我希望在同一个图上绘制两个直方图——胡萝卜长度和黄瓜长度。它们会重叠,所以我猜我还需要一些透明度。我还需要使用相对频率而不是绝对数量,因为每个组中的实例数是不同的。
像这样的效果会很好,但是我该如何从我的两个表格中创建它呢?

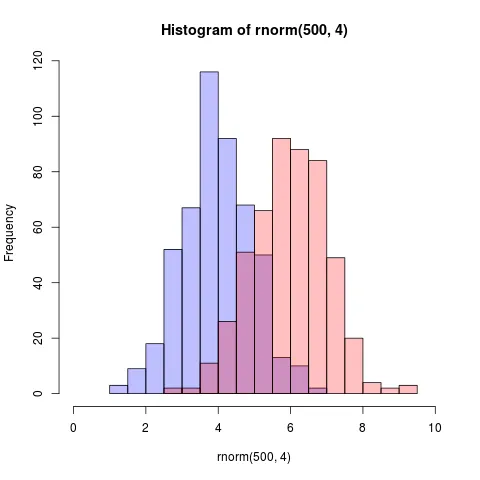
这里有一个更简单的解决方案,使用基本图形和alpha-blending(不适用于所有图形设备):
set.seed(42)
p1 <- hist(rnorm(500,4)) # centered at 4
p2 <- hist(rnorm(500,6)) # centered at 6
plot( p1, col=rgb(0,0,1,1/4), xlim=c(0,10)) # first histogram
plot( p2, col=rgb(1,0,0,1/4), xlim=c(0,10), add=T) # second
hist命令中,而不是像我说的那样将其放入plot命令中。发帖代码并不是评论的目的。 - John你提供的那个图片是用于密度曲线而不是直方图。
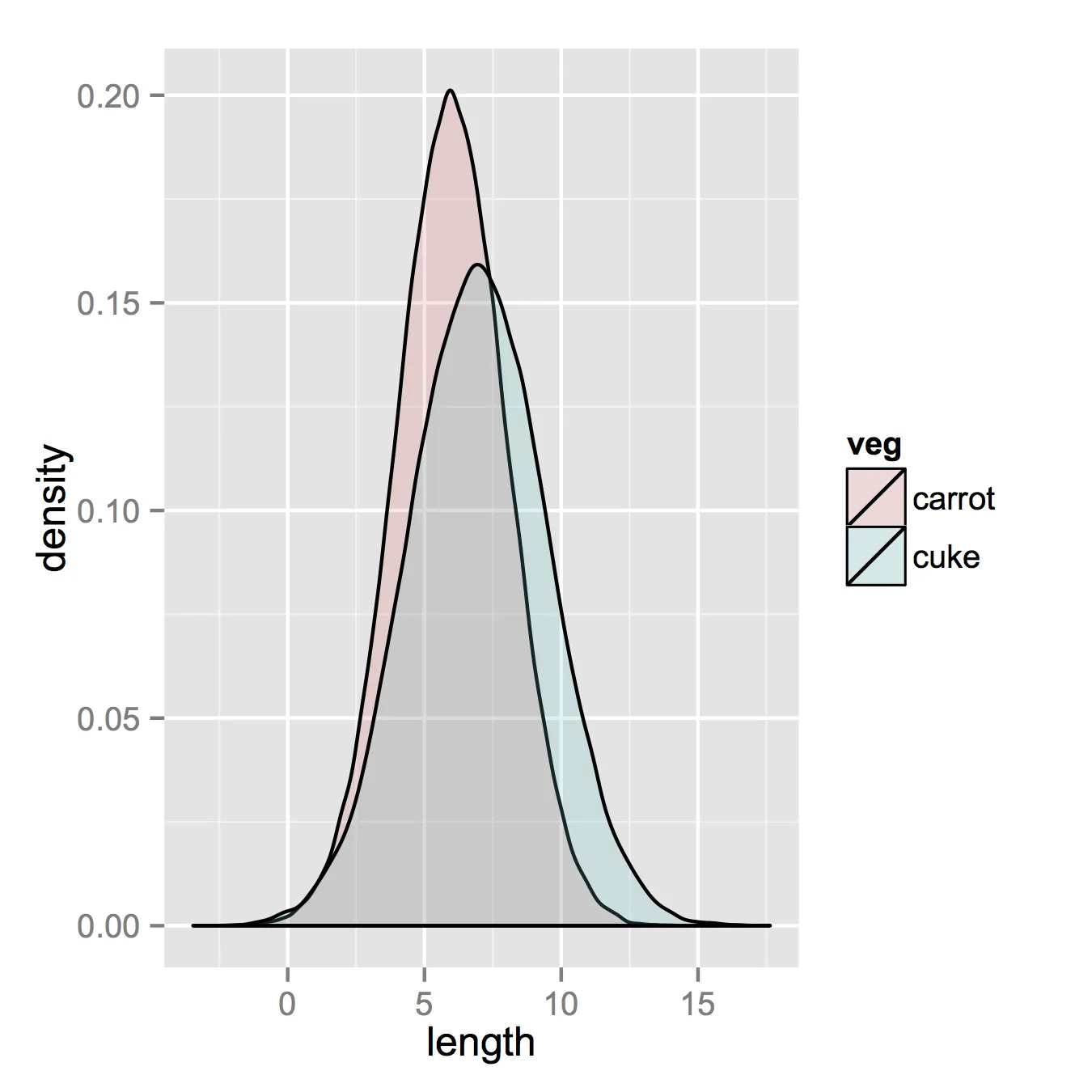
如果你一直在学习ggplot,那么可能你唯一缺少的就是将两个数据框组合成一个长数据框。
因此,让我们从类似于你所拥有的两个独立数据集开始,将它们组合成一个长数据集。
carrots <- data.frame(length = rnorm(100000, 6, 2))
cukes <- data.frame(length = rnorm(50000, 7, 2.5))
# Now, combine your two dataframes into one.
# First make a new column in each that will be
# a variable to identify where they came from later.
carrots$veg <- 'carrot'
cukes$veg <- 'cuke'
# and combine into your new data frame vegLengths
vegLengths <- rbind(carrots, cukes)
