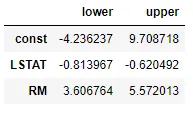
我想获得一次线性回归结果的置信区间。我正在使用波士顿房价数据集。
我找到了这个问题:如何在python中计算线性回归模型斜率的99%置信区间?,但是这并不能完全回答我的问题。
这是我的代码:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from math import pi
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
# import the data
boston_dataset = load_boston()
boston = pd.DataFrame(boston_dataset.data, columns=boston_dataset.feature_names)
boston['MEDV'] = boston_dataset.target
X = pd.DataFrame(np.c_[boston['LSTAT'], boston['RM']], columns=['LSTAT', 'RM'])
Y = boston['MEDV']
# splits the training and test data set in 80% : 20%
# assign random_state to any value.This ensures consistency.
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.2, random_state=5)
lin_model = LinearRegression()
lin_model.fit(X_train, Y_train)
# model evaluation for training set
y_train_predict = lin_model.predict(X_train)
rmse = (np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(Y_train, y_train_predict)))
r2 = r2_score(Y_train, y_train_predict)
# model evaluation for testing set
y_test_predict = lin_model.predict(X_test)
# root mean square error of the model
rmse = (np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(Y_test, y_test_predict)))
# r-squared score of the model
r2 = r2_score(Y_test, y_test_predict)
plt.scatter(Y_test, y_test_predict)
plt.show()
我该如何从这个数据中获取95%或99%的置信区间?是否有内置函数或代码可以使用?