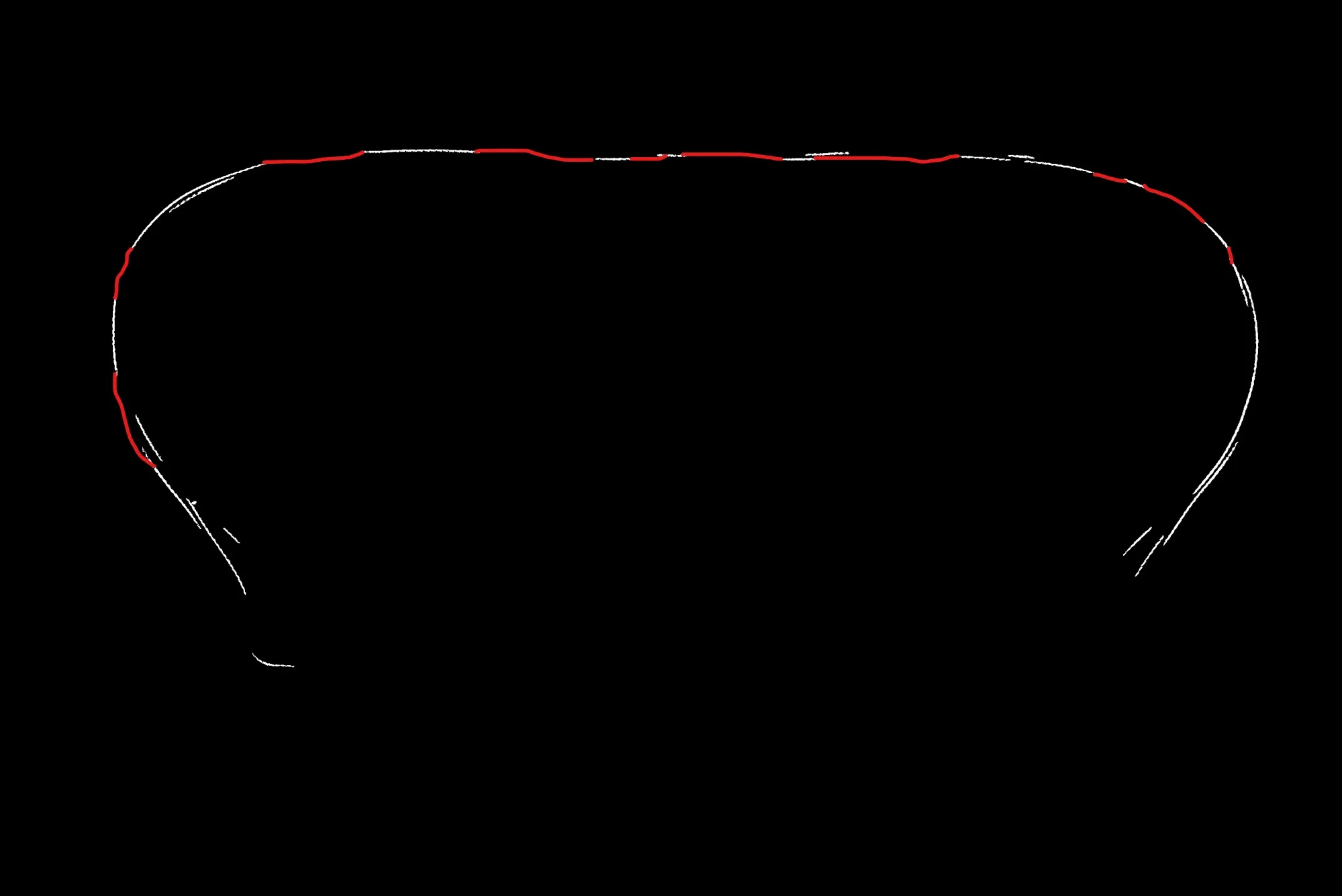
使用以下方法序列,我能够得到一个粗略的近似值。这是一个非常简单的解决方案,可能不适用于所有情况。
1. 形态学操作
要合并相邻的线,请对二进制图像执行形态学(膨胀)操作。
img = cv2.imread('image_path', 0)
img1 = cv2.imread('image_path', 1)
th = cv2.threshold(img, 150, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (19, 19))
morph = cv2.morphologyEx(th, cv2.MORPH_DILATE, kernel)
2. 查找轮廓和极值点
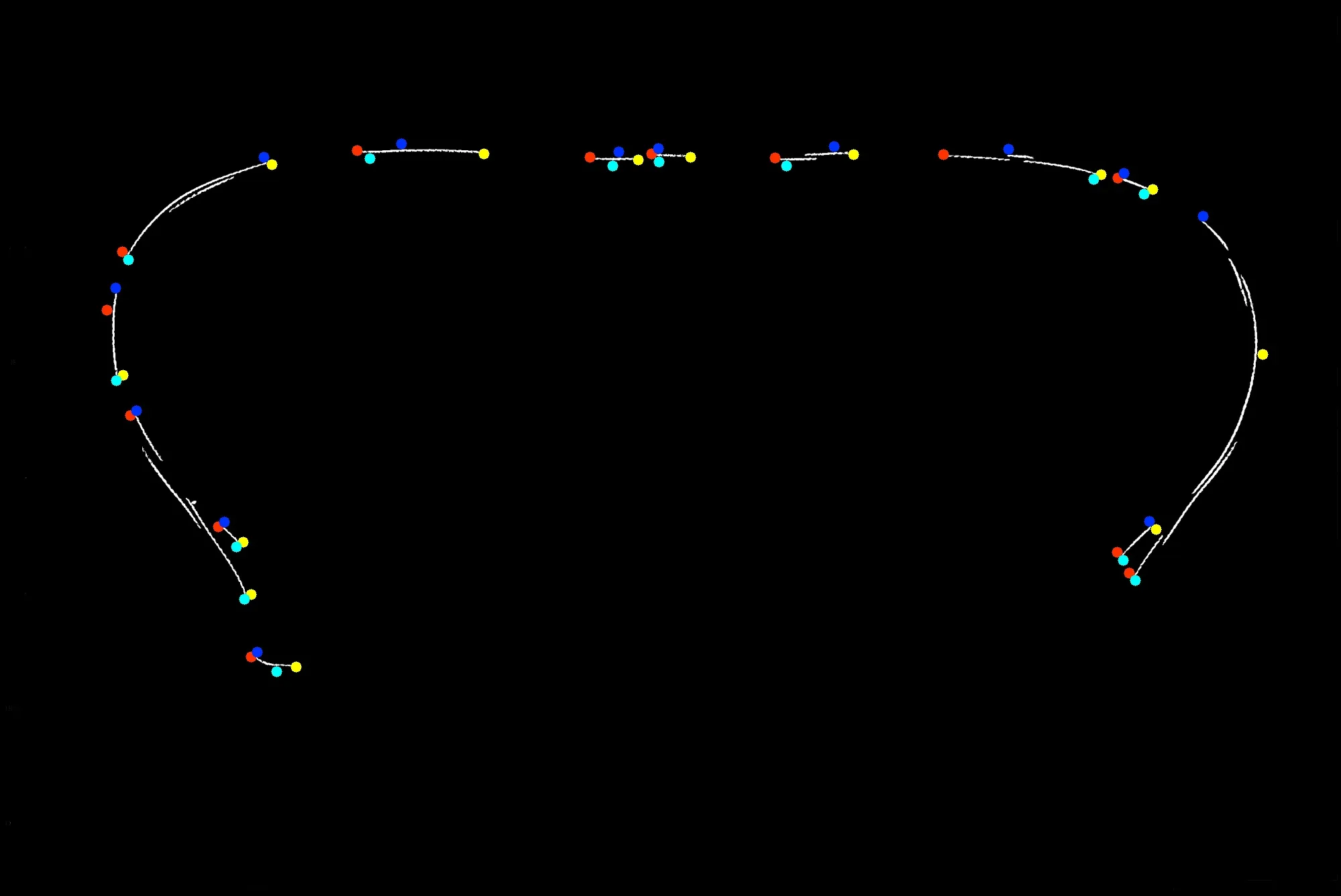
我的想法是查找轮廓。
然后找到每个轮廓的极值点。
最后在相邻轮廓的这些极值点之间找到最近距离并画一条线连接它们。
cnts1 = cv2.findContours(morph, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = cnts1[0] # 将轮廓存储在一个变量中
现在让我们快速看一下这些极值点所在的位置:
for c in cnts:
left = tuple(c[c[:, :, 0].argmin()][0])
right = tuple(c[c[:, :, 0].argmax()][0])
top = tuple(c[c[:, :, 1].argmin()][0])
bottom = tuple(c[c[:, :, 1].argmax()][0])
cv2.circle(img1, left, 8, (0, 50, 255), -1)
cv2.circle(img1, right, 8, (0, 255, 255), -1)
cv2.circle(img1, top, 8, (255, 50, 0), -1)
cv2.circle(img1, bottom, 8, (255, 255, 0), -1)
< p >(< em >< strong >注意: 极值点基于形态学运算的轮廓,但绘制在原始图像上)
< p >
3. 查找相邻轮廓之间的最近距离
< p >很抱歉循环次数较多。
First, iterate through every contour (split line) in the image.
Find the extreme points for them. Extreme points mean top-most, bottom-most, right-most and left-most points based on its respective bounding box.