如果您的数据已经是长格式,则不需要进行此操作,接下来只需要一行代码即可绘制图表。
ggplot(vegLengths, aes(length, fill = veg)) + geom_density(alpha = 0.2)
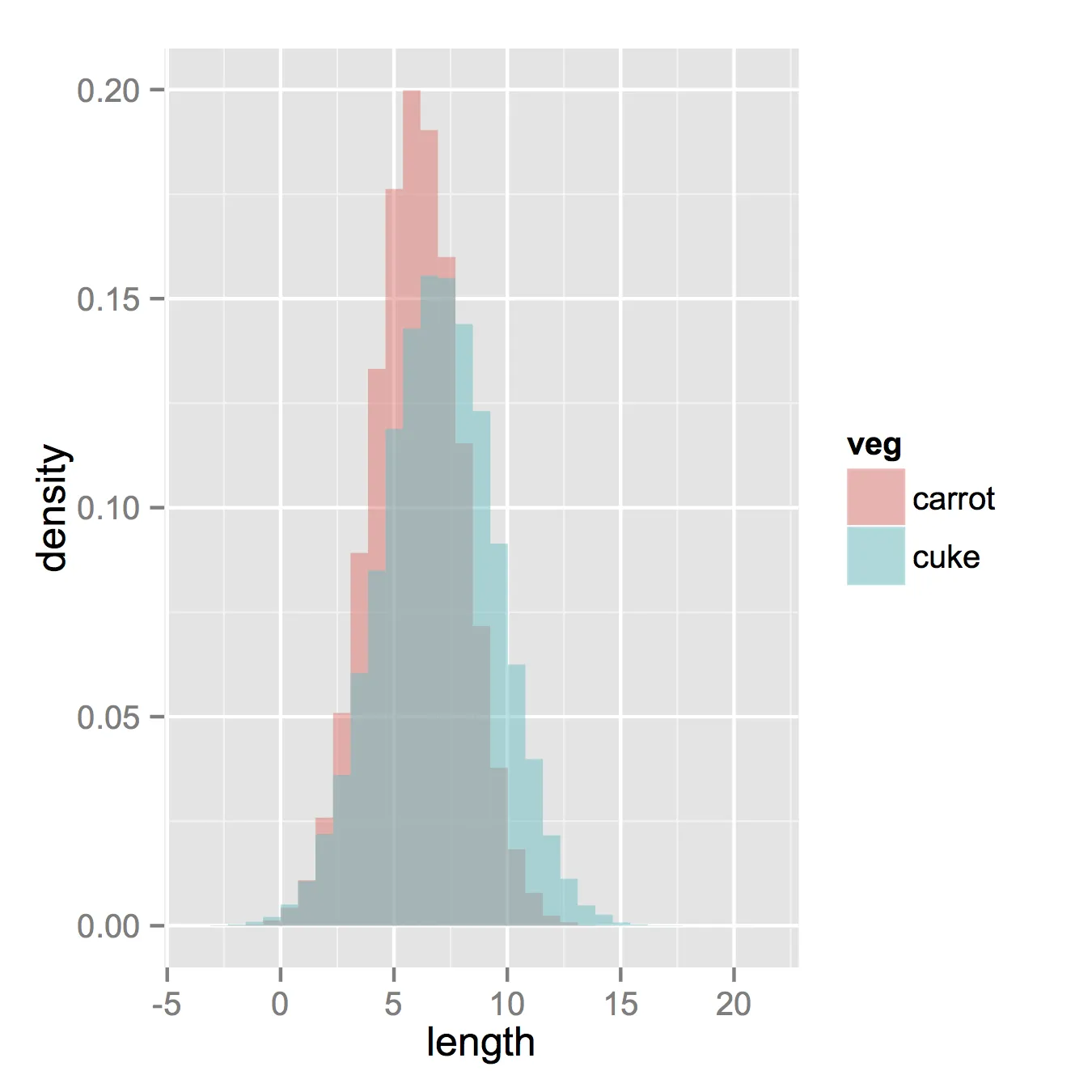
如果您真的想要直方图,下面的代码可以实现。请注意,您必须更改默认的“stack”参数。如果您不确定数据应该是什么样子,可能会忽略这一点。使用更高的alpha值看起来更好。还要注意,我将其设置为密度直方图。要将其恢复为计数,请删除y = ..density..。
ggplot(vegLengths, aes(length, fill = veg)) +
geom_histogram(alpha = 0.5, aes(y = ..density..), position = 'identity')
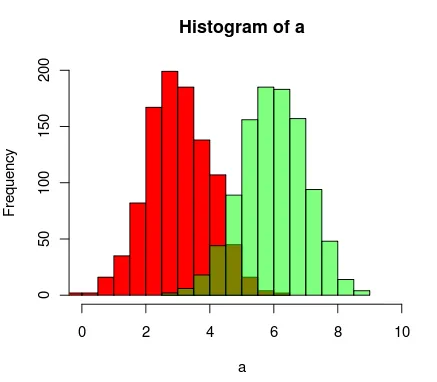
另外,我在Dirk的问题下评论说所有参数都可以直接放在hist命令中。有人问我怎么做。下面的内容可以生成与Dirk的图像完全相同的结果。
set.seed(42)
hist(rnorm(500,4), col=rgb(0,0,1,1/4), xlim=c(0,10))
hist(rnorm(500,6), col=rgb(1,0,0,1/4), xlim=c(0,10), add = TRUE)
ggplot(vegLengths, aes(length, fill = veg)) + geom_bar(pos="dodge")。这将创建交错的直方图,类似于MATLAB中的效果。 - mbq这是我编写的一个函数,使用伪透明度来表示重叠的直方图
plotOverlappingHist <- function(a, b, colors=c("white","gray20","gray50"),
breaks=NULL, xlim=NULL, ylim=NULL){
ahist=NULL
bhist=NULL
if(!(is.null(breaks))){
