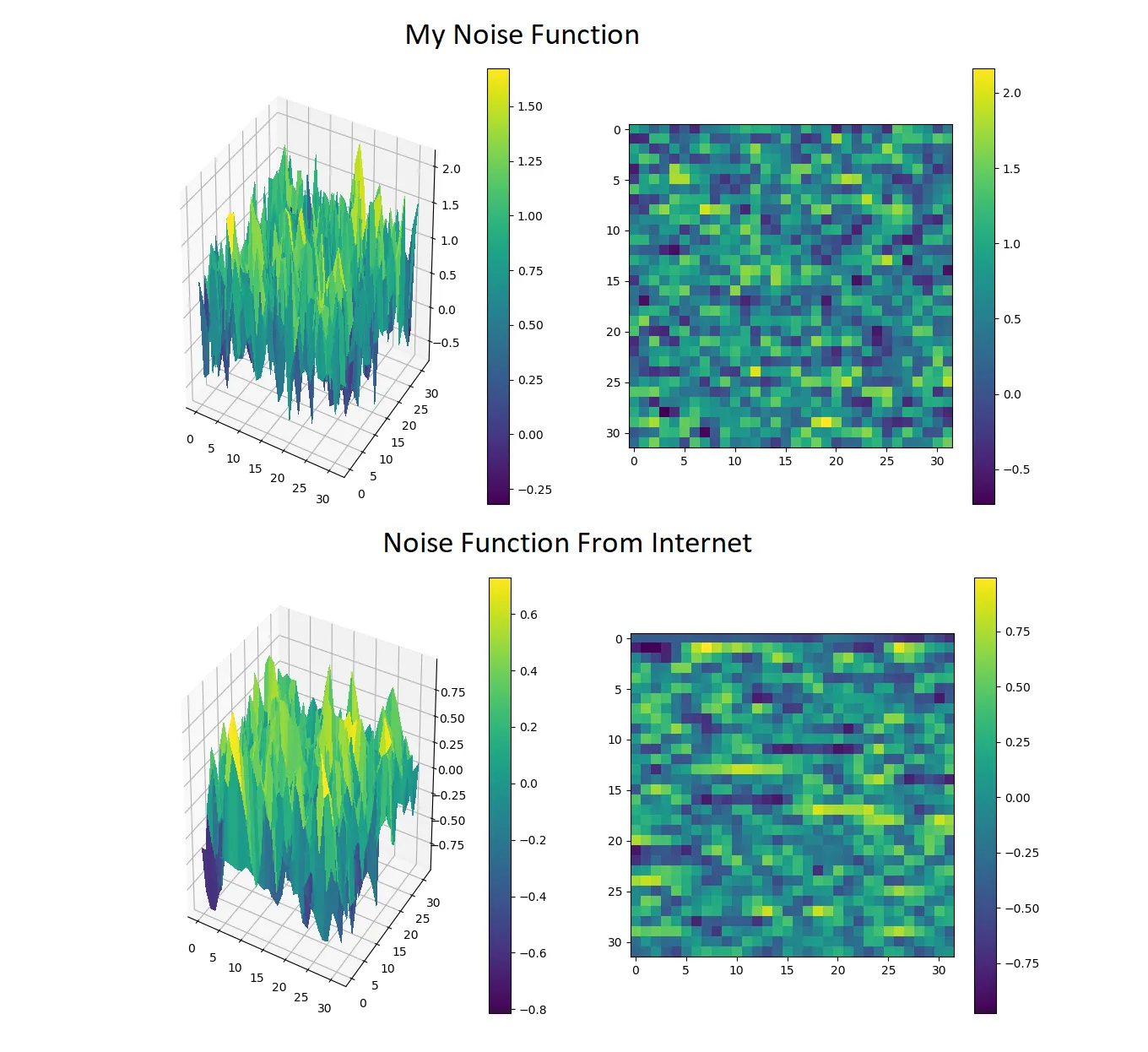
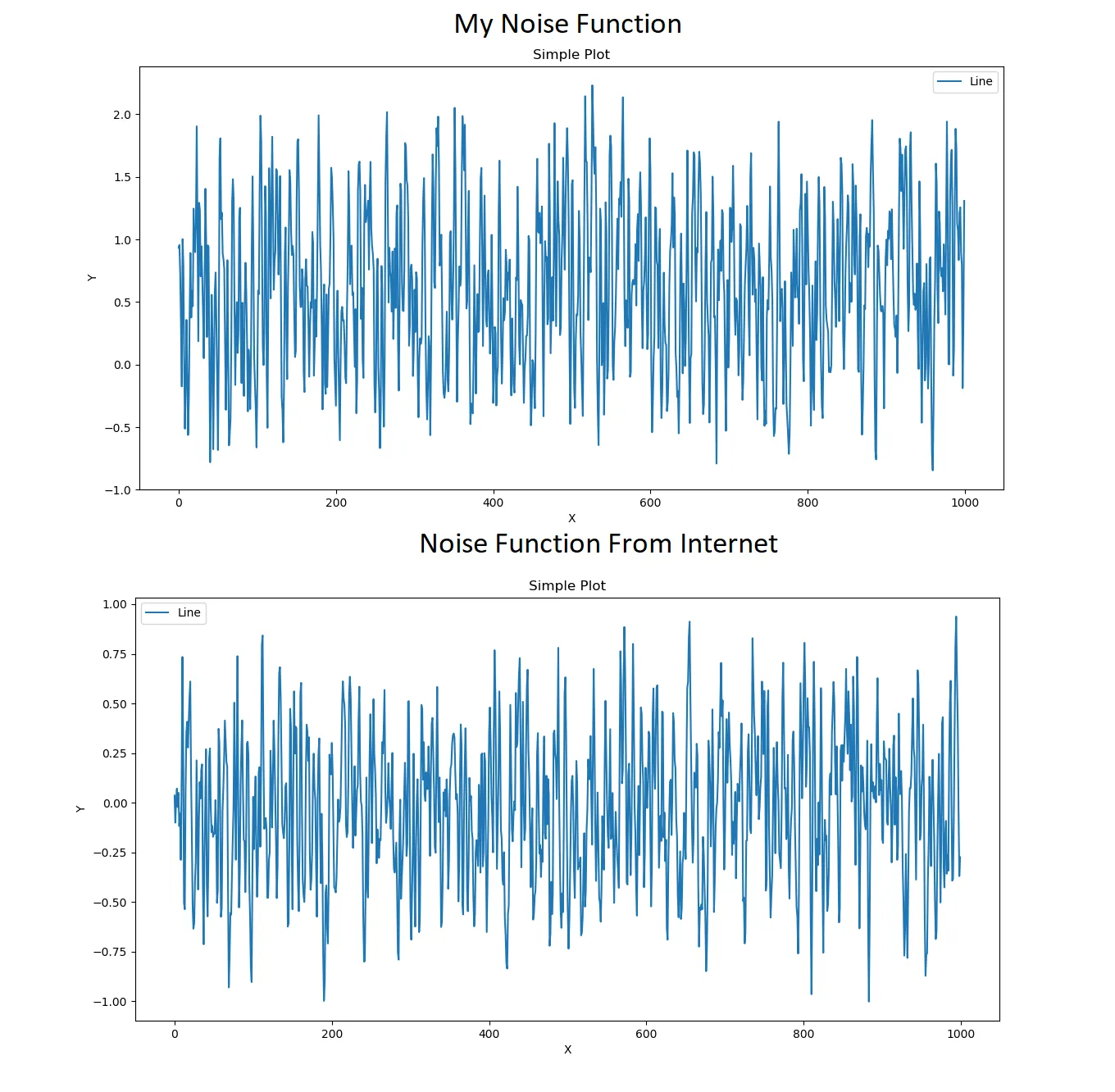
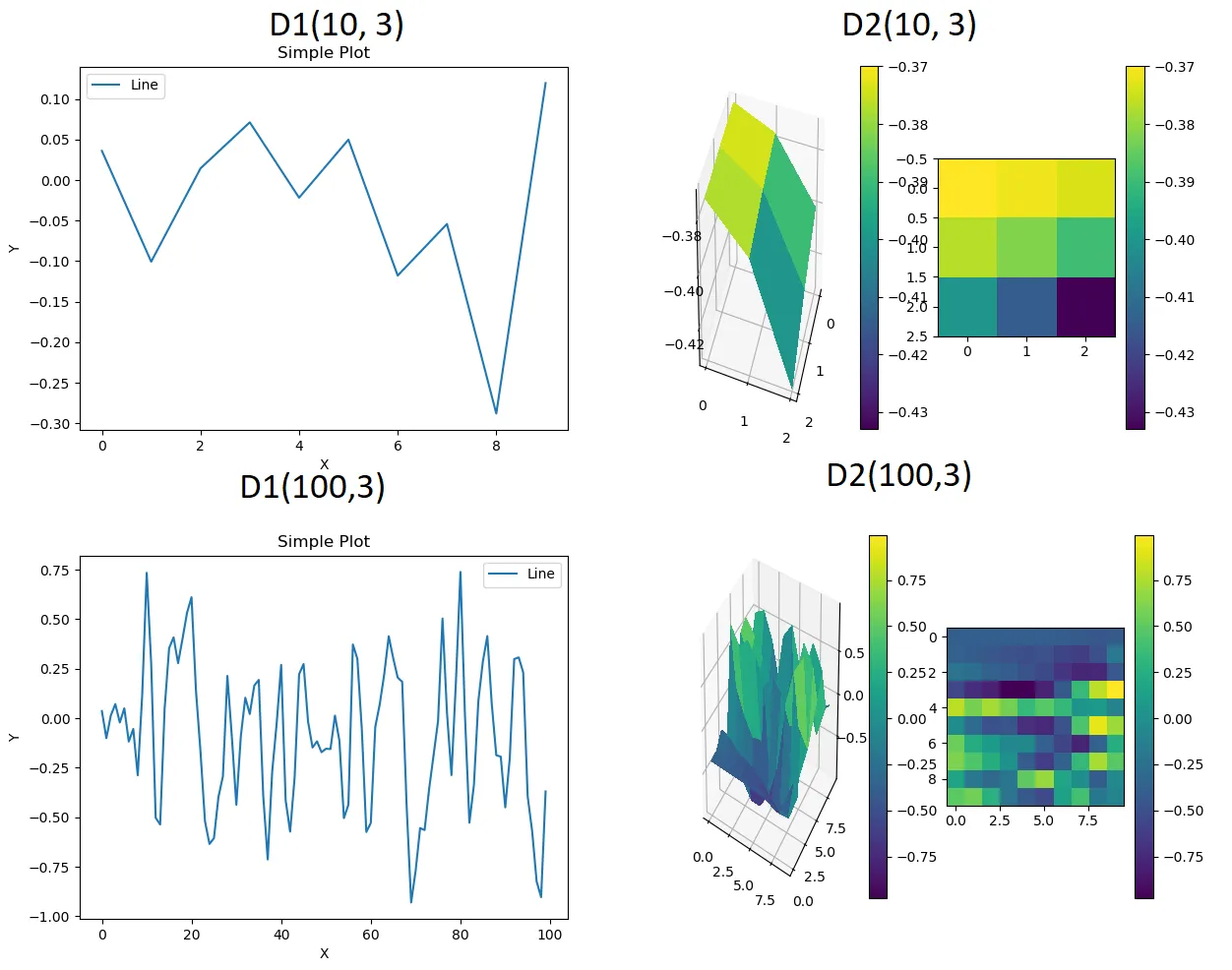
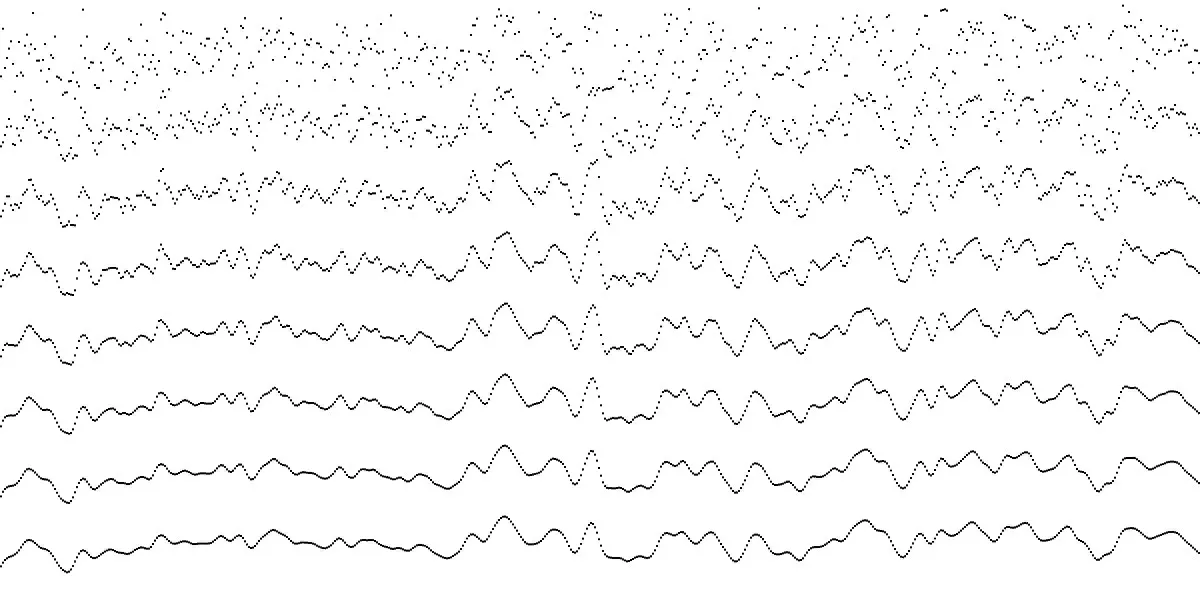
使用Perlin噪声生成器来制作地图的瓦片,噪声太过尖锐。它有许多高低起伏的地形,没有平坦的区域。它们看起来不像山脉、岛屿或湖泊;它们是随机的,有很多峰值。
2D: 二维:
你不需要使用Matplotlib或NumPy;我只是用它们来绘制图形以便更直观地展示结果。
输出不适合用于地图。使用以下方式查看此输出:
def Noise(self, x): # I wrote this noise function but it seems too random
random.seed(x)
number = random.random()
if number < 0.5:
final = 0 - number * 2
elif number > 0.5:
final = number * 2
return final
def Noise(self, x): # I found this noise function on the internet
x = (x<<13) ^ x
