dwMajorVersion、dwMinorVersion和wProductType的变量来确定Windows版本,例如Windows 8.1、Windows 10、Windows Server 2012 R2等。大家通常使用的代码类似于:OSVERSIONINFOEX osvi;
SecureZeroMemory(&osvi, sizeof(OSVERSIONINFOEX));
osvi.dwOSVersionInfoSize = sizeof(OSVERSIONINFOEX);
if (GetVersionEx(&osvi)) {
if (osvi.dwMajorVersion == 10 &&
osvi.dwMinorVersion == 0 &&
osvi.wProductType != VER_NT_WORKSTATION) {
Console->Log("We are running on Windows Server 2016");
}
}
根据维基百科的说法,Windows Server 2019与Server 2016具有相同的NT 10.0版本号。因此上述代码不再起作用。
此外,Microsoft Docs包含以下注释:GetVersionEx可能在Windows 8.1之后的版本中被更改或不可用。请改用Version Helper函数。 不幸的是,Version Helper函数没有一个函数可以检测Server 2019。而且奇怪的是,关于Targeting的Docs页面仅涵盖了Windows 10,并未讨论Server版本,尽管这些Targeting清单对于检测高于Windows 8.1或Server 2012的OS是强制性的。 更新1。由于@IInspectable和@RbMm评论了
RtlGetVersion函数的使用。因此,我运行了以下代码(取自此答案):typedef LONG NTSTATUS, *PNTSTATUS;
#define STATUS_SUCCESS (0x00000000)
typedef NTSTATUS (WINAPI* RtlGetVersionPtr)(PRTL_OSVERSIONINFOW);
RTL_OSVERSIONINFOW GetRealOSVersion() {
HMODULE hMod = ::GetModuleHandleW(L"ntdll.dll");
if (hMod) {
RtlGetVersionPtr fxPtr = (RtlGetVersionPtr)::GetProcAddress(hMod, "RtlGetVersion");
if (fxPtr != nullptr) {
RTL_OSVERSIONINFOW rovi = { 0 };
rovi.dwOSVersionInfoSize = sizeof(rovi);
if ( STATUS_SUCCESS == fxPtr(&rovi) ) {
return rovi;
}
}
}
RTL_OSVERSIONINFOW rovi = { 0 };
return rovi;
}
以下是Windows 10的结果:
- dwMajorVersion = 10
- dwMinorVersion = 0
- dwBuildNumber = 17134
- dwPlatformId = 2
