JPanel实际上只是一个容器,您可以在其中放置不同的元素(甚至是其他
JPanels)。因此,在您的情况下,我建议使用一个大型
JPanel作为窗口的某种
主容器。您可以为该
主面板分配适合您需求的
Layout(
这里是布局介绍)。
设置了
主面板的布局后,您可以添加
绘图面板和其他想要的JPanels(例如带有文本的那些)。
JPanel mainPanel = new JPanel();
mainPanel.setLayout(new BoxLayout(mainPanel, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS));
JPanel paintPanel = new JPanel();
JPanel textPanel = new JPanel();
mainPanel.add(paintPanel);
mainPanel.add(textPanel);
这只是一个示例,将所有的
子面板在垂直方向(Y 轴)上排序。因此,如果你想要在主面板底部放置其他东西(例如一些图标或按钮),应该使用另一种布局(如水平布局),只需创建一个新的JPanel作为其他所有内容的容器,然后设置
setLayout(new BoxLayout(mainPanel, BoxLayout.X_AXIS)。
如你所见,布局相当严格,可能很难找到最适合你的面板的最佳布局方式。所以不要放弃,阅读简介(上面的链接),并查看图片-这就是我做的方式 :)
或者你可以使用NetBeans编写程序。那里有一个相当容易的可视化编辑器(拖放),可以创建各种窗口和框架。(仅在之后理解代码有时会有点棘手。)
编辑
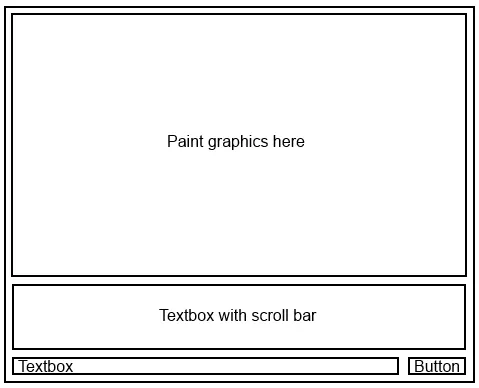
由于有这么多人关注这个问题,我想提供一个完整的示例,说明如何布局JFrame以使其看起来像OP想要的那样。
该类名为
MyFrame,继承了Swings的
JFrame。
public class MyFrame extends javax.swing.JFrame{
private final JSplitPane splitPane;
private final JPanel topPanel;
private final JPanel bottomPanel;
private final JScrollPane scrollPane;
private final JTextArea textArea;
private final JPanel inputPanel;
private final JTextField textField;
private final JButton button;
public MyFrame(){
splitPane = new JSplitPane();
topPanel = new JPanel();
bottomPanel = new JPanel();
scrollPane = new JScrollPane();
textArea = new JTextArea();
inputPanel = new JPanel();
textField = new JTextField();
button = new JButton("send");
setPreferredSize(new Dimension(400, 400));
getContentPane().setLayout(new GridLayout());
getContentPane().add(splitPane);
splitPane.setOrientation(JSplitPane.VERTICAL_SPLIT);
splitPane.setDividerLocation(200);
splitPane.setTopComponent(topPanel);
splitPane.setBottomComponent(bottomPanel);
bottomPanel.setLayout(new BoxLayout(bottomPanel, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS));
bottomPanel.add(scrollPane);
scrollPane.setViewportView(textArea);
bottomPanel.add(inputPanel);
inputPanel.setMaximumSize(new Dimension(Integer.MAX_VALUE, 75));
inputPanel.setLayout(new BoxLayout(inputPanel, BoxLayout.X_AXIS));
inputPanel.add(textField);
inputPanel.add(button);
pack();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
new MyFrame().setVisible(true);
}
});
}
}
请注意,这只是一个例子,有多种方法可以布局窗口。这取决于您的需求,以及是否希望内容可调整大小/响应式。另一个非常好的方法是GridBagLayout,它可以处理相当复杂的布局,但学习起来也相当复杂。
EventQueue.invokeLater(...)?new Example3().setVisible(true)独立使用似乎没有问题。 - Little Helper