ahist=hist(a,breaks=breaks,plot=F)
bhist=hist(b,breaks=breaks,plot=F)
} else {
ahist=hist(a,plot=F)
bhist=hist(b,plot=F)
dist = ahist$breaks[2]-ahist$breaks[1]
breaks = seq(min(ahist$breaks,bhist$breaks),max(ahist$breaks,bhist$breaks),dist)
ahist=hist(a,breaks=breaks,plot=F)
bhist=hist(b,breaks=breaks,plot=F)
}
if(is.null(xlim)){
xlim = c(min(ahist$breaks,bhist$breaks),max(ahist$breaks,bhist$breaks))
}
if(is.null(ylim)){
ylim = c(0,max(ahist$counts,bhist$counts))
}
overlap = ahist
for(i in 1:length(overlap$counts)){
if(ahist$counts[i] > 0 & bhist$counts[i] > 0){
overlap$counts[i] = min(ahist$counts[i],bhist$counts[i])
} else {
overlap$counts[i] = 0
}
}
plot(ahist, xlim=xlim, ylim=ylim, col=colors[1])
plot(bhist, xlim=xlim, ylim=ylim, col=colors[2], add=T)
plot(overlap, xlim=xlim, ylim=ylim, col=colors[3], add=T)
}
a=rnorm(1000, 3, 1)
b=rnorm(1000, 6, 1)
hist(a, xlim=c(0,10), col="red")
hist(b, add=T, col=rgb(0, 1, 0, 0.5) )
postscript)都可用的选项。 - Lenna已经有很好的答案了,但是我想再补充一点。对我来说看起来不错。