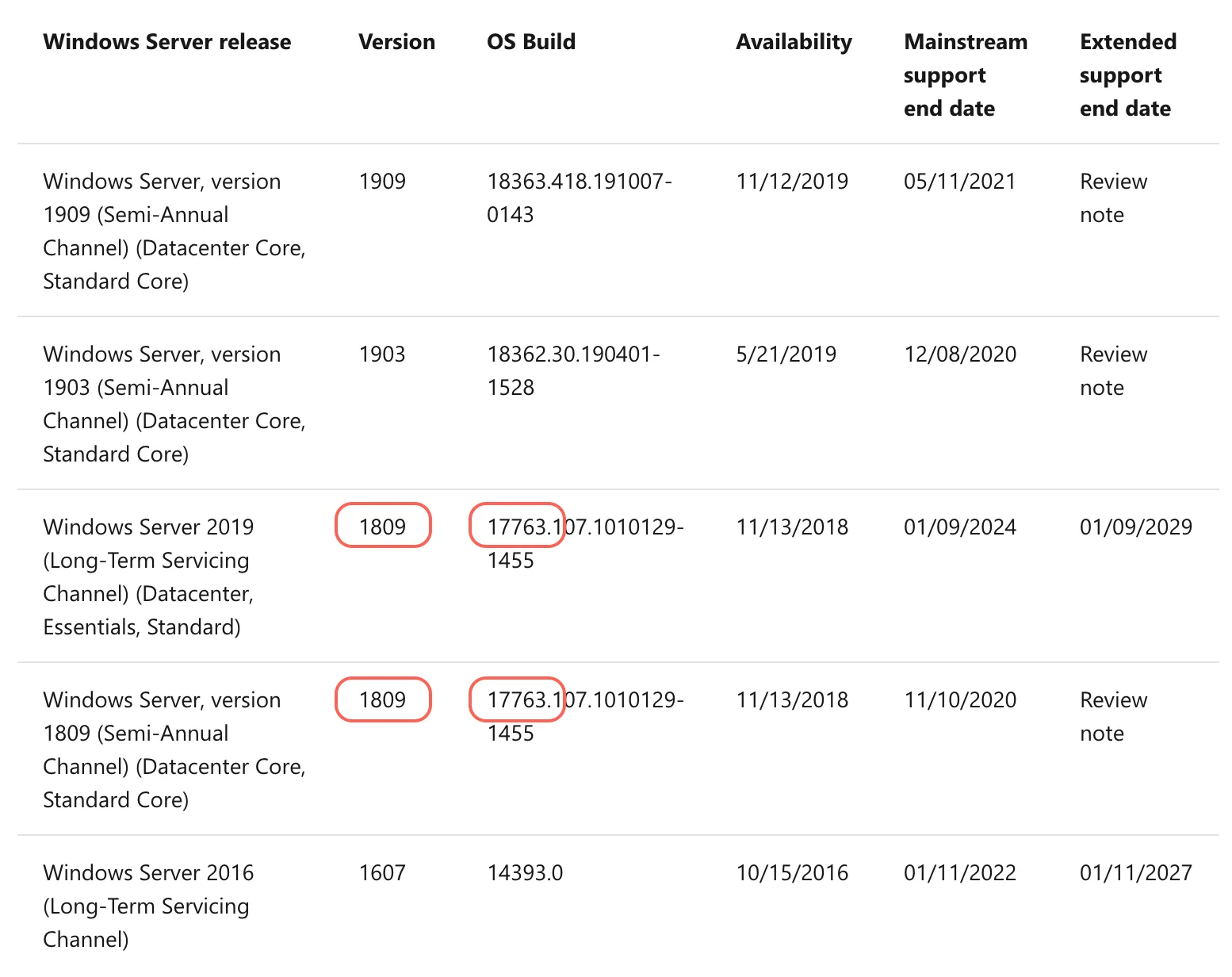
Windows Server 2019:
- dwMajorVersion = 10
- dwMinorVersion = 0
- dwBuildNumber = 17763
- dwPlatformId = 2
更新2。 根据要求,发布了通过包含所有目标直到Windows 10的清单文件进行的GetVersionEx调用获得的OSVERSIONINFOEX结构的完整信息(请参见上面的目标链接):
// Windows 10
osvi.dwOSVersionInfoSize = 284
osvi.dwMajorVersion = 10
osvi.dwMinorVersion = 0
osvi.dwBuildNumber = 17134
osvi.dwPlatformId = 2
osvi.szCSDVersion =
osvi.wServicePackMinor = 0
osvi.wServicePackMinor = 0
osvi.wSuiteMask = 256 // 0x100
osvi.wProductType = 1
osvi.wReserved = 0
// Windows Server 2016
osvi.dwOSVersionInfoSize = 284
osvi.dwMajorVersion = 10
osvi.dwMinorVersion = 0
osvi.dwBuildNumber = 14393
osvi.dwPlatformId = 2
osvi.szCSDVersion =
osvi.wServicePackMinor = 0
osvi.wServicePackMinor = 0
osvi.wSuiteMask = 400
osvi.wProductType = 3
osvi.wReserved = 0
// Windows Server 2019
osvi.dwOSVersionInfoSize = 284
osvi.dwMajorVersion = 10
osvi.dwMinorVersion = 0
osvi.dwBuildNumber = 17763
osvi.dwPlatformId = 2
osvi.szCSDVersion =
osvi.wServicePackMinor = 0
osvi.wServicePackMinor = 0
osvi.wSuiteMask = 400 // 0x190
osvi.wProductType = 3
osvi.wReserved = 0
更新3。 使用结构体RTL_OSVERSIONINFOEXW调用RtlGetVersion,我们得到与更新2完全相同的结果。
OSVERSIONINFO结构的结果。相应地初始化一个OSVERSIONINFOEX结构并传递它。该结构具有额外的成员,可以存储您正在寻找的信息。Matteo 提出了一个有效的观点:如果您计划根据运行代码的操作系统版本做出运行时决策,最好测试功能而不是版本。另一方面,如果你需要这个信息来进行诊断,那么这样做没有任何问题。 - IInspectablewProductType == VER_NT_SERVER来检测,但具体是哪种类型的服务器,只能根据dwBuildNumber确定。 - RbMm