我有一些彩色照片,但照片的照明不规则:图像的一侧比另一侧更亮。
我想通过校正照明来解决这个问题。我认为局部对比度会对我有所帮助,但我不知道如何实现 :(
请您提供一个代码或流程来帮助我吗?
我有一些彩色照片,但照片的照明不规则:图像的一侧比另一侧更亮。
我想通过校正照明来解决这个问题。我认为局部对比度会对我有所帮助,但我不知道如何实现 :(
请您提供一个代码或流程来帮助我吗?
将RGB图像转换为Lab颜色空间(例如,任何带有亮度通道的颜色空间都可以正常工作),然后对L通道应用自适应直方图均衡化。最后将得到的Lab再转换回RGB。
你需要的是OpenCV的CLAHE(对比度受限自适应直方图均衡化)算法。然而,据我所知,它没有文档记录。这里有一个Python示例。你可以在《图形宝石IV》第474-485页中了解CLAHE。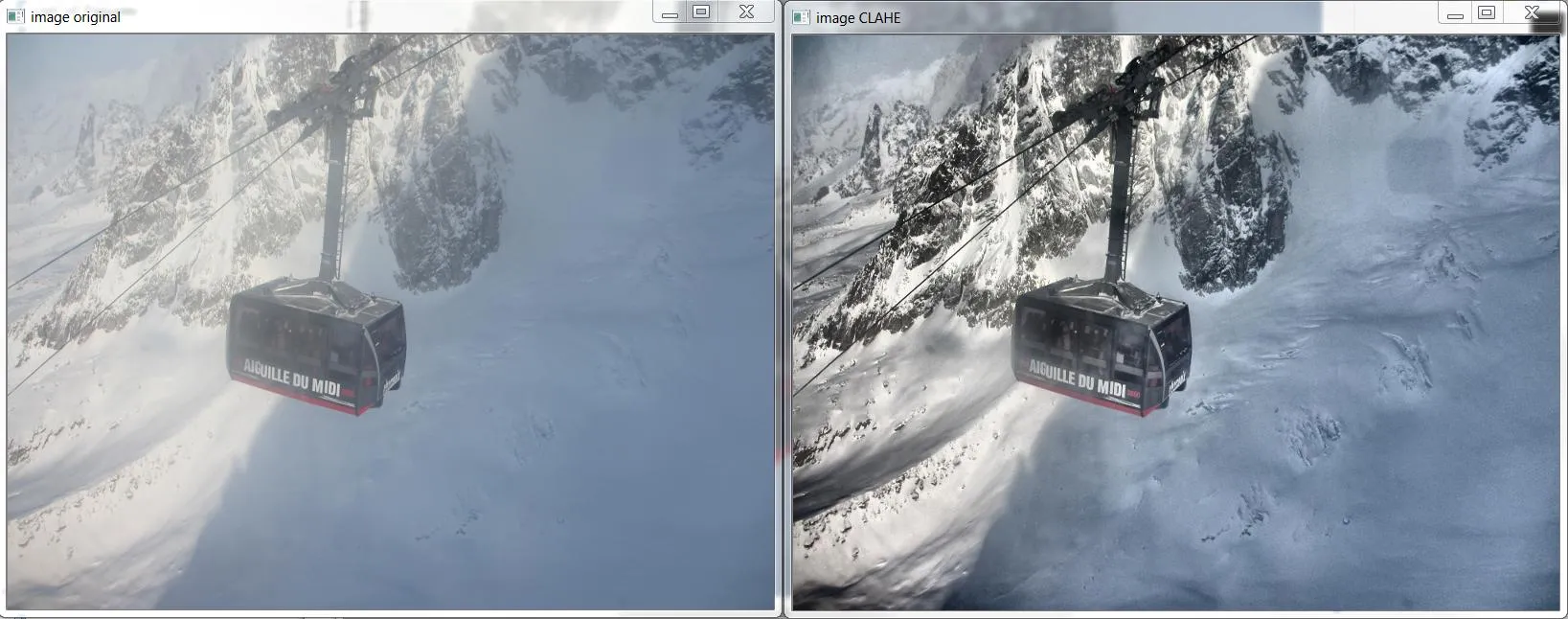 以下是生成上述图像的C++代码,基于http://answers.opencv.org/question/12024/use-of-clahe/,但针对彩色图像进行了扩展。
以下是生成上述图像的C++代码,基于http://answers.opencv.org/question/12024/use-of-clahe/,但针对彩色图像进行了扩展。#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <vector> // std::vector
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// READ RGB color image and convert it to Lab
cv::Mat bgr_image = cv::imread("image.png");
cv::Mat lab_image;
cv::cvtColor(bgr_image, lab_image, CV_BGR2Lab);
// Extract the L channel
std::vector<cv::Mat> lab_planes(3);
cv::split(lab_image, lab_planes); // now we have the L image in lab_planes[0]
// apply the CLAHE algorithm to the L channel
cv::Ptr<cv::CLAHE> clahe = cv::createCLAHE();
clahe->setClipLimit(4);
cv::Mat dst;
clahe->apply(lab_planes[0], dst);
// Merge the the color planes back into an Lab image
dst.copyTo(lab_planes[0]);
cv::merge(lab_planes, lab_image);
// convert back to RGB
cv::Mat image_clahe;
cv::cvtColor(lab_image, image_clahe, CV_Lab2BGR);
// display the results (you might also want to see lab_planes[0] before and after).