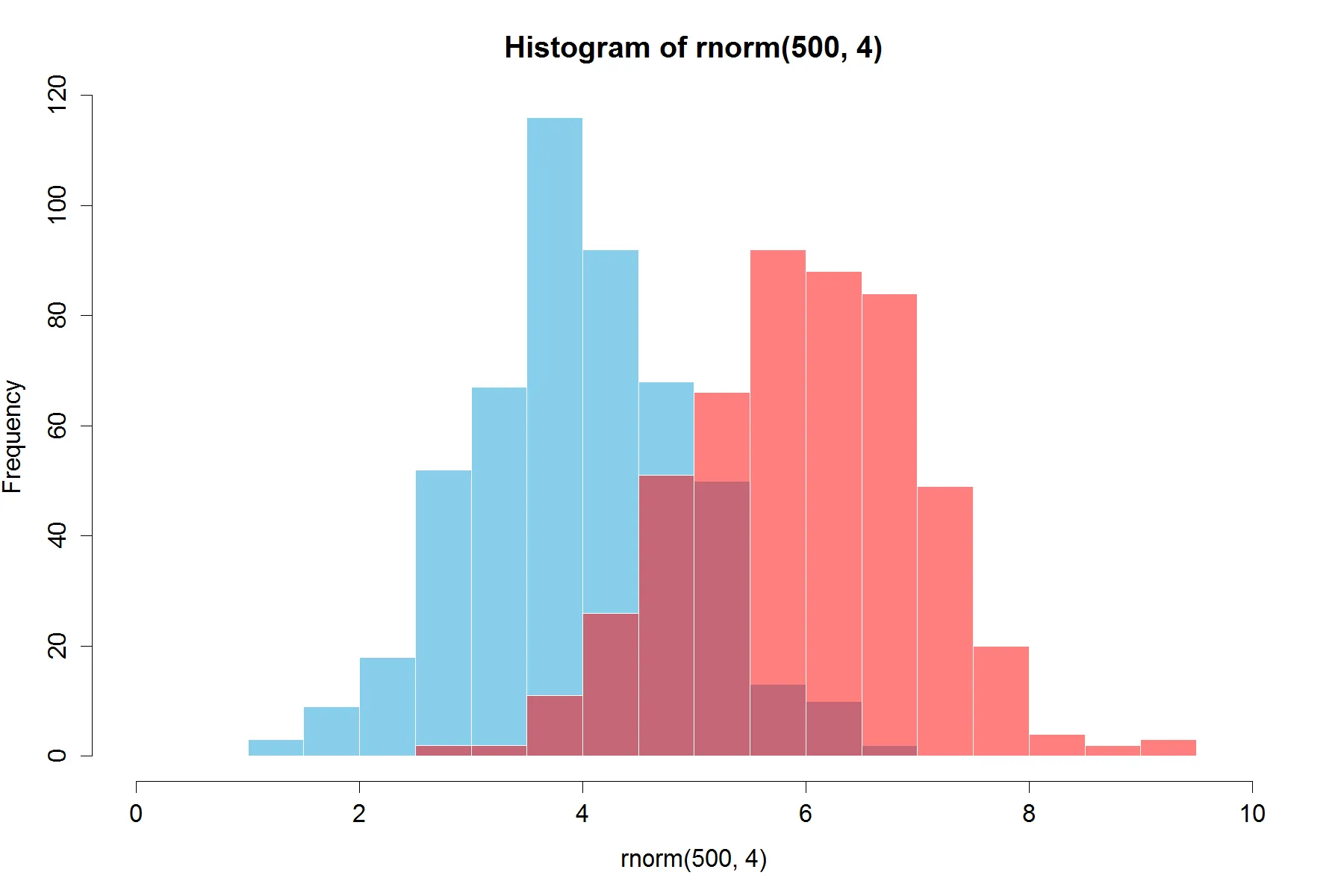
(从@Dirk中复制了随机数)。需要使用library(scales)
set.seed(42)
hist(rnorm(500,4),xlim=c(0,10),col='skyblue',border=F)
hist(rnorm(500,6),add=T,col=scales::alpha('red',.5),border=F)
hist0 <- function(...,col='skyblue',border=T) hist(...,col=col,border=border)
hist0的结果比hist更美观。hist2 <- function(var1, var2,name1='',name2='',
breaks = min(max(length(var1), length(var2)),20),
main0 = "", alpha0 = 0.5,grey=0,border=F,...) {
library(scales)
colh <- c(rgb(0, 1, 0, alpha0), rgb(1, 0, 0, alpha0))
if(grey) colh <- c(alpha(grey(0.1,alpha0)), alpha(grey(0.9,alpha0)))
max0 = max(var1, var2)
min0 = min(var1, var2)
den1_max <- hist(var1, breaks = breaks, plot = F)$density %>% max
den2_max <- hist(var2, breaks = breaks, plot = F)$density %>% max
den_max <- max(den2_max, den1_max)*1.2
var1 %>% hist0(xlim = c(min0 , max0) , breaks = breaks,
freq = F, col = colh[1], ylim = c(0, den_max), main = main0,border=border,...)
