当我在Python中进行数学计算时,我们使用哪个库?例如:
>>> 2**0.5
1.4142135623730951
我该如何找到被使用的源代码?这只是math.pow()函数吗?不幸的是,inspect.getsource(pow)返回了一种错误。
在Github上搜索将其缩小为13个可能的文件。而我并不完全理解cPython是如何构建的。
/*[clinic input]
math.pow
x: double
y: double
/
Return x**y (x to the power of y).
[clinic start generated code]*/
static PyObject *
math_pow_impl(PyObject *module, double x, double y)
/*[clinic end generated code: output=fff93e65abccd6b0 input=c26f1f6075088bfd]*/
{
double r;
int odd_y;
/* deal directly with IEEE specials, to cope with problems on various
platforms whose semantics don't exactly match C99 */
r = 0.; /* silence compiler warning */
if (!Py_IS_FINITE(x) || !Py_IS_FINITE(y)) {
errno = 0;
if (Py_IS_NAN(x))
r = y == 0. ? 1. : x; /* NaN**0 = 1 */
else if (Py_IS_NAN(y))
r = x == 1. ? 1. : y; /* 1**NaN = 1 */
else if (Py_IS_INFINITY(x)) {
odd_y = Py_IS_FINITE(y) && fmod(fabs(y), 2.0) == 1.0;
if (y > 0.)
r = odd_y ? x : fabs(x);
else if (y == 0.)
r = 1.;
else /* y < 0. */
r = odd_y ? copysign(0., x) : 0.;
}
else if (Py_IS_INFINITY(y)) {
if (fabs(x) == 1.0)
r = 1.;
else if (y > 0. && fabs(x) > 1.0)
r = y;
else if (y < 0. && fabs(x) < 1.0) {
r = -y; /* result is +inf */
if (x == 0.) /* 0**-inf: divide-by-zero */
errno = EDOM;
}
else
r = 0.;
}
}
else {
/* let libm handle finite**finite */
errno = 0;
PyFPE_START_PROTECT("in math_pow", return 0);
r = pow(x, y);
PyFPE_END_PROTECT(r);
/* a NaN result should arise only from (-ve)**(finite
non-integer); in this case we want to raise ValueError. */
if (!Py_IS_FINITE(r)) {
if (Py_IS_NAN(r)) {
errno = EDOM;
}
/*
an infinite result here arises either from:
(A) (+/-0.)**negative (-> divide-by-zero)
(B) overflow of x**y with x and y finite
*/
else if (Py_IS_INFINITY(r)) {
if (x == 0.)
errno = EDOM;
else
errno = ERANGE;
}
}
}
if (errno && is_error(r))
return NULL;
else
return PyFloat_FromDouble(r);
}
这段代码是用来计算Python中的平方根2**0.5的吗?
查找后发现,**与pow()相同,我们可以在源代码中查找__pow__()方法:
- 查找
__pow__的结果 - Python中浮点数的内置
pow()和math.pow()有何区别? numbers.py:Python中数字的处理方式
普遍认为,pow来自libm库。可能类似于这个,e_powf.c。还有e_pow.c
/* e_powf.c -- float version of e_pow.c.
* Conversion to float by Ian Lance Taylor, Cygnus Support, ian@cygnus.com.
*/
/*
* ====================================================
* Copyright (C) 1993 by Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.
*
* Developed at SunPro, a Sun Microsystems, Inc. business.
* Permission to use, copy, modify, and distribute this
* software is freely granted, provided that this notice
* is preserved.
