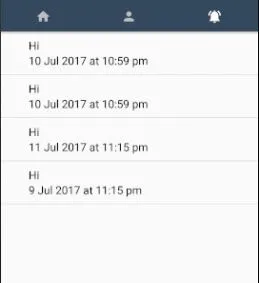
我正在尝试按日期对我的
我在stackoverflow上看到了一些示例,但我不知道如何使其在我的情况下起作用。我将在下面发布屏幕截图和我的代码。
日期未排序。
arrayList进行排序。每次我收到通知并从Firebase检索时,我都会将日期存储在那里。我正在使用Collections.sort,但我不知道如何在我的代码中实现,因为我的日期格式以字符串格式的数字开头,如“2017年7月12日上午12:00”。我在stackoverflow上看到了一些示例,但我不知道如何使其在我的情况下起作用。我将在下面发布屏幕截图和我的代码。
日期未排序。
NotificationFragment.java
public class NotificationFragment extends Fragment {
prepareNotification1();
sortDate();
return v;
}
private void prepareNotification1() {
FirebaseUser user = FirebaseAuth.getInstance().getCurrentUser();
String userID = user.getUid();
mRef.child("customers").child(userID).child("Notification").addChildEventListener(new ChildEventListener() {
@Override
public void onChildAdded(DataSnapshot dataSnapshot, String s) {
Notification menu = dataSnapshot.getValue(Notification.class);
notificationList.add(menu);
mAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
}
});
}
public void sortDate() {
Collections.sort(notificationList, new Comparator<Notification>() {
@Override
public int compare(Notification lhs, Notification rhs) {
return lhs.getDate().compareTo(rhs.getDate());
}
});
mAdapter = new NotificationAdapter(getContext(), notificationList);
mRecyclerView.setAdapter(mAdapter);
}
}
MyFirebaseMessagingService.java
public class MyFirebaseMessagingService extends FirebaseMessagingService {
@Override
public void onMessageReceived(RemoteMessage remoteMessage) {
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
String currentDateTimeString = DateFormat.getDateInstance().format(new Date());
SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("hh:mm a");
String currentTime = df.format(cal.getTime());
String notificationTime = currentDateTimeString + " at " + currentTime;
Notification newNotification = new Notification(remoteMessage.getData().get("body"), notificationTime);
mRef.child("customers").child(userID).child("Notification").push().setValue(newNotification);
}
Notification.java
public class Notification {
private String message;
private String date;
public Notification(){
}
public Notification(String message, String date){
this.message = message;
this.date = date;
}
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}