return ( 1.0 - ( (x * (x * x * 15731 + 789221) + 1376312589) & 0x7fffffff) / 1073741824.0)
2D: 二维:
def Noise(self, x, y): # I wrote this noise function but it seems too random
n = x + y
random.seed(n)
number = random.random()
if number < 0.5:
final = 0 - number * 2
elif number > 0.5:
final = number * 2
return final
def Noise(self, x, y): # I found this noise function on the internet
n = x + y * 57
n = (n<<13) ^ n
return ( 1.0 - ( (x * (x * x * 15731 + 789221) + 1376312589) & 0x7fffffff) / 1073741824.0)
你不需要使用Matplotlib或NumPy;我只是用它们来绘制图形以便更直观地展示结果。
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # To make graphs
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D # To make 3D graphs
import numpy as np # To make graphs
class D(): # Base of classes D1 and D2
def Cubic_Interpolate(self, v0, v1, v2, v3, x):
P = (v3 - v2) - (v0 - v1)
Q = (v0 - v1) - P
R = v2 - v0
S = v1
return P * x**3 + Q * x**2 + R * x + S
class D1(D):
def __init__(self, lenght, octaves):
self.result = self.Perlin(lenght, octaves)
def Noise(self, x): # I wrote this noise function but it seems too random
random.seed(x)
number = random.random()
if number < 0.5:
final = 0 - number * 2
elif number > 0.5:
final = number * 2
return final
def Noise(self, x): # I found this noise function on the internet
x = (x<<13) ^ x
return ( 1.0 - ( (x * (x * x * 15731 + 789221) + 1376312589) & 0x7fffffff) / 1073741824.0)
def Perlin(self, lenght, octaves):
result = []
for x in range(lenght):
value = 0
for y in range(octaves):
frequency = 2 ** y
amplitude = 0.25 ** y
value += self.Interpolate_Noise(x * frequency) * amplitude
result.append(value)
print(f"{x} / {lenght} ({x/lenght*100:.2f}%): {round(x/lenght*10) * '#'} {(10-round(x/lenght*10)) * ' '}. Remaining {lenght-x}.") # I don't use `os.system('cls')` because it slow down the code.