* ====================================================
*/
#include <math.h>
#include <math_private.h>
static const float huge = 1.0e+30, tiny = 1.0e-30;
static const float
bp[] = {1.0, 1.5,},
dp_h[] = { 0.0, 5.84960938e-01,}, /* 0x3f15c000 */
dp_l[] = { 0.0, 1.56322085e-06,}, /* 0x35d1cfdc */
zero = 0.0,
one = 1.0,
two = 2.0,
two24 = 16777216.0, /* 0x4b800000 */
/* poly coefs for (3/2)*(log(x)-2s-2/3*s**3 */
L1 = 6.0000002384e-01, /* 0x3f19999a */
L2 = 4.2857143283e-01, /* 0x3edb6db7 */
L3 = 3.3333334327e-01, /* 0x3eaaaaab */
L4 = 2.7272811532e-01, /* 0x3e8ba305 */
L5 = 2.3066075146e-01, /* 0x3e6c3255 */
L6 = 2.0697501302e-01, /* 0x3e53f142 */
P1 = 1.6666667163e-01, /* 0x3e2aaaab */
P2 = -2.7777778450e-03, /* 0xbb360b61 */
P3 = 6.6137559770e-05, /* 0x388ab355 */
P4 = -1.6533901999e-06, /* 0xb5ddea0e */
P5 = 4.1381369442e-08, /* 0x3331bb4c */
lg2 = 6.9314718246e-01, /* 0x3f317218 */
lg2_h = 6.93145752e-01, /* 0x3f317200 */
lg2_l = 1.42860654e-06, /* 0x35bfbe8c */
ovt = 4.2995665694e-08, /* -(128-log2(ovfl+.5ulp)) */
cp = 9.6179670095e-01, /* 0x3f76384f =2/(3ln2) */
cp_h = 9.6179199219e-01, /* 0x3f763800 =head of cp */
cp_l = 4.7017383622e-06, /* 0x369dc3a0 =tail of cp_h */
ivln2 = 1.4426950216e+00, /* 0x3fb8aa3b =1/ln2 */
ivln2_h = 1.4426879883e+00, /* 0x3fb8aa00 =16b 1/ln2*/
ivln2_l = 7.0526075433e-06; /* 0x36eca570 =1/ln2 tail*/
float
__ieee754_powf(float x, float y)
{
float z,ax,z_h,z_l,p_h,p_l;
float y1,t1,t2,r,s,t,u,v,w;
int32_t i,j,k,yisint,n;
int32_t hx,hy,ix,iy,is;
GET_FLOAT_WORD(hx,x);
GET_FLOAT_WORD(hy,y);
ix = hx&0x7fffffff; iy = hy&0x7fffffff;
/* y==zero: x**0 = 1 */
if(iy==0) return one;
/* x==+-1 */
if(x == 1.0) return one;
if(x == -1.0 && isinf(y)) return one;
/* +-NaN return x+y */
if(__builtin_expect(ix > 0x7f800000 ||
iy > 0x7f800000, 0))