var2 %>% hist0(xlim = c(min0 , max0), breaks = breaks,
freq = F, col = colh[2], ylim = c(0, den_max), add = T,border=border,...)
legend(min0,den_max, legend = c(
ifelse(nchar(name1)==0,substitute(var1) %>% deparse,name1),
ifelse(nchar(name2)==0,substitute(var2) %>% deparse,name2),
"Overlap"), fill = c('white','white', colh[1]), bty = "n", cex=1,ncol=3)
legend(min0,den_max, legend = c(
ifelse(nchar(name1)==0,substitute(var1) %>% deparse,name1),
ifelse(nchar(name2)==0,substitute(var2) %>% deparse,name2),
"Overlap"), fill = c(colh, colh[2]), bty = "n", cex=1,ncol=3) }
的结果
par(mar=c(3, 4, 3, 2) + 0.1)
set.seed(100)
hist2(rnorm(10000,2),rnorm(10000,3),breaks = 50)
这是一张图片,无法翻译。
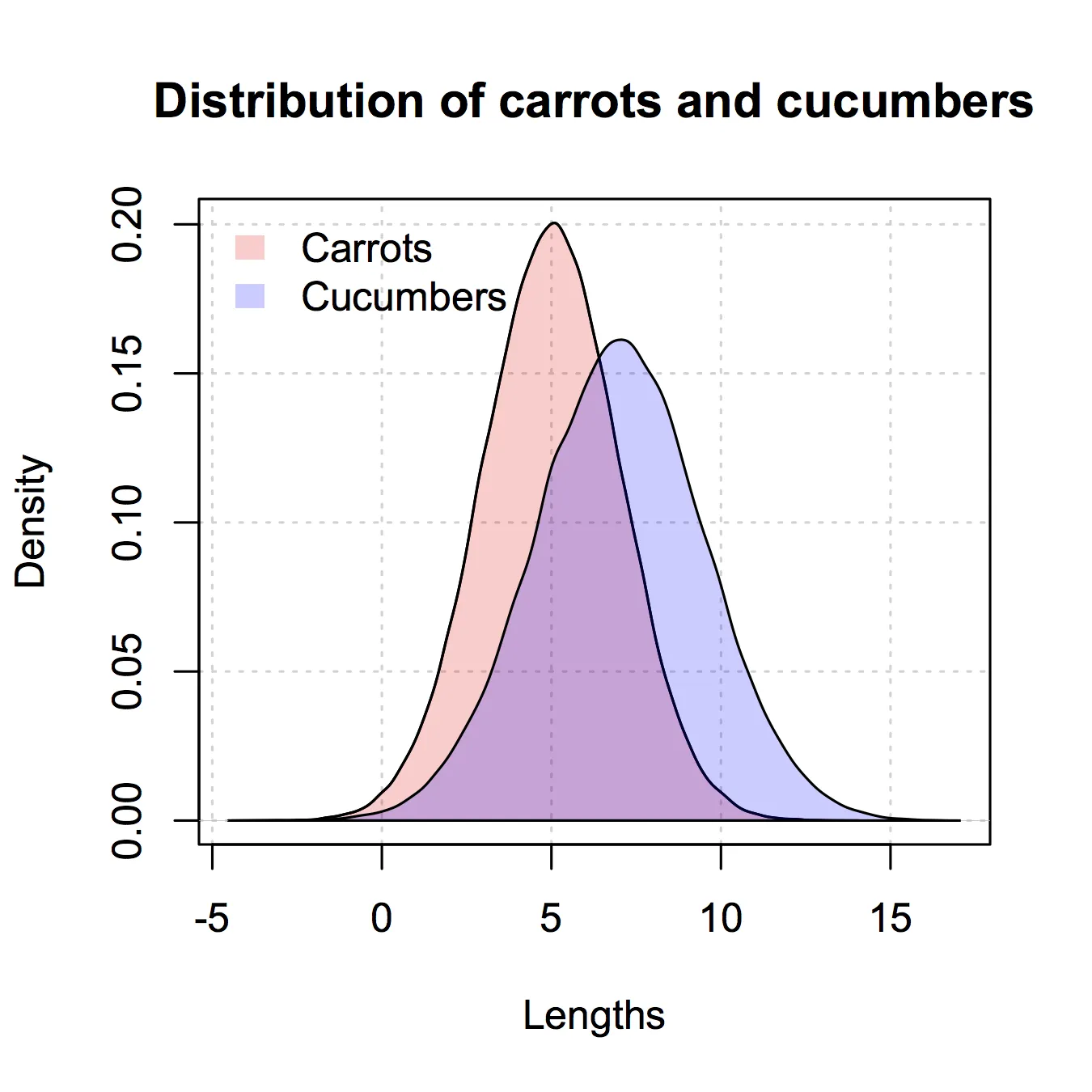
以下是如何在“传统”的R图形中实现的示例:
## generate some random data
carrotLengths <- rnorm(1000,15,5)
cucumberLengths <- rnorm(200,20,7)
## calculate the histograms - don't plot yet
histCarrot <- hist(carrotLengths,plot = FALSE)
histCucumber <- hist(cucumberLengths,plot = FALSE)
## calculate the range of the graph
xlim <- range(histCucumber$breaks,histCarrot$breaks)
ylim <- range(0,histCucumber$density,
histCarrot$density)
## plot the first graph
plot(histCarrot,xlim = xlim, ylim = ylim,
col = rgb(1,0,0,0.4),xlab = 'Lengths',
freq = FALSE, ## relative, not absolute frequency
main = 'Distribution of carrots and cucumbers')
## plot the second graph on top of this
opar <- par(new = FALSE)
plot(histCucumber,xlim = xlim, ylim = ylim,
xaxt = 'n', yaxt = 'n', ## don't add axes
col = rgb(0,0,1,0.4), add = TRUE,
