我有一个类型为np.float64的二维numpy数组,我想将其显示为QLabel中的图像(或任何其他有效方式):
self.img = np.rot90(get_my_data()) # this line returns a 2D numpy array of type np.float64
self.qimg = QtGui.QImage(self.img, self.img.shape[0], self.img.shape[1], QtGui.QImage.Format_Grayscale8)
self.myLabel.setPixmap(QtGui.QPixmap(self.qimg))
我上面的代码返回了以下错误:
TypeError: arguments did not match any overloaded call:
QImage(): too many arguments
QImage(QSize, QImage.Format): argument 1 has unexpected type 'numpy.ndarray'
QImage(int, int, QImage.Format): argument 1 has unexpected type 'numpy.ndarray'
QImage(bytes, int, int, QImage.Format): argument 1 has unexpected type 'numpy.ndarray'
QImage(sip.voidptr, int, int, QImage.Format): argument 1 has unexpected type 'numpy.ndarray'
QImage(bytes, int, int, int, QImage.Format): argument 1 has unexpected type 'numpy.ndarray'
QImage(sip.voidptr, int, int, int, QImage.Format): argument 1 has unexpected type 'numpy.ndarray'
QImage(List[str]): argument 1 has unexpected type 'numpy.ndarray'
QImage(str, format: str = None): argument 1 has unexpected type 'numpy.ndarray'
QImage(QImage): argument 1 has unexpected type 'numpy.ndarray'
QImage(Any): too many arguments
但是,如果我在第一行的末尾添加.copy(),那么它就可以工作了!但是它不会正确地显示数据。
self.img = np.rot90(get_my_data()).copy()
self.qimg = QtGui.QImage(self.img, self.img.shape[0], self.img.shape[1], QtGui.QImage.Format_Grayscale8)
self.myLabel.setPixmap(QtGui.QPixmap(self.qimg))
以下是标签与pyplot.imshow()的显示效果对比:
self.img = 20 * np.log10(np.rot90(get_my_data()).copy())
self.qimg = QtGui.QImage(self.img, self.img.shape[0], self.img.shape[1], QtGui.QImage.Format_Grayscale8)
self.myLabel.setPixmap(QtGui.QPixmap(self.qimg))
pyplot.imshow(self.img)
pyplot.show()
pyplot.imshow() 的结果是:
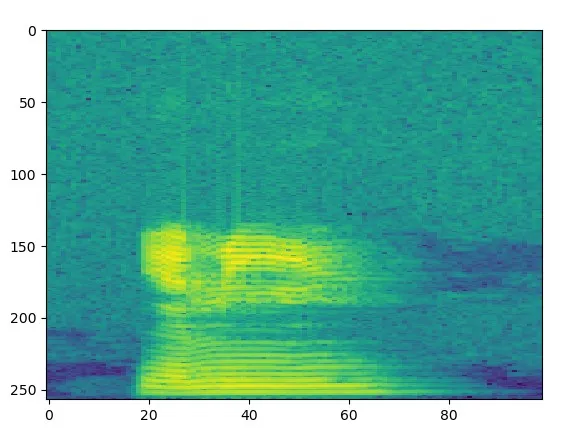
而 myLabel 显示的结果如下:

那么,我的代码有什么问题吗?
有没有更好的方法将我的 2D numpy 数组显示为图像?
get_my_data()函数返回的数值范围是多少?如果它们是浮点数,那么你不能直接使用它们。图像格式接受 1、8、16、24、32 或 64 位(作为“整数”值)格式。如果你知道数据的范围,那么你可以将数组转换为整数值。例如,如果它们在 0 到 1 之间,那么类似这样的代码可能会起作用(假设你想要 8 位转换):self.img = np.multiply(get_my_data(), 127).astype('int8')- musicamante20 * np.log10操作,正如您所看到的那样。 - catfour