return x+y;
/* determine if y is an odd int when x < 0
* yisint = 0 ... y is not an integer
* yisint = 1 ... y is an odd int
* yisint = 2 ... y is an even int
*/
yisint = 0;
if(hx<0) {
if(iy>=0x4b800000) yisint = 2; /* even integer y */
else if(iy>=0x3f800000) {
k = (iy>>23)-0x7f; /* exponent */
j = iy>>(23-k);
if((j<<(23-k))==iy) yisint = 2-(j&1);
}
}
/* special value of y */
if (__builtin_expect(iy==0x7f800000, 0)) { /* y is +-inf */
if (ix==0x3f800000)
return y - y; /* inf**+-1 is NaN */
else if (ix > 0x3f800000)/* (|x|>1)**+-inf = inf,0 */
return (hy>=0)? y: zero;
else /* (|x|<1)**-,+inf = inf,0 */
return (hy<0)?-y: zero;
}
if(iy==0x3f800000) { /* y is +-1 */
if(hy<0) return one/x; else return x;
}
if(hy==0x40000000) return x*x; /* y is 2 */
if(hy==0x3f000000) { /* y is 0.5 */
if(__builtin_expect(hx>=0, 1)) /* x >= +0 */
return __ieee754_sqrtf(x);
}
ax = fabsf(x);
/* special value of x */
if(__builtin_expect(ix==0x7f800000||ix==0||ix==0x3f800000, 0)){
z = ax; /*x is +-0,+-inf,+-1*/
if(hy<0) z = one/z; /* z = (1/|x|) */
if(hx<0) {
if(((ix-0x3f800000)|yisint)==0) {
z = (z-z)/(z-z); /* (-1)**non-int is NaN */
} else if(yisint==1)
z = -z; /* (x<0)**odd = -(|x|**odd) */
}
return z;
}
/* (x<0)**(non-int) is NaN */
if(__builtin_expect(((((u_int32_t)hx>>31)-1)|yisint)==0, 0))
return (x-x)/(x-x);
/* |y| is huge */
if(__builtin_expect(iy>0x4d000000, 0)) { /* if |y| > 2**27 */
/* over/underflow if x is not close to one */
if(ix<0x3f7ffff8) return (hy<0)? huge*huge:tiny*tiny;
if(ix>0x3f800007) return (hy>0)? huge*huge:tiny*tiny;
/* now |1-x| is tiny <= 2**-20, suffice to compute
log(x) by x-x^2/2+x^3/3-x^4/4 */
t = ax-1; /* t has 20 trailing zeros */
w = (t*t)*((float)0.5-t*((float)0.333333333333-t*(float)0.25));
u = ivln2_h*t; /* ivln2_h has 16 sig. bits */