Compare the distance between every extreme point of a contour with those of every other contour. And draw a line between points with the least distance.
for i in range(len(cnts)):
min_dist = max(img.shape[0], img.shape[1])
cl = []
ci = cnts[i]
ci_left = tuple(ci[ci[:, :, 0].argmin()][0])
ci_right = tuple(ci[ci[:, :, 0].argmax()][0])
ci_top = tuple(ci[ci[:, :, 1].argmin()][0])
ci_bottom = tuple(ci[ci[:, :, 1].argmax()][0])
ci_list = [ci_bottom, ci_left, ci_right, ci_top]
for j in range(i + 1, len(cnts)):
cj = cnts[j]
cj_left = tuple(cj[cj[:, :, 0].argmin()][0])
cj_right = tuple(cj[cj[:, :, 0].argmax()][0])
cj_top = tuple(cj[cj[:, :, 1].argmin()][0])
cj_bottom = tuple(cj[cj[:, :, 1].argmax()][0])
cj_list = [cj_bottom, cj_left, cj_right, cj_top]
for pt1 in ci_list:
for pt2 in cj_list:
dist = int(np.linalg.norm(np.array(pt1) - np.array(pt2)))
if dist < min_dist:
min_dist = dist
cl = []
cl.append([pt1, pt2, min_dist])
if len(cl) > 0:
cv2.line(img1, cl[0][0], cl[0][1], (255, 255, 255), thickness = 5)
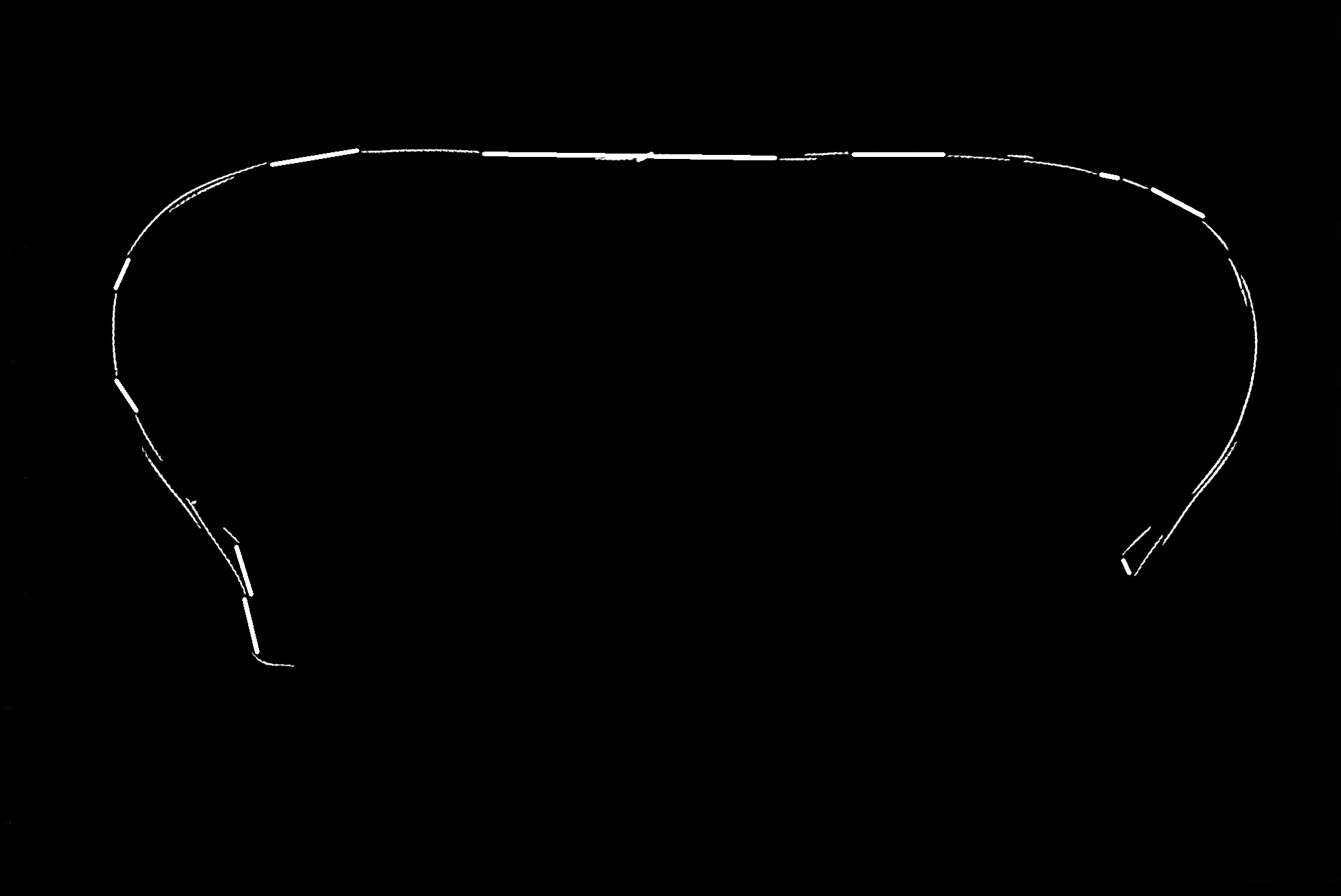

4. 后处理
由于最终输出不是完美的,因此您可以执行其他形态学操作,然后将其骨架化。