freq = FALSE) ## relative, not absolute frequency
## add a legend in the corner
legend('topleft',c('Carrots','Cucumbers'),
fill = rgb(1:0,0,0:1,0.4), bty = 'n',
border = NA)
par(opar)
hist的参数中)。ggplot中的那些回答之外,这个回答是唯一直接考虑两个直方图具有显著不同样本大小的回答。 - MichaelChiricobreaks=seq(min(data$some_property), max(data$some_property), by=(max_prop - min_prop)/20) - Deruijtercarrots <- rnorm(100000,5,2)
cukes <- rnorm(50000,7,2.5)
你不需要像使用ggplot2一样将它放入数据框中。这种方法的缺点是你必须写出更多细节的图表。 优点是你可以控制更多图表的细节。
## calculate the density - don't plot yet
densCarrot <- density(carrots)
densCuke <- density(cukes)
## calculate the range of the graph
xlim <- range(densCuke$x,densCarrot$x)
ylim <- range(0,densCuke$y, densCarrot$y)
#pick the colours
carrotCol <- rgb(1,0,0,0.2)
cukeCol <- rgb(0,0,1,0.2)
## plot the carrots and set up most of the plot parameters
plot(densCarrot, xlim = xlim, ylim = ylim, xlab = 'Lengths',
main = 'Distribution of carrots and cucumbers',
panel.first = grid())
#put our density plots in
polygon(densCarrot, density = -1, col = carrotCol)
polygon(densCuke, density = -1, col = cukeCol)
## add a legend in the corner
legend('topleft',c('Carrots','Cucumbers'),
fill = c(carrotCol, cukeCol), bty = 'n',
border = NA)
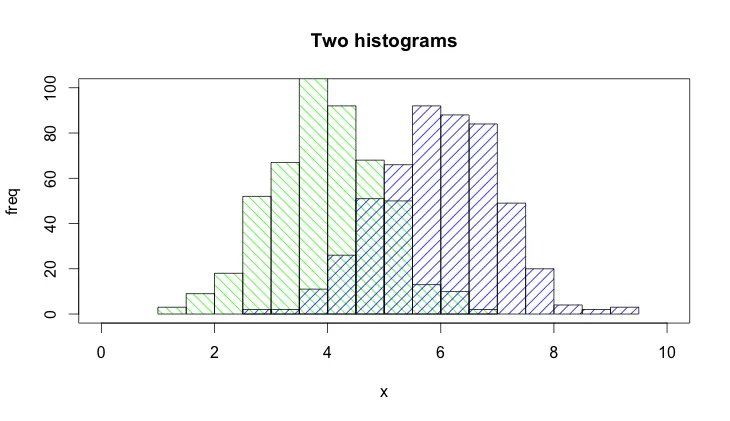
@Dirk Eddelbuettel: 基本思路很不错,但是所示代码可以改进。[需要讲解的内容较多,因此我单独回答而不是在评论中回答。]
hist() 函数默认绘制图形,因此您需要添加 plot=FALSE 选项。此外,更清晰的方法是通过 plot(0,0,type="n",...) 调用来建立绘图区域,在其中可以添加轴标签、图表标题等。最后,我想提到的是,我们也可以使用阴影来区分两个直方图。以下是代码:
set.seed(42)
p1 <- hist(rnorm(500,4),plot=FALSE)
p2 <- hist(rnorm(500,6),plot=FALSE)
