我正在尝试将一个因子列转换为多个布尔列,如下图所示。数据来自气象站,使用精细的weatherData包检索。我想要将要转换为多个布尔列的因子列包含11个因子。其中一些是单个“事件”,而另一些是“事件”组合。
这里有一张图片展示了我想要实现的内容:
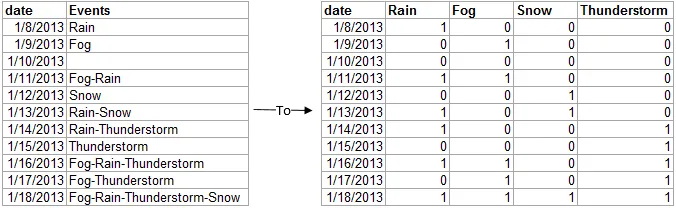 这是生成我想要转换为多个布尔列的组合因子数据框的R代码:
这是生成我想要转换为多个布尔列的组合因子数据框的R代码:
df <- read.table(text="
date Events
1/8/2013 Rain
1/9/2013 Fog
1/10/2013 ''
1/11/2013 Fog-Rain
1/12/2013 Snow
1/13/2013 Rain-Snow
1/14/2013 Rain-Thunderstorm
1/15/2013 Thunderstorm
1/16/2013 Fog-Rain-Thunderstorm
1/17/2013 Fog-Thunderstorm
1/18/2013 Fog-Rain-Thunderstorm-Snow",
header=T)
df$date <- as.character(as.Date(df$date, "%m/%d/%Y"))
提前致谢。
reshape2和data.table,dcast就可以正常工作。看来dcast.data.table是不需要使用reshape2的。 - akrundata.table_1.9.2。 - akrun