v = t*ivln2_l-w*ivln2;
t1 = u+v;
GET_FLOAT_WORD(is,t1);
SET_FLOAT_WORD(t1,is&0xfffff000);
t2 = v-(t1-u);
} else {
float s2,s_h,s_l,t_h,t_l;
/* Avoid internal underflow for tiny y. The exact value
of y does not matter if |y| <= 2**-32. */
if (iy < 0x2f800000)
SET_FLOAT_WORD (y, (hy & 0x80000000) | 0x2f800000);
n = 0;
/* take care subnormal number */
if(ix<0x00800000)
{ax *= two24; n -= 24; GET_FLOAT_WORD(ix,ax); }
n += ((ix)>>23)-0x7f;
j = ix&0x007fffff;
/* determine interval */
ix = j|0x3f800000; /* normalize ix */
if(j<=0x1cc471) k=0; /* |x|<sqrt(3/2) */
else if(j<0x5db3d7) k=1; /* |x|<sqrt(3) */
else {k=0;n+=1;ix -= 0x00800000;}
SET_FLOAT_WORD(ax,ix);
/* compute s = s_h+s_l = (x-1)/(x+1) or (x-1.5)/(x+1.5) */
u = ax-bp[k]; /* bp[0]=1.0, bp[1]=1.5 */
v = one/(ax+bp[k]);
s = u*v;
s_h = s;
GET_FLOAT_WORD(is,s_h);
SET_FLOAT_WORD(s_h,is&0xfffff000);
/* t_h=ax+bp[k] High */
SET_FLOAT_WORD (t_h,
((((ix>>1)|0x20000000)+0x00400000+(k<<21))
& 0xfffff000));
t_l = ax - (t_h-bp[k]);
s_l = v*((u-s_h*t_h)-s_h*t_l);
/* compute log(ax) */
s2 = s*s;
r = s2*s2*(L1+s2*(L2+s2*(L3+s2*(L4+s2*(L5+s2*L6)))));
r += s_l*(s_h+s);
s2 = s_h*s_h;
t_h = (float)3.0+s2+r;
GET_FLOAT_WORD(is,t_h);
SET_FLOAT_WORD(t_h,is&0xfffff000);
t_l = r-((t_h-(float)3.0)-s2);
/* u+v = s*(1+...) */
u = s_h*t_h;
v = s_l*t_h+t_l*s;
/* 2/(3log2)*(s+...) */
p_h = u+v;
GET_FLOAT_WORD(is,p_h);
SET_FLOAT_WORD(p_h,is&0xfffff000);
p_l = v-(p_h-u);
z_h = cp_h*p_h; /* cp_h+cp_l = 2/(3*log2) */
z_l = cp_l*p_h+p_l*cp+dp_l[k];
/* log2(ax) = (s+..)*2/(3*log2) = n + dp_h + z_h + z_l */
t = (float)n;
t1 = (((z_h+z_l)+dp_h[k])+t);
GET_FLOAT_WORD(is,t1);
SET_FLOAT_WORD(t1,is&0xfffff000);
t2 = z_l-(((t1-t)-dp_h[k])-z_h);
}
s = one; /* s (sign of result -ve**odd) = -1 else = 1 */
if(((((u_int32_t)hx>>31)-1)|(yisint-1))==0)