plot(0,0,type="n",xlim=c(0,10),ylim=c(0,100),xlab="x",ylab="freq",main="Two histograms")
plot(p1,col="green",density=10,angle=135,add=TRUE)
plot(p2,col="blue",density=10,angle=45,add=TRUE)
这是结果(由于RStudio的原因有点宽 :- )):
postscript设备上是一个非常简单的选项。 - MichaelChiricoPlotly的R API可能对您有用。下面的图表在这里。
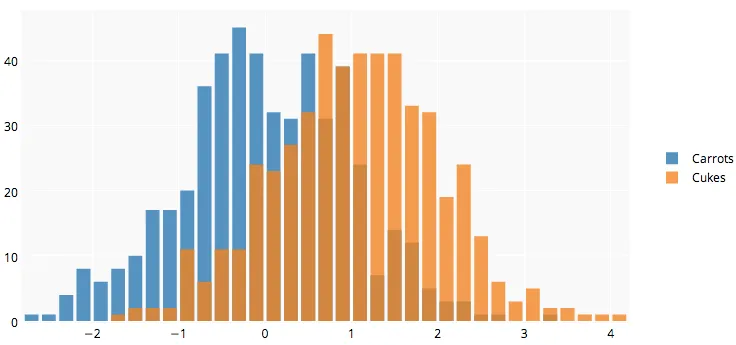
library(plotly)
#add username and key
p <- plotly(username="Username", key="API_KEY")
#generate data
x0 = rnorm(500)
x1 = rnorm(500)+1
#arrange your graph
data0 = list(x=x0,
name = "Carrots",
type='histogramx',
opacity = 0.8)
data1 = list(x=x1,
name = "Cukes",
type='histogramx',
opacity = 0.8)
#specify type as 'overlay'
layout <- list(barmode='overlay',
plot_bgcolor = 'rgba(249,249,251,.85)')
#format response, and use 'browseURL' to open graph tab in your browser.
response = p$plotly(data0, data1, kwargs=list(layout=layout))
url = response$url
filename = response$filename
browseURL(response$url)
plotMultipleHistograms()在'basicPlotteR'包中)来完成这个任务,所以我想再添加一个答案。# Install the plotteR package
install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("JosephCrispell/basicPlotteR")
library(basicPlotteR)
# Set the seed
set.seed(254534)
# Create random samples from a normal distribution
distributions <- list(rnorm(500, mean=5, sd=0.5),
rnorm(500, mean=8, sd=5),
rnorm(500, mean=20, sd=2))
# Plot overlapping histograms
plotMultipleHistograms(distributions, nBins=20,
colours=c(rgb(1,0,0, 0.5), rgb(0,0,1, 0.5), rgb(0,1,0, 0.5)),
las=1, main="Samples from normal distribution", xlab="Value")
las,main等)。