cv::imshow("image original", bgr_image);
cv::imshow("image CLAHE", image_clahe);
cv::waitKey();
}
Bull提供的答案是我目前为止发现的最好的答案,我觉得它非常有用。以下代码适用于Python用户。
细节:
(注意: 以下代码已更新以包含rayryeng在评论中提出的指针)
代码:
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('flower.jpg', 1)
# converting to LAB color space
lab = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2LAB)
将CLAHE应用于L通道(亮度),即LAB中的第一个通道,表示为lab [:,:,0]。可以随意尝试不同的值,以获得clipLimit和tileGridSize:
clahe = cv2.createCLAHE(clipLimit=2.0, tileGridSize=(8,8))
lab[:,:,0] = clahe.apply(lab[:,:,0])
# Converting image from LAB Color model to BGR color space
enhanced_img = cv2.cvtColor(lab, cv2.COLOR_LAB2BGR)
# Stacking the original image with the enhanced image
result = np.hstack((img, enhanced_img))
cv2.imshow('Result', result)
结果:
原始图像(左)和增强图像(右)并排放置。
cv2.split。创建CLAHE对象后,只需执行lab[...,0] = clahe.apply(lab[...,0])即可。你还可以删除cv2.merge。 - rayryeng基于Bull编写的优秀C++示例,我能够为Android编写此方法。
我用"Core.extractChannel"替换了"Core.split"。这避免了一个已知的内存泄漏问题。
public void applyCLAHE(Mat srcArry, Mat dstArry) {
//Function that applies the CLAHE algorithm to "dstArry".
if (srcArry.channels() >= 3) {
// READ RGB color image and convert it to Lab
Mat channel = new Mat();
Imgproc.cvtColor(srcArry, dstArry, Imgproc.COLOR_BGR2Lab);
// Extract the L channel
Core.extractChannel(dstArry, channel, 0);
// apply the CLAHE algorithm to the L channel
CLAHE clahe = Imgproc.createCLAHE();
clahe.setClipLimit(4);
clahe.apply(channel, channel);
// Merge the the color planes back into an Lab image
Core.insertChannel(channel, dstArry, 0);
// convert back to RGB
Imgproc.cvtColor(dstArry, dstArry, Imgproc.COLOR_Lab2BGR);
// Temporary Mat not reused, so release from memory.
channel.release();
}
}
并这样调用:
public Mat onCameraFrame(CvCameraViewFrame inputFrame){
Mat col = inputFrame.rgba();
applyCLAHE(col, col);//Apply the CLAHE algorithm to input color image.
return col;
}
from skimage import exposure
img_adapteq = exposure.equalize_adapthist(img, clip_limit=0.03)
我已经在这个通道上应用了CLAHE,效果很好。
计算图像的感知亮度通道
a -> 我将图像转换为HSV颜色空间,并将CLAHE应用的感知亮度通道添加到图像的V通道中。
b -> 我将图像转换为LAB颜色空间。并将CLAHE应用的感知亮度通道添加到图像的L通道中。
然后再将图像转换为BGR格式。
我的步骤的Python代码:
import cv2
import numpy as np
original = cv2.imread("/content/rqq0M.jpg")
def get_perceive_brightness(img):
float_img = np.float64(img) # unit8 will make overflow
b, g, r = cv2.split(float_img)
float_brightness = np.sqrt(
(0.241 * (r ** 2)) + (0.691 * (g ** 2)) + (0.068 * (b ** 2)))
brightness_channel = np.uint8(np.absolute(float_brightness))
return brightness_channel
perceived_brightness_channel = get_perceive_brightness(original)
clahe = cv2.createCLAHE(clipLimit=3.0, tileGridSize=(8,8))
clahe_applied_perceived_channel = clahe.apply(perceived_brightness_channel)
def hsv_equalizer(img, new_channel):
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(original, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
h,s,v = cv2.split(hsv)
merged_hsv = cv2.merge((h, s, new_channel))
bgr_img = cv2.cvtColor(merged_hsv, cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR)
return bgr_img
def lab_equalizer(img, new_channel):
lab = cv2.cvtColor(original, cv2.COLOR_BGR2LAB)
l,a,b = cv2.split(lab)
merged_lab = cv2.merge((new_channel,a,b))