return result
def Smooth_Noise(self, x):
return self.Noise(x) / 2 + self.Noise(x-1) / 4 + self.Noise(x+1) / 4
def Interpolate_Noise(self, x):
round_x = round(x)
frac_x = x - round_x
v0 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x - 1)
v1 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x)
v2 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x + 1)
v3 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x + 2)
return self.Cubic_Interpolate(v0, v1, v2, v3, frac_x)
def graph(self, *args):
plt.plot(np.array(self.result), '-', label = "Line")
for x in args:
plt.axhline(y=x, color='r', linestyle='-')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.title("Simple Plot")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
class D2(D):
def __init__(self, lenght, octaves = 1):
self.lenght_axes = round(lenght ** 0.5)
self.lenght = self.lenght_axes ** 2
self.result = self.Perlin(self.lenght, octaves)
def Noise(self, x, y): # I wrote this noise function but it seems too random
n = x + y
random.seed(n)
number = random.random()
if number < 0.5:
final = 0 - number * 2
elif number > 0.5:
final = number * 2
return final
def Noise(self, x, y): # I found this noise function on the internet
n = x + y * 57
n = (n<<13) ^ n
return ( 1.0 - ( (x * (x * x * 15731 + 789221) + 1376312589) & 0x7fffffff) / 1073741824.0)
def Smooth_Noise(self, x, y):
corners = (self.Noise(x - 1, y - 1) + self.Noise(x + 1, y - 1) + self.Noise(x - 1, y + 1) + self.Noise(x + 1, y + 1) ) / 16
sides = (self.Noise(x - 1, y) + self.Noise(x + 1, y) + self.Noise(x, y - 1) + self.Noise(x, y + 1) ) / 8
center = self.Noise(x, y) / 4
return corners + sides + center
def Interpolate_Noise(self, x, y):
round_x = round(x)
frac_x = x - round_x
round_y = round(y)
frac_y = y - round_y
v11 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x - 1, round_y - 1)
v12 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x , round_y - 1)
v13 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x + 1, round_y - 1)
v14 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x + 2, round_y - 1)
i1 = self.Cubic_Interpolate(v11, v12, v13, v14, frac_x)
v21 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x - 1, round_y)
v22 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x , round_y)
v23 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x + 1, round_y)
v24 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x + 2, round_y)
i2 = self.Cubic_Interpolate(v21, v22, v23, v24, frac_x)
v31 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x - 1, round_y + 1)
v32 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x , round_y + 1)
v33 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x + 1, round_y + 1)
v34 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x + 2, round_y + 1)
i3 = self.Cubic_Interpolate(v31, v32, v33, v34, frac_x)
v41 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x - 1, round_y + 2)
v42 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x , round_y + 2)
v43 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x + 1, round_y + 2)
v44 = self.Smooth_Noise(round_x + 2, round_y + 2)
i4 = self.Cubic_Interpolate(v41, v42, v43, v44, frac_x)
return self.Cubic_Interpolate(i1, i2, i3, i4, frac_y)
def Perlin(self, lenght, octaves):
result = []
for x in range(lenght):
value = 0
for y in range(octaves):
frequency = 2 ** y
amplitude = 0.25 ** y
value += self.Interpolate_Noise(x * frequency, x * frequency) * amplitude
result.append(value)
print(f"{x} / {lenght} ({x/lenght*100:.2f}%): {round(x/lenght*10) * '#'} {(10-round(x/lenght*10)) * ' '}. Remaining {lenght-x}.") # I don't use `os.system('cls')` because it slow down the code.
return result
def graph(self, color = 'viridis'):
# Other colors: https://matplotlib.org/examples/color/colormaps_reference.html
fig = plt.figure()
Z = np.array(self.result).reshape(self.lenght_axes, self.lenght_axes)
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1, projection='3d')
X = np.arange(self.lenght_axes)
Y = np.arange(self.lenght_axes)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
d3 = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=color, linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
fig.colorbar(d3)
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2)
d2 = ax.imshow(Z, cmap=color, interpolation='none')
fig.colorbar(d2)
plt.show()
输出不适合用于地图。使用以下方式查看此输出:
test = D2(1000, 3)
test.graph()
test = D1(1000, 3)
test.graph()
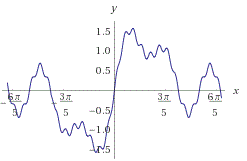
我根据这个伪代码制作了这个。
Pikalek:
即使数值较低,它仍然有峰值,没有曲线或平滑/平坦的线条。