh Batth
1
1我认为android:layout_width="0dp"是正确的,但将每个权重设置为0.5并将weightSum设置为它们的总和是不必要的。似乎你只需要在两个子视图上有相同的权重。 - Redoman
5
将单个项目置于屏幕中心的另一种方法是,使其填充屏幕的一半:
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<View
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:visibility="invisible" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="2" />
<View
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:visibility="invisible" />
</LinearLayout>
- Denys_Sh
2
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textD_Author"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:text="Author : "
android:textColor="#0404B4"
android:textSize="20sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textD_Tag"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:text="Edition : "
android:textColor="#0404B4"
android:textSize="20sp" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:weightSum="1" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/btbEdit"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="0.5"
android:text="Edit" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnDelete"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="0.5"
android:text="Delete" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
- Shahzad Shameer
1
0
对于 Constraintlayout 中的布局,可以使用以下方法:
app:layout_constraintHeight_percent="x"
用于垂直排列和布局
app:layout_constraintWidth_percent="y"
对于水平排列,其中0<=x,y<=1
- C.F.G
网页内容由stack overflow 提供, 点击上面的可以查看英文原文,
原文链接
原文链接