bgr_img = cv2.cvtColor(merged_hsv, cv2.COLOR_LAB2BGR)
return bgr_img
hsv_equalized_img = hsv_equalizer(original,clahe_applied_perceived_channel)
lab_equalized_img = lab_equalizer(original,clahe_applied_perceived_channel)
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
cout<<"Usage: ./executable input_image output_image \n";
if(argc!=3)
{
return 0;
}
int filterFactor = 1;
Mat my_img = imread(argv[1]);
Mat orig_img = my_img.clone();
imshow("original",my_img);
Mat simg;
cvtColor(my_img, simg, CV_BGR2GRAY);
long int N = simg.rows*simg.cols;
int histo_b[256];
int histo_g[256];
int histo_r[256];
for(int i=0; i<256; i++){
histo_b[i] = 0;
histo_g[i] = 0;
histo_r[i] = 0;
}
Vec3b intensity;
for(int i=0; i<simg.rows; i++){
for(int j=0; j<simg.cols; j++){
intensity = my_img.at<Vec3b>(i,j);
histo_b[intensity.val[0]] = histo_b[intensity.val[0]] + 1;
histo_g[intensity.val[1]] = histo_g[intensity.val[1]] + 1;
histo_r[intensity.val[2]] = histo_r[intensity.val[2]] + 1;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i<256; i++){
histo_b[i] = histo_b[i] + filterFactor * histo_b[i-1];
histo_g[i] = histo_g[i] + filterFactor * histo_g[i-1];
histo_r[i] = histo_r[i] + filterFactor * histo_r[i-1];
}
int vmin_b=0;
int vmin_g=0;
int vmin_r=0;
int s1 = 3;
int s2 = 3;
while(histo_b[vmin_b+1] <= N*s1/100){
vmin_b = vmin_b +1;
}
while(histo_g[vmin_g+1] <= N*s1/100){
vmin_g = vmin_g +1;
}
while(histo_r[vmin_r+1] <= N*s1/100){
vmin_r = vmin_r +1;
}
int vmax_b = 255-1;
int vmax_g = 255-1;
int vmax_r = 255-1;
while(histo_b[vmax_b-1]>(N-((N/100)*s2)))
{
vmax_b = vmax_b-1;
}
if(vmax_b < 255-1){
vmax_b = vmax_b+1;
}
while(histo_g[vmax_g-1]>(N-((N/100)*s2)))
{
vmax_g = vmax_g-1;
}
if(vmax_g < 255-1){
vmax_g = vmax_g+1;
}
while(histo_r[vmax_r-1]>(N-((N/100)*s2)))
{
vmax_r = vmax_r-1;
}
if(vmax_r < 255-1){
vmax_r = vmax_r+1;
}
for(int i=0; i<simg.rows; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<simg.cols; j++)
{
intensity = my_img.at<Vec3b>(i,j);
if(intensity.val[0]<vmin_b){
intensity.val[0] = vmin_b;
}
if(intensity.val[0]>vmax_b){
intensity.val[0]=vmax_b;
}
if(intensity.val[1]<vmin_g){
intensity.val[1] = vmin_g;
}
if(intensity.val[1]>vmax_g){
intensity.val[1]=vmax_g;
}
if(intensity.val[2]<vmin_r){
intensity.val[2] = vmin_r;
}
if(intensity.val[2]>vmax_r){
intensity.val[2]=vmax_r;
}
my_img.at<Vec3b>(i,j) = intensity;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<simg.rows; i++){
for(int j=0; j<simg.cols; j++){
intensity = my_img.at<Vec3b>(i,j);
intensity.val[0] = (intensity.val[0] - vmin_b)*255/(vmax_b-vmin_b);
intensity.val[1] = (intensity.val[1] - vmin_g)*255/(vmax_g-vmin_g);
intensity.val[2] = (intensity.val[2] - vmin_r)*255/(vmax_r-vmin_r);
my_img.at<Vec3b>(i,j) = intensity;
}
}
// sharpen image using "unsharp mask" algorithm
Mat blurred; double sigma = 1, threshold = 5, amount = 1;
GaussianBlur(my_img, blurred, Size(), sigma, sigma);
Mat lowContrastMask = abs(my_img - blurred) < threshold;
Mat sharpened = my_img*(1+amount) + blurred*(-amount);
my_img.copyTo(sharpened, lowContrastMask);
imshow("New Image",sharpened);
waitKey(0);
Mat comp_img;
hconcat(orig_img, sharpened, comp_img);
imwrite(argv[2], comp_img);
}
请点击这里获取更多详细信息。