s = -one; /* (-ve)**(odd int) */
/* split up y into y1+y2 and compute (y1+y2)*(t1+t2) */
GET_FLOAT_WORD(is,y);
SET_FLOAT_WORD(y1,is&0xfffff000);
p_l = (y-y1)*t1+y*t2;
p_h = y1*t1;
z = p_l+p_h;
GET_FLOAT_WORD(j,z);
if (__builtin_expect(j>0x43000000, 0)) /* if z > 128 */
return s*huge*huge; /* overflow */
else if (__builtin_expect(j==0x43000000, 0)) { /* if z == 128 */
if(p_l+ovt>z-p_h) return s*huge*huge; /* overflow */
}
else if (__builtin_expect((j&0x7fffffff)>0x43160000, 0))/* z <= -150 */
return s*tiny*tiny; /* underflow */
else if (__builtin_expect((u_int32_t) j==0xc3160000, 0)){/* z == -150*/
if(p_l<=z-p_h) return s*tiny*tiny; /* underflow */
}
/*
* compute 2**(p_h+p_l)
*/
i = j&0x7fffffff;
k = (i>>23)-0x7f;
n = 0;
if(i>0x3f000000) { /* if |z| > 0.5, set n = [z+0.5] */
n = j+(0x00800000>>(k+1));
k = ((n&0x7fffffff)>>23)-0x7f; /* new k for n */
SET_FLOAT_WORD(t,n&~(0x007fffff>>k));
n = ((n&0x007fffff)|0x00800000)>>(23-k);
if(j<0) n = -n;
p_h -= t;
}
t = p_l+p_h;
GET_FLOAT_WORD(is,t);
SET_FLOAT_WORD(t,is&0xfffff000);
u = t*lg2_h;
v = (p_l-(t-p_h))*lg2+t*lg2_l;
z = u+v;
w = v-(z-u);
t = z*z;
t1 = z - t*(P1+t*(P2+t*(P3+t*(P4+t*P5))));
r = (z*t1)/(t1-two)-(w+z*w);
z = one-(r-z);
GET_FLOAT_WORD(j,z);
j += (n<<23);
if((j>>23)<=0) /* subnormal output */
{
z = __scalbnf (z, n);
float force_underflow = z * z;
math_force_eval (force_underflow);
}
else SET_FLOAT_WORD(z,j);
return s*z;
}
strong_alias (__ieee754_powf, __powf_finite)
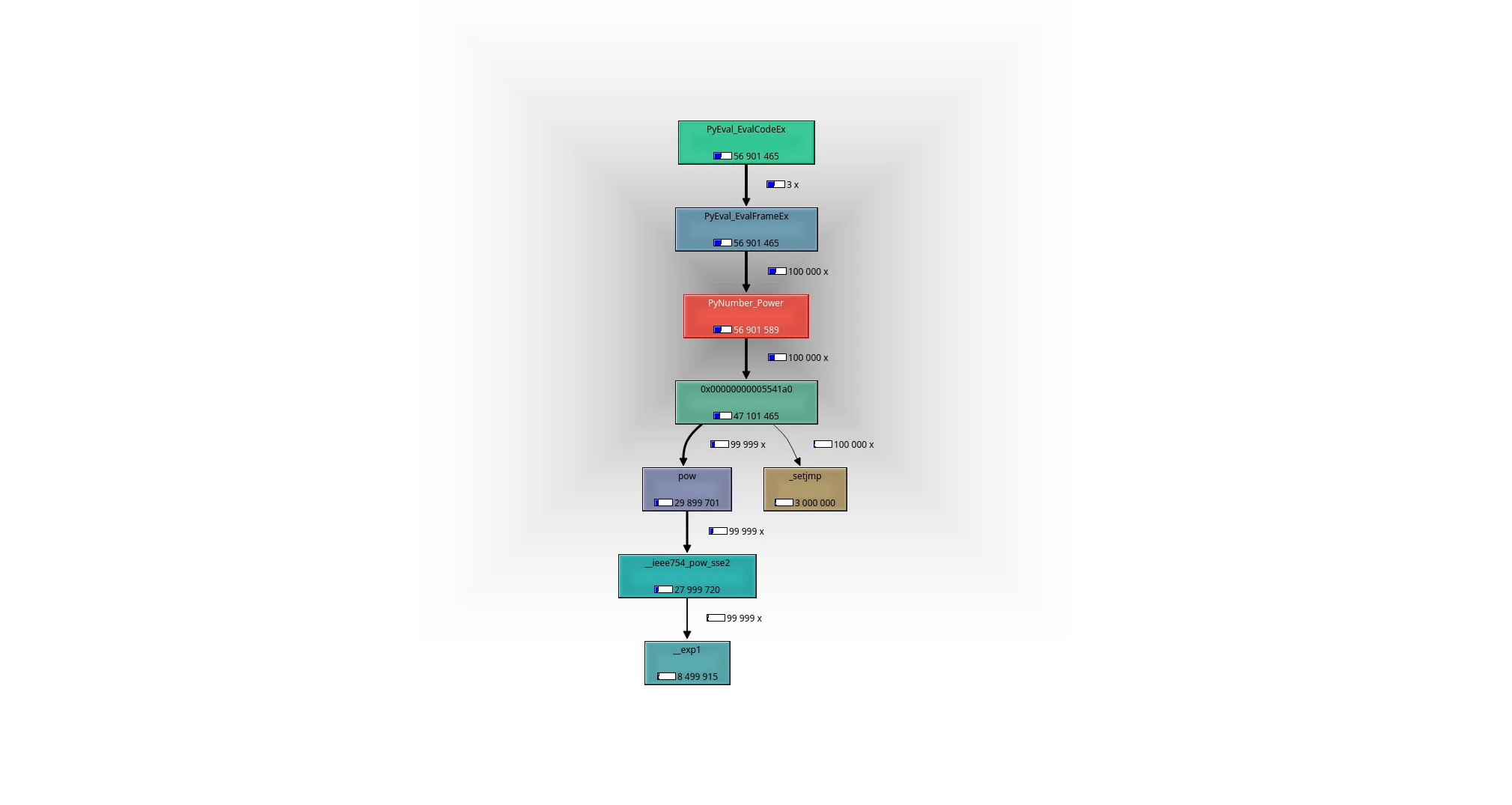
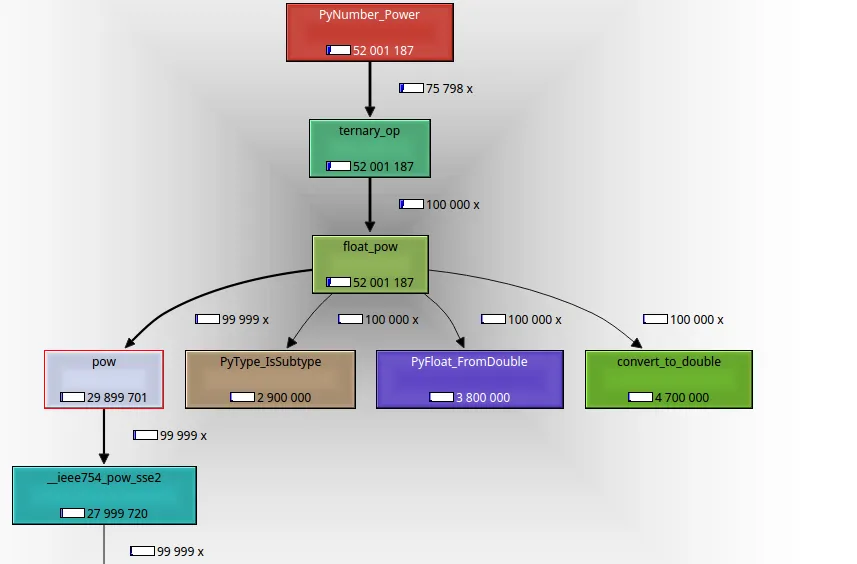
2转换为双精度浮点数2.0,但除此之外,我认为这就是真正工作的代码。在检查了一些特殊情况后,最终只会调用pow(x, y)函数。 - Barmarmath.pow实现是分开的,并且在一些细节上有所不同(例如,处理溢出的方式)。但就像math.pow一样,它最终会调用C libmpow函数来处理基数为finite ** finite的情况,具体请看这里。 - Mark Dickinsonix = pow(iv, iw);,其中float_pow调用了pow函数。 - john mangual