[batch_number, max_sentence_length]的数据集,我在行尾添加了 EOF并用足够的占位符(例如#)填充每个句子。然后将句子中的每个字符转换为一个one-hot向量,以便数据集具有3-D形状[batch_number, max_sentence_length, character_number]。在LSTM编码器和解码器层之后,计算输出和目标之间的softmax交叉熵。为了消除模型训练中的填充效应,可以在输入和损失函数上使用掩码。在Keras中,可以使用
layers.core.Masking来进行屏蔽输入。在TensorFlow中,可以按如下方式对损失函数进行屏蔽:custom masked loss function in TensorFlow。然而,由于Keras中用户定义的损失函数只接受参数
y_true和y_pred,我找不到一种方法来实现这一点。那么如何将真正的sequence_lengths 输入到损失函数并进行屏蔽?此外,我发现
\keras\engine\training.py中有一个_weighted_masked_objective(fn)函数。它的定义是:
但似乎该函数只能接受Adds support for masking and sample-weighting to an objective function.
fn(y_true, y_pred)。是否有一种使用此函数来解决我的问题的方法?具体来说,我修改了Yu-Yang的示例。
from keras.models import Model
from keras.layers import Input, Masking, LSTM, Dense, RepeatVector, TimeDistributed, Activation
import numpy as np
from numpy.random import seed as random_seed
random_seed(123)
max_sentence_length = 5
character_number = 3 # valid character 'a, b' and placeholder '#'
input_tensor = Input(shape=(max_sentence_length, character_number))
masked_input = Masking(mask_value=0)(input_tensor)
encoder_output = LSTM(10, return_sequences=False)(masked_input)
repeat_output = RepeatVector(max_sentence_length)(encoder_output)
decoder_output = LSTM(10, return_sequences=True)(repeat_output)
output = Dense(3, activation='softmax')(decoder_output)
model = Model(input_tensor, output)
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam')
model.summary()
X = np.array([[[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0]],
[[0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0], [1, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0]]])
y_true = np.array([[[0, 0, 1], [0, 0, 1], [1, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0]], # the batch is ['##abb','#babb'], padding '#'
[[0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0], [1, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0]]])
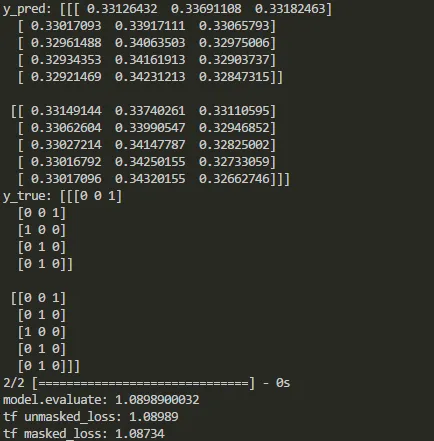
y_pred = model.predict(X)
print('y_pred:', y_pred)
print('y_true:', y_true)
print('model.evaluate:', model.evaluate(X, y_true))
# See if the loss computed by model.evaluate() is equal to the masked loss
import tensorflow as tf
logits=tf.constant(y_pred, dtype=tf.float32)
target=tf.constant(y_true, dtype=tf.float32)
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(target * tf.log(logits),axis=2))
losses = -tf.reduce_sum(target * tf.log(logits),axis=2)
sequence_lengths=tf.constant([3,4])
mask = tf.reverse(tf.sequence_mask(sequence_lengths,maxlen=max_sentence_length),[0,1])
losses = tf.boolean_mask(losses, mask)
masked_loss = tf.reduce_mean(losses)
with tf.Session() as sess:
c_e = sess.run(cross_entropy)
m_c_e=sess.run(masked_loss)
print("tf unmasked_loss:", c_e)
print("tf masked_loss:", m_c_e)
在Keras和TensorFlow中,输出的比较如下:
如上所示,在某些类型的层之后,掩码被禁用。那么当添加这些层时,如何在Keras中掩盖损失函数呢?