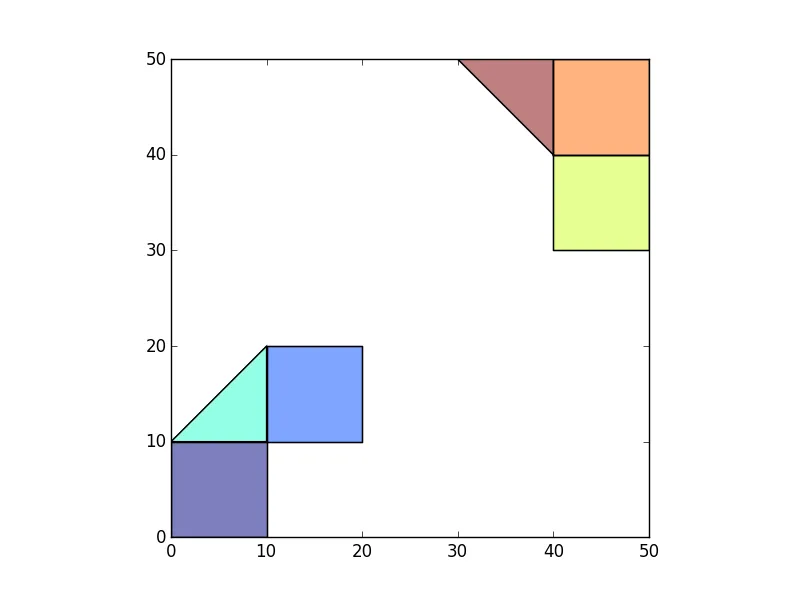
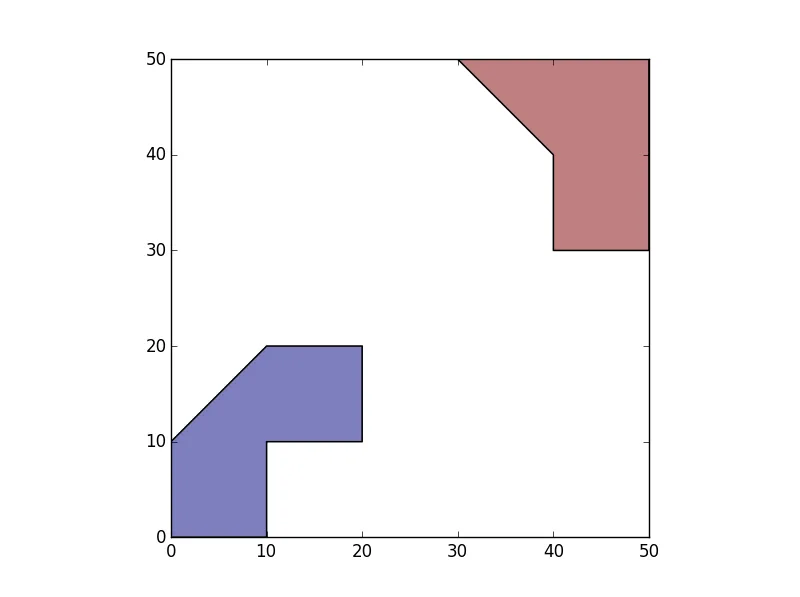
假设我有两个不相交的多边形组/“岛屿”(比如说两个非相邻县份的人口普查区域)。我的数据可能长这样:
>>> p1=Polygon([(0,0),(10,0),(10,10),(0,10)])
>>> p2=Polygon([(10,10),(20,10),(20,20),(10,20)])
>>> p3=Polygon([(10,10),(10,20),(0,10)])
>>>
>>> p4=Polygon([(40,40),(50,40),(50,30),(40,30)])
>>> p5=Polygon([(40,40),(50,40),(50,50),(40,50)])
>>> p6=Polygon([(40,40),(40,50),(30,50)])
>>>
>>> df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(geometry=[p1,p2,p3,p4,p5,p6])
>>> df
geometry
0 POLYGON ((0 0, 10 0, 10 10, 0 10, 0 0))
1 POLYGON ((10 10, 20 10, 20 20, 10 20, 10 10))
2 POLYGON ((10 10, 10 20, 0 10, 10 10))
3 POLYGON ((40 40, 50 40, 50 30, 40 30, 40 40))
4 POLYGON ((40 40, 50 40, 50 50, 40 50, 40 40))
5 POLYGON ((40 40, 40 50, 30 50, 40 40))
>>>
>>> df.plot()
我希望对每个岛屿内的多边形分配一个代表其组的ID(可以是任意值)。例如,左下角的3个多边形可以有IslandID = 1,右上角的3个多边形可以有IslandID=2。
我已经开发了一种方法来完成这个任务,但我想知道它是否是最好/最有效的方法。我执行以下操作:
1)创建一个GeoDataFrame,其中几何图形等于多面体单元并集中的多边形。这给我两个多边形,一个代表每个“岛屿”。
>>> SepIslands=gpd.GeoDataFrame(geometry=list(df.unary_union))
>>> SepIslands.plot()
2)为每个组创建一个ID。
>>> SepIslands['IslandID']=SepIslands.index+1
3) 将岛屿与原始多边形进行空间连接,使每个多边形具有相应的岛屿ID。
>>> Final=gpd.tools.sjoin(df, SepIslands, how='left').drop('index_right',1)
>>> Final
geometry IslandID
0 POLYGON ((0 0, 10 0, 10 10, 0 10, 0 0)) 1
1 POLYGON ((10 10, 20 10, 20 20, 10 20, 10 10)) 1
2 POLYGON ((10 10, 10 20, 0 10, 10 10)) 1
3 POLYGON ((40 40, 50 40, 50 30, 40 30, 40 40)) 2
4 POLYGON ((40 40, 50 40, 50 50, 40 50, 40 40)) 2
5 POLYGON ((40 40, 40 50, 30 50, 40 40)) 2
这确实是最好/最有